Abstract
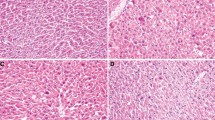
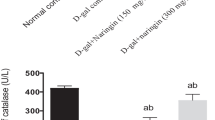
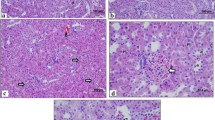
Objective of this study was to obtain a better understanding of the mechanism responsible for the d-galactosamine (d-GalN) induced hepatotoxicity and to study the effect of catechin against d-GalN induced hepatotoxicity. Catechin 50 and 100 mg/kg b.wt was administered for 1 week by oral route. Liver damage was induced by intra-peritoneal administration of 400 mg/kg b.wt d-galactosamine on the last day of catechin treatment. At the end of treatment all animals were killed and liver enzyme levels were estimated. Dissected hepatic samples were used for histopathology, RNA isolation, expression studies of Bax, Bcl-2 and p53 mRNA levels and mitochondrial membrane potential studies. We found that increases in the liver enzyme activity and decrease in antioxidant enzyme activity by d-GalN were significantly restricted by oral pretreatment with catechin. Disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential, up regulation of p53, Bax and down regulation of Bcl-2 mRNA levels in the liver of d-GalN intoxicated rats were effectively prevented by pretreatment with catechin.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gupta M, Mazumder U, Kumar T, Gomathi P, Kumar R. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects of Buhiniaracemosa against paracetamol and carbon tetrachloride induced liver damage in rats. Iranian J Pharma Ther. 2004;3:12–20.
Frei B, Higdon J. Antioxidant activity of tea polyphenols in vivo: evidence from animal studies. J Nutr. 2003;133:3275–84.
Babich H, Gold T, Gold R. Mediation of the in vitro cytotoxicity of green tea and black tea polyphenols by cobalt chloride. Toxicol Lett. 2005;155:195–205.
Okada K, Wangpoengtrakut C, Tanaka T, Tomoyuki T, Toyokuni S, Uchida K, et al. Curcumin and especially tetrahydrocurcumin ameliorate oxidative stress induced renal injury in mice. J Nutr. 2001;131:2090–5.
Arts I, Hollman P, Kromhout D. Chocolate as a source of tea flavonoids. Lancet. 1999;61:354–88.
Matito C, Mastoraku F, Centelles J, Torres J, Cascante M. Antiproliferative effect of antioxidant polyphenols from grape in murine Hep1c1c7. Eur J Nutr. 2003;42:43–9.
Graham H. Green tea composition, consumption and phenol chemistry. Prev Med. 1992;21:334–50.
Sato M, Toyazaki H, Yoshioka Y, Yokoi N, Yamasaki T. Structural characteristics for superoxide anion radical scavenging and productive activities of green tea polyphenols including proanthocyanidin dimers. Chem Pharm Bull. 2010;58:98–102.
Shimizu K, Kinouchi Shimizu N, Hakamata W, Unno K, Asai T, Oku N. Preventive effect of green tea catechins on experimental tumor metastasis in senescence-accelerated mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33:117–21.
Ostrowska J, Luczaj W, Kasacka I, Rozanski A, Skrzydlewska E. Green tea protects against ethanol induced lipid peroxidation in rat organs. Alcohol. 2004;32:25–32.
El-Beshbishy HA. Hepatoprotective effect of green tea (Camellia sinensis) Extract against tamoxifen-induced liver injury in rats. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2005;38:563–70.
Wan Y, Vinson J, Etherton T, Porch J, Lazarus S, Kris-Etherton P. Effects of cocoa powder and dark chocolate on LDL oxidative susceptibility and prostaglandin concentration in humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001;74:596–602.
Arteel GE, Uesugi T, Bevan LN, Gabele E, Wheeler MD, Mckim SE, et al. Green tea extract protects against early alcohol-induced liver injury in rats. Biol Chem. 2002;383:663–70.
Baltaziak M, Skrzydlewska E, Sulik A, Famulski W, Koda M. Green tea as an antioxidant which protects against alcohol induced injury in rats—a histopathological examination. Folia Morphol Warsz. 2004;63:123–6.
Skrzydlewska E, Ostrowska J, Stankiewicz A, Farbiszewski R. Green tea as a potent antioxidant in alcohol intoxication. Addict Biol. 2002;7:307–14.
Lee Sang ll, Kim Hyo Jung, Boo Young Chool. Effect of green tea and (-)-epigallocatechin gallate on ethanol-induced toxicity in HepG2 cells. Phytother Res. 2008;22:669–74.
Kono Y. Generation of superoxide radical during autoxidation of hydroxylamine and an assay for superoxide dismutase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978;186:189–95.
Goth L. A simple method for determination of serum catalase activity and revision of the reference range. Clin Chim Acta. 1991;196:143–52.
Keegan A, Martini R, Batey R. Ethanol-related liver injury in the rat: a model of steatosis, inflammation and pericentral fibrosis. J Hepatol. 1995;23:591–600.
Galindo MF, Jordan J, Gonzalez-Garcia C, Cena V. Chromaffin cell death induced by 6-hydroxydopamine is independent of mitochondrial swelling and caspase activation. J Neurochem. 2003;84:1066–73.
Chaung SS, Lin CC, Lin J, Yu KH, Hsu YF, Yen MH. The hepatoprotective effects of Limonium sinense against carbon tetrachloride and beta-D-galactosamine intoxication in rats. Phytother Res. 2003;17:784–91.
Nakagiri R, Hashizume E, Kavahashi S, Sakai Y, Kamiya T. Suppression by Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium of D-galactosamine-induced liver injury in vitro and in vivo. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2003;67:2641–3.
MacDonald JR, Gandolfi AJ, Sipes IG. Structural requirements for cytoprotective agents in galactosamine-induced hepatic necrosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1985;81:17–24.
Tang XH, Gao L, Gao J, Fan YM, Xu LZ, Zhao XN, et al. Mechanisms of hepatoprotection of Terminalia catappa L. extract on D-galactosamine-induced liver damage. Am J Chin Med. 2004;32:509–19.
Cummings MC, Winterford CM, Walker NI. Apoptosis. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997;21:01–88.
Kromer G, Reed JC. Mitochondrial control of cell death. Nat Med. 2000;6:513–9.
Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Green DR, Newmeyer DD. The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: a primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science. 1997;275:1132–6.
Wolter KG, Hsu YT, Smith CL, Nechushtan A, Xi XG, Youle RJ. Movement of Bax from cytosol to mitochondria during apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 1997;139:1281–92.
Green DR, Reed JC. Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science. 1998;281:1309–12.
Yan Y, Shay JW, Wright WE, Mumby MC. Inhibition of protein phosphatase activity induces p53-dependent apoptosis in the absence of p53 transactivation. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:15220–6.
Mihara M, Erster S, Zaika A, Petrenko O, Chittenden T, Pancoska P, et al. p53 has a direct apoptogenic role at the mitochondria. Mol Cell. 2003;11:577–90.
Acknowledgment
We thank All India Council of Technical Education (AICTE) for funding (200-62/FIN/04/05/1784/268).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasanth Raj, P., Nitesh, K., Sagar Gang, S. et al. Protective Role of Catechin on d-Galactosamine Induced Hepatotoxicity Through a p53 Dependent Pathway. Ind J Clin Biochem 25, 349–356 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-010-0073-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-010-0073-3