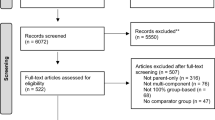
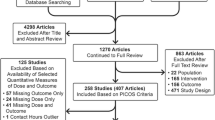
Abstract
There is limited research on optimal treatment formats for childhood obesity. Group-based interventions are popular, but it is unclear whether outcomes can be obtained without an additional individual component. The aim of the study was to examine statistically and clinically significant outcomes of recent group-based and mixed-format (group + individual) pediatric obesity interventions. Effect sizes and magnitudes of weight change were calculated for studies published between January 2013 and September 2014. Approximately half of the group-based studies reviewed produced significant results compared to control, and effect sizes were small. Mixed-format studies were less likely to include a control group, but those that did evidenced medium to large effects. Magnitudes of weight change post-intervention were generally greater in mixed-format studies than group-only studies. Recent studies in pediatric obesity interventions suggest including an individual component in a group-based intervention produces optimal outcomes. Future research should directly compare group-only and mixed formats to confirm this observation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Medians reported due to small sample size; therefore, effect size was not calculated.
Post-intervention average SDs not available to calculate effect size
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Flegal KM. Prevalence of childhood and adult obesity in the United States, 2011–2012. JAMA. 2014;311(8):806–14.
Dabelea D, Bell RA, D’Agostino Jr RB, Imperatore G, Johansen JM, Linder B, et al. Incidence of diabetes in youth in the United States. JAMA J Am Med Assoc. 2007;297(24):2716–24.
Freedman DS, Khan LK, Dietz WH, Srinivasan SR, Berenson GS. Relationship of childhood obesity to coronary heart disease risk factors in adulthood: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Pediatrics. 2001;108(3):712–8.
Franks PW, Hanson RL, Knowler WC, Sievers ML, Bennett PH, Looker HC. Childhood obesity, other cardiovascular risk factors, and premature death. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(6):485–93.
Baker JL, Olsen LW, Sørensen TI. Childhood body-mass index and the risk of coronary heart disease in adulthood. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(23):2329–37.
Pulgarón ER. Childhood obesity: a review of increased risk for physical and psychological comorbidities. Clin Ther. 2013;35(1):A18–32.
Whitaker RC, Wright JA, Pepe MS, Seidel KD, Dietz WH. Predicting obesity in young adulthood from childhood and parental obesity. N Engl J Med. 1997;337(13):869–73.
Singh AS, Mulder C, Twisk JW, Van Mechelen W, Chinapaw MJ. Tracking of childhood overweight into adulthood: a systematic review of the literature. Obes Rev. 2008;9(5):474–88.
Gordon-Larsen P, The NS, Adair LS. Longitudinal trends in obesity in the United States from adolescence to the third decade of life. Obesity. 2010;18(9):1801–4.
Force UPST. Screening for obesity in children and adolescents: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Pediatrics. 2010;125(2):361–7.
Wilfley DE, Buren DJ, Theim KR, Stein RI, Saelens BE, Ezzet F, et al. The use of biosimulation in the design of a novel multilevel weight loss maintenance program for overweight children. Obesity. 2010;18(S1):S91–8.
Epstein LH, Valoski A, Wing RR, McCurley J. Ten-year outcomes of behavioral family-based treatment for childhood obesity. Health Psychol. 1994;13(5):373.
Coppock JH, Ridolfi DR, Hayes JF, St. Paul M, Wilfley DE. Current approaches to the management of pediatric overweight and obesity. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2014.;16(11):343.
Epstein LH, Myers MD, Raynor HA, Saelens BE. Treatment of pediatric obesity. Pediatrics. 1998;101(Supplement 2):554–70.
Goldfield G, Epstein L, Kilