Abstract
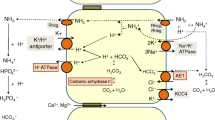
The kidneys are vital organs for maintaining homeostasis and have two important roles in maintaining the acid-base balance: to reabsorb bicarbonate from and to excrete hydrogen ions into urine. Renal tubular acidosis (RTA) is a form of metabolic acidosis that arises from a lack of urine excretion of H+ ions or loss of bicarbonate (\(\text{HCO}_{3}^{-}\)) ions due to a variety of renal tubular disorders. Acid-base disturbances can result in changes in dental health and in the development and the structure of the teeth. This article describes, to the best of the authors’ knowledge, the first case report of dental abnormalities occurring in two siblings with distal RTA.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brewer DE. Disorders of acid-base balance. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1990;37:429–47.
Winsnes A, Monn E, Stokke O, Feyling T. Congenital persistent proximal type renal tubular acidosis in two brothers. Acta Pedatr Scand. 1979;68:861–8.
Koppang HS, Stene T, Solheim T, Larheim TA, Wisnes A, Monn E, et al. Dental features in congenital persistent renal tubular acidosis of proximal type. Scand J Dent Res. 1984;92:489–95.
Soriano JR. Renal tubular acidosis, the clinical entity. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:2160–70.
Dunger DB, Brenton DP, Cain AR. Renal tubular acidosis and nerve deafness. Arch Dis Child. 1980;55:221–5.
Backman T, Pajari U, Larmas M. Effect of metabolic acidosis on dentinogenesis in rat. In: Shimano M, Maeda T, Suda H, Takahashi K, editors. Dentin pulp complex. Tokyo: Quintessence; 1999. pp. 291–2.
Koch MJ, Buhrer R, Pioch T, Schrarer K. Enamel hypoplasia of primary teeth in chronic renal failure. Pediatr Nephrol. 1999;13:68–72.
Whitford GM, Pashley DH. Fluoride absorption: the influence of gastric acidity. Calcif Tissue Int. 1984;36:302–7.
Angmar-Mansson B, Whitford GM. Effects of acid-base status and fluoride on developing canine enamel (abstract). Caries Res. 1986;20:159.
Woodhead JC, Nowak AJ, Crall JJ, Robillard JE. Dental abnormalities in children with chronic renal failure. Pediatr Dent. 1982;4:281–5.
Jaffe EC, Roberts J, Chantker C, Carter JE. Dental findings in chronic renal failure. Br Dent J. 1986;160:18–20.
Bender IB, Naidorf IJ. Dental observations in vitamin D-resistant rickets with special reference to periapical lesions. J Endod. 1985;11:514–20.
Ganibegovic M. Dental radiographic changes in chronic renal failure. Med Arch. 2000;54:115–8.
Zambrano M, Nikitakis G, Sanchez-Queved MC, Saukk JJ, Sedano H, Rivera H. Oral and dental manifestations of vitamin D-resistant rickets type 1: report of a pediatric case. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2003;95(6):705–9.
Sampathkumar K, Sah A, Seralathan G. Dental caries in renal tubular acidosis. Kidney Int. 2011;801:248.
Bahadure RN, Thosar N, Kriplani R, Baliga S, Fulzele P. Dental aspect of distal tubular renal acidosis with genu valgum secondary to rickets: a case report. Case Rep Dent. 2012; doi:10.1155/2012/374945.
Procter R, Kumar N, Stein A, Moles D, Porter S. Oral and dental aspects of chronic renal failure. J Dent Res. 2005;84:199–208.
Al-Nowaiser A, Roberts GJ, Trompter RS, Wilson M, Lucas VS. Oral health in children with chronic renal failure. Pediatr Nephrol. 2003;18:39–45.
Jain M, Agarwal MP, Wasir JS, Dwivedi S. Amelogenesis imperfecta and distal renal tubular acidosis presenting as hypokalemic periodic paralysis. J Assoc Physicians India. 1999;47(12):1205–6.
Seow WK. The effect of medical therapy on dentin formation in vitamin D-resistant rickets. Pediatr Dent. 1991;13(2):97–102.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishnan, B., Krishnamurthy, S. & Daniel, M. Distal renal tubular acidosis. J. Stomat. Occ. Med. 5, 183–187 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12548-012-0061-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12548-012-0061-8