Abstract
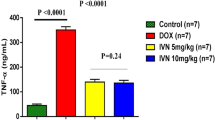
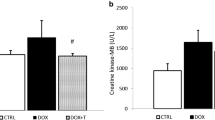
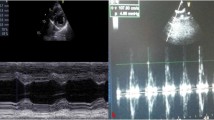
The protective effect of eugenol and its possible mechanisms were investigated in rats with acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Cardiac toxicity was induced by a single intraperitoneal injection of doxorubicin (20 mg/kg). Eugenol treatment (5 mg/kg/day, orally) was started 2 days before doxorubicin administration and continued for five consecutive days. Eugenol significantly reduced the elevated serum creatine kinase and lactate dehydrogenase levels, and restored the electrocardiographic disturbances resulted from doxorubicin administration. Also, eugenol reversed doxorubicin-induced deficits in the antioxidant defense mechanisms, decreased lipid peroxidation and attenuated the elevations in cytosolic Ca2+ and nitric oxide levels in cardiac tissue. In addition, doxorubicin-induced cardiac tissue damage observed by histopathological examination was markedly ameliorated with eugenol. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed that eugenol prevented the doxorubicin-induced activation of caspase-3 in cardiomyocytes. The cardioprotective effect afforded by eugenol was not significantly inhibited by prior administration of capsazepine, the transient potential vanilloid receptor-1 antagonist. It was concluded that eugenol, through its antioxidant activity and its ability to reduce cardiac Ca2+ accumulation and nitric oxide levels, is a potential candidate to protect against acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity, a major and dose-limiting clinical problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, S. K., Anti-genotoxicity of trans-anethole and eugenol in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol., 39, 493–498 (2001).
Andreadou, I., Sigala, F., Iliodromitis, E. K., Papaefthimiou, M., Sigalas, C., Aligiannis, N., Savvari, P., Gorgoulis, V., Papalabros, E., and Kremastinos, D. T., Acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity is successfully treated with the phytochemical oleuropein through suppression of oxidative and nitrosative stress. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol., 42, 549–558 (2007).
Burkey, J. L., Sauer, J. M., McQueen, C. A., and Sipes, I. G., Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of methyleugenol and related congeners-a mechanism of activation for methyleugenol. Mutat. Res., 453, 25–33 (2000).
Choi, C. Y., Park, K. R., Lee, J-.H., Jeon, Y. J., Liu, K. H., Oh, S., Kim, D. E., and Yea, S. S., Isoeugenol suppression of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression is mediated by down-regulation of NF-B, ERK1/2, and p38 kinase. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 576, 151–159 (2007).
Choudhary, R., Mishra, K. P., and Subramanyam, C., Interrelations between oxidative stress and calcineurin in the attenuation of cardiac apoptosis by eugenol. Mol. Cell. Biochem., 283, 115–122 (2006).
Franco-Cereceda, A., Saria, A., and Lundberg, J. M., Differential release of calcitonin gene-related peptide and neuropeptide Y from the isolated heart by capsaicin, ischaemia, nicotine, bradykinin and ouabain. Acta Physiol. Scand., 135, 173–187 (1989).
Huang, R., Karve, A., Shah, I., Bowers, M. C., DiPette, D. J., Supowit, S. C., and Abela, G. S., Deletion of the mouse alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide gene increases the vulnerability of the heart to ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol., 294, H1291–H1297 (2008).
Jiang, B., Zhang, L., Li, M., Wu, W., Yang, M., Wang, J., and Guo, D.-a., Salvianolic acids prevent acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity in mice through suppression of oxidative stress. Food Chem. Toxicol., 46, 1510–1515 (2008).
Ito, M., Murakami, K., and Yoshino, M., Antioxidant action of eugenol compounds: role of metal ion in the inhibition of lipid peroxidation. Food Chem. Toxicol., 43, 461–466 (2005).
Kabuto, H., Tada, M., and Kohno, M., Eugenol [2-methoxy-4-(2-propenyl)phenol] prevents 6-hydroxydopamine-induced dopamine depression and lipid peroxidation inductivity in mouse striatum. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 30, 423–427 (2007).
Keung, E. C., Toll, L., Ellis, M., and Jensen, R. A., L-type cardiac calcium channels in doxorubicin cardiomyopathy in rats morphological, biochemical, and functional correlations. J. Clin. Invest., 87, 2108–2113 (1991).
Kim, S. Y., Kim, S. J., Kim, B. J., Rah, S. Y., Chung, S. M., Im, M. J., and Kim, U. H., Doxorubicin-induced reactive oxygen species generation and intracellular Ca2+ increase are reciprocally modulated in rat cardiomyocytes. Exp. Mol. Med., 38, 535–545 (2006).
