Abstract
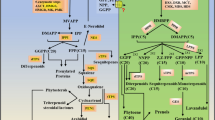
Stevia rebaudiana extract is globally approved as a low-calorie sweetener. Increasing glycosides content using biotechnological methods is particularly important. In this study, stevia plant was treated with silver nanoparticles at various concentrations (0, 10, 20, and 40 mM). Subsequently, the transcription of key gene levels in the biosynthesis of rebaudioside and stevioside glycosides, including UGT85C2 (UDP-glycosyltransferases), KAH (Kaurenoic acid-13 hydroxylase), UGT74G1, and UGT76G1 was measured using real time PCR assays. The HPLC was used to evaluate the glycosides content. UGT85C2 demonstrated the highest transcriptional level changes in plants treated with silver nanoparticles. The plants treated with silver nanoparticles at concentration of 10 and 20 mM showed a lower gene expression than the control plant, but plant treated with silver nanoparticles at 40 mM concentration showed significantly higher gene expression than the control samples. The results suggested that the treatment with AgNPs at 40 mM leads to similar positive effects on the transcription of all genes. HPLC results also revealed that the plants treated with 40 mM nanoparticles contains a higher glycosides content comparing to the control sample. Thus, the present experiment suggests that silver nanoparticles can act as a strong amplifier of the transcriptional trigger for steviol glycoside biosynthesis pathway genes which have the potential to control the production of steviol glycosides positively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelova, Z., S. Georgiev, and W. Roos. 2006. Elicitation of plant. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment 20: 72–83.
Brandle, J.E., A. Richman, A.K. Swanson, and B.P. Chapman. 2002. Leaf ESTs from Stevia rebaudiana: A resource for gene discovery in diterpene synthesis. Plant Molecular Biology 50: 613–622.
Brandle, J.E., and P.G. Telmer. 2007. Steviol glycoside biosynthesis. Phytochemistry 68: 1855–1863.
Ceunen, S., and J.M.C. Geuns. 2013. Steviol glycosides: Chemical diversity, metabolism, and function. Journal of Natural Product 76: 1201–1228.
Che, P., S. Lall, D. Nettleton, and S.H. Howell. 2006. Gene transcript accumulation programs during shoot, root, and callus development in Arabidopsis tissue culture. Plant Physiology 141: 620–637.
Chichiriccó, G., and A. Poma. 2015. Penetration and toxicity of nanomaterials in higher plants. Nanomaterials 5: 851–873.
Comotto, M., A.A. Casazza, B. Aliakbarian, V. Caratto, M. Ferretti, and P. Perego. 2014. Influence of TiO2 nanoparticles on growth and phenolic compounds production in photosynthetic microorganisms. Scientific World Journal 9: 324–333.
Da Costa, M.V.J., and P.K. Sharma. 2016. Effect of copper oxide nanoparticles on growth, morphology, photosynthesis, and antioxidant response in Oryza sativa. Photosynthetica 54: 110–119.
El-Temsah, Y.S., and E.J. Joner. 2012. Impact of Fe and Ag nanoparticles on seed germination and differences in bioavailability during exposure in aqueous suspension and soil. Environmental Toxicology 27: 42–49.
Eom, H.J., and J. Choi. 2010. P38 MAPK activation, DNA damage, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis as mechanisms of toxicity of silver nanoparticles in Jurkat T cells. Environmental Science & Technology 44: 8337–8342.
Garcia-Sanchez, S., I. Bernales, and S. Cristobal. 2015. Early response to nanoparticles in the Arabidopsis transcriptome compromises plant defence and root-hair development through salicylic acid signalling. BMC Genomics 16: 341–349.
Geuns, J.M.C. 2003. Molecules of interest – stevioside. Phytochemistry 64: 913–921.
Ghanati, F., and S. Bakhtiarian. 2014. Effect of methyl jasmonate and silver nanoparticles on production of secondary metabolites by Calendula officinalis L. (Asteraceae). Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 13(11): 1783–1789.
Ghazi, Y.A., S. Bouro, T. Arioli, E.S. Dennis, and J. Danny. 2009. Transcript profiling during fiber development identifies pathways in secondary metabolism and cell wall structure that may contribute to cotton fiber quality. Plant and Cell Physiology 50: 1364–1381.
Gomes, S.I.L., S.C. Novais, and C. Gravato. 2012. Effect of Cu-nanoparticles versus one Cu-salt: Analysis of stress biomarkers response in Enchytraeus albidus (Oligochaeta). Nanotoxicology 6: 134–143.
Goyal, S.K., G.R.K. Samsher, and R.K. Goyal. 2010. Stevia (Stevia rebaudiana) a bio-sweetener: A review. International Journal of Food Science and Nutrition 61: 1–10.
Gupta, E., S. Purwar, S. Sandaram, and G.K. Gai. 2013. Nutritional and therapeutic values of Stevia rebaudiana: A review. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research 7: 3343–3353.