Li, H. Y., Park, C. K., Jung, S. J., Choi, S. Y., Lee, S. J., Park, K., Kim, J. S., and Oh, S. B., Eugenol inhibits K+ currents in trigeminal ganglion neurons. J. Dent. Res., 86, 898–902 (2007).
Li, W., Tsubouchi, R., Qiao, S., Haneda, M., Murakami, K., and Yoshino, M., Inhibitory action of eugenol compounds on the production of nitric oxide in RAW264.7 macrophages. Biomed. Res., 27, 69–74 (2006).
Li, Y. J. and Peng, J., The cardioprotection of calcitonin gene-related peptide-mediated preconditioning. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 442, 173–177 (2002).
Magyar, J., Szentandrássy, N., Bányász, T., Fülöp, L., Varró, A., and Nánási, P. P., Effects of terpenoid phenol derivatives on calcium current in canine and human ventricular cardiomyocytes. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 487, 29–36 (2004).
Manzini, S., Perretti, F., De Benedetti, L., Pradelles, P., Maggi, C. A., and Geppetti, P., A comparison of bradykinin- and capsaicin-induced myocardial and coronary effects in isolated perfused heart of guinea-pig: involvement of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide release. Br. J. Pharmacol., 97, 303–312 (1989).
Minotti, G., Menna, P., Salvatorelli, E., Cairo, G., and Gianni, L., Anthracyclines: molecular advances and pharmacologic developments in antitumor activity and cardiotoxicity. Pharmacol. Rev., 56, 185–229 (2004).
Mizutani, T., Satoh, K., and Nomura, H., Hepatotoxicity of eugenol and related compounds in mice depleted of glutathione: structural requirements for toxic potency. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol., 73, 87–95 (1991).
Morsy, M. A. and Fouad, A. A., Mechanisms of gastroprotective effect of eugenol in indomethacin-induced ulcer in rats. Phytother. Res., 22, 1361–1366 (2008).
Nagababu, E., Sesikeran, B., and Lakshmaiah, N., The protective effects of eugenol on carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Free Radic. Res., 23, 617–627 (1995).
Ou, H. C., Chou, F. P., Lin, T. M., Yang, C. H., and Sheu, W. H.-H., Protective effects of eugenol against oxidized LDL-induced cytotoxicity and adhesion molecule expression in endothelial cells. Food Chem. Toxicol., 44, 1485–1495 (2006).
Pacher, P., Liaudet, L., Bai, P., Mabley, J. G., Kaminski, P. M., Virág, L., Deb, A., Szabó, E., Ungvári, Z., Wolin, M. S., Groves, J. T., and Szabó, C., Potent metalloporphyrin peroxynitrite decomposition catalyst protects against the development of doxorubicin-induced cardiac dysfunction. Circulation, 107, 896–904 (2003).
Sayed-Ahmed, M. M., Khattab, M. M., Gad, M. Z., and Osman, A. M., Increased plasma endothelin-1 and cardiac nitric oxide during doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 89, 140–144 (2001).
Singal, P. K. and Iliskovic, N., Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med., 339, 900–905 (1998).
Singh, G., Singh, A. T., Abraham, A., Bhat, B., Mukherjee, A., Verma, R., Agarwal, S. K., Jha, S., Mukherjee, R., and Burman, A. C., Protective effects of Terminalia arjuna against Doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. J. Ethnopharmacol., 117, 123–129 (2008).
Thompson, D. C., Constantin-Teodosiu, D., and Moldéus, P., Metabolism and cytotoxicity of eugenol in isolated rat hepatocytes. Chem. Biol. Interact., 77, 137–147 (1991).
Thompson, D. C., Barhoumi, R., and Burghardt, R. C., Comparative toxicity of eugenol and its quinone methide metabolite in cultured liver cells using kinetic fluorescence bioassays. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 149, 55–63 (1998).
Tiku, A. B., Abraham, S. K., and Kale, R. K., Eugenol as an in vivo radioprotective agent. J. Radiat. Res., 45, 435–440 (2004).
Wang, L., Hu, C. P., Deng, P. Y., Shen, S. S., Zhu, H. Q., Ding, J. S., Tan, G. S., and Li, Y. J., The protective effects of rutaecarpine on gastric mucosa injury in rats. Planta Med., 71, 416–419 (2005).
Yang, B. H., Piao, Z. G., Kim, Y.-B., Lee, C.-H., Lee, J. K., Park, K., Kim, J. S., and Oh, S. B., Activation of vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1) by eugenol. J. Dent. Res., 82, 781–785 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fouad, A.A., Yacoubi, M.T. Mechanisms underlying the protective effect of eugenol in rats with acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Arch. Pharm. Res. 34, 821–828 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0516-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0516-2