Hajihashemi, S., J.M.C. Geuns, and A. Ehsanpour. 2012. Physiological analysis of Stevia rebaudiana after treatment with polyethylene glycol, paclobutrazol and gibberellic acid. In Proceedings of the 6th Eustas Stevia Symposium, Stevia: Six months beyond authorisation (ed JMC Geuns), 157–180, Belgium: KULeuven. ISBN: 9789074253208.
Hajihashemi, S., J.M.C. Geuns, and A.A. Ehsanpour. 2013. Gene transcription of steviol glycoside biosynthesis in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni under polyethylene glycol, paclobutrazol and gibberellic acid treatments in vitro. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum 35: 2009–2014.
Jackson, R.G., E.K. Lim, Y. Li, M. Kowalczyk, G. Sandberg, J. Hoggett, D.A. Ashford, and D.J. Bowles. 2001. Identification and biochemical characterization of an Arabidopsis indole-3-acetic acid glucosyltransferase. Journal of Biological Chemistry 276: 4350–4356.
Jain, S.M., and M.M. Spencer. 2006. In Floriculture and ornamental biotechnology: Advances and tropical issues, ed. J.A. Teixeira da Silva, Vol. 1, 589–600. Global Science Books, ISSN 1749–0294 (Paper), 1749–0308 (Online), 1749–0316 (CD-ROM).
Jasim, B., R. Thomas, J. Mathew, and E.K. Radhakrishnan. 2017. Plant growth and diosgenin enhancement effect of silver nanoparticles in Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.). Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal 25: 443–447.
Kanipandian, N., S. Kannan, R. Ramesh, P. Subramanian, and R. Thirumurugan. 2014. Characterization, antioxidant and cytotoxicity evaluation of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Cleistanthus collinus extract as surface modifier. Materials Research Bulletin 49: 494–502.
Kha, M.N., M. Mobin, Z.K. Abbas, K.A. Almutairi, and Z.H. Siddiqui. 2017. Role of nanomaterials in plants under challenging environments. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 110: 194–209.
Kim, J.S., E. Kuk, and K.N. Yu. 2007. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 3: 95–101.
Kohan-Baghkheirati, E., and J. Geisler-Lee. 2015. Gene expression, protein function and pathways of Arabidopsis thaliana responding to silver nanoparticles in comparison to silver ions, cold, salt, drought, and heat. Nanomaterial 5: 436–467.
Kumar, H., K. Kaul, S. Bajpai-Gupta, V. Kumar Kau, and S. Kumar. 2012. A comprehensive analysis of fifteen genes of steviol glycosides biosynthesis pathway in Stevia rebaudiana (Bertoni). Gene 492: 276–284.
Lemus-Mondaca, R., A. Vega-Gálvez, L. Zura-Bravo, and K. Ah-Hen. 2012. Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni, source of a high-potency natural sweetener: A comprehensive review on the biochemical, nutritional and functional aspects. Food Chemistry 132: 1121–1132.
Lim, D., J.Y. Roh, H.J. Eom, J.Y. Choi, J. Hyun, and J. Choi. 2012. Oxidative stress-related PMK-1 P38 MAPK activation as a mechanism for toxicity of silver nanoparticles to reproduction in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 31: 585–592.
Majlesi, Z., M. Ramezani, and M. Gerami. 2018. Investigation on some main glycosides content of Stevia rebaudian B under different concentration of commercial and synthesized silver nanoparticles. Pharmacheutical and Biomedical Research 4(1): 1–10.
Masarovicova, E., and K. Kralova. 2013. Metal nanoparticles and plants. Ecological Chemistry and Engineering S 20: 9–22.
Mirzajani, F., H. Askari, S. Hamzelou, Y. Schober, A. Rompp, and A. Ghassempour. 2014. Proteomics study of silver nanoparticles toxicity on Oryza sativa L. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 108: 335–339.
Modi, A.R., Y.M. Shukla, N.S. Litoriya, N.J. Patel, and S. Narayanan. 2011. Effect of gibberellic acid foliar spray on growth parameters and stevioside content of ex vitro grown plants of Stevia rebaudiana B. Journal of Medicinal Plants 3: 157–160.
Mohanpuria, P., N.K. Rana, and S.K.J. Yadav. 2008. Bio-synthesis of nanoparticles: Technological concepts and future applications. Nanoparticle Research 10: 507–517.
Moteriya, P., H. Padalia, R. Jadeja, and S. Chanda. 2014. Screening of silver nanoparticle synthetic e cacy of some medicinal plants of Saurashtra region: A review, Natural Products: Research Reviews, Gupta VK Ed., 3, Indian Institute of Integrative Medicine, JammuTavi, India (2014) (In press).
Mulabagal, V., and H.S. Tsay. 2004. Plant cell cultures—An alternative and efficient source for the production of biologically important secondary metabolites. International Journal of Applied Sciences and Engineering 2: 29–48.
Navarro, E., A. Baun, and R. Behra. 2008. Environmental behavior and ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to algae, plants, and fungi. Ecotoxicology 17: 372–386.
Phukan, U.J., G.S. Jeena, and R.K. Shukla. 2016. WRKY transcription factors: Molecular regulation and stress responses in plants. Frontier in Plant Science 7: 760–767.
Pitta-Alvarez, S.I., T.C. Spollansky, and A.M. Giulietti. 2000. The influence of different biotic and abiotic elicitors on the production and profile of tropane alkaloids in hairy root cultures of Brugmansia candida. Enzyme and Microbial Technology 26: 491–504.
Rahi, P., V. Pathania, A. Gulati, B. Singh, R.K. Bhanwra, and R. Tewari. 2010. Stimulatory effect of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria on plant growth, stevioside and rebaudioside-A contents of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. Applied Soil Ecology 46: 222–229.
Ramezani, M., M. Gerami, and Z. Majlesi. 2018a. Comparison between various concentrations of commercial and synthesized silver nanoparticles on biochemical parameters and growth of Stevia rebaudian B. Plant Physiology Reports 24: 1–12.
Ramezani, M., F. Ramezani, F. Rahmani, and A. Dehestani. 2018b. Exogenous potassium phosphite application improved PR-protein expression and associated physio-biochemical events in cucumber challenged by Pseudoperonospora cubensis. Scientia Horticulturae 234: 335–343.
Ramezani, M., F. Rahmani, and A. Dehestani. 2017a. The effect of potassium phosphite on PR genes expression and the phenylpropanoid pathway in cucumber (Cucumis sativus) plants inoculated with Pseudoperonospora cubensis. Scientia Horticulture 234: 335–343.
Ramezani, M., F. Rahmani, and A. Dehestani. 2017b. Study of physio-biochemical responses elicited by potassium phosphite in downy mildew-infected cucumber plants. Archive of Phytopathology and Plant Protectection 50(11–12): 540–554.
Richman, S.A., M. Gijzen, A.N. Starratt, Z. Yang, and J.E. Brandle. 1999. Diterpene synthesis in Stevia rebaudiana: Recruitment and upregulation of key enzymes from the gibberellin biosynthetic pathway. The Plant Journal 19: 411–421.
Rico, C.M., S. Majumdar, M. Duarte-Gardea, J.R. Peralta-Videa, and J.L. Gardea-Torresdey. 2011. Interaction of nanoparticles with edible plants and their possible implications in the food chain. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 59: 3485–3498.
Schluttenhofer, C., and L. Yuan. 2015. Regulation of specialized metabolism by WRKY transcription factors. Plant Physiology 167: 295–306.
Scolnik, P.A., and G. Giuliano. 1994. Regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis genes during plant development. Pure and Applied Chemistry 66: 1063–1068.
Shibata, H., Y. Sawa, T. Oka, S. Sonoke, K.K. Kim, and M. Yoshioka. 1999. Steviol and steviol-glycoside-glucosyltransferase activities in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni purification and partial character-ization. Archive of Biochemistry and Biophysics 321: 390–396.
Song, J., B. Guo, F. Song, H. Peng, Y. Yao, Y. Zhang, Q. Sun, and Z. Ni. 2011. Genome-wide identification of gibberellins metabolic enzyme genes and expression profiling analysis during seed germination in maize. Gene 482: 34–42.
Sosan, A., D. Svistunenko, D. Straltsova, K. Tsiurkina, I. Smolich, and T. Lawson. 2016. Engineered silver nanoparticles are sensed at the plasma membrane and dramatically modify the physiology of Arabidopsis thaliana plants. Plant Journal 85: 245–257.
Vecerova, K., Z. Vecera, B. Docekal, M. Oravec, A. Pompeiano, and J. Tríska. 2016. Changes of primary and secondary metabolites in barley plants exposed to CdO nanoparticles. Environmental Pollution 218: 207–218.
Zhang, B., L.P. Zheng, W. Li, and J. Wang. 2013. Stimulation of artemisinin production in Artemisia annua hairy roots by Ag–SiO2 core–shell nanoparticles. Current Nanoscience 9: 363–370.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the SANA Institute, Sari, IRAN for staff collaboration.
Funding
The authors acknowledged the following support: the IRAN University of Medical Sciences (Grant number 96-04-130-32710, Tehran, IRAN).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The experiments performed under control of ethics committee of IRAN University of Medical Sciences with ethics number IR.IUMS.REC 1396.32710.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramezani, M., Asghari, S., Gerami, M. et al. Effect of Silver Nanoparticle Treatment on the Expression of Key Genes Involved in Glycosides Biosynthetic Pathway in Stevia rebaudiana B. Plant. Sugar Tech 22, 518–527 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-019-00786-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-019-00786-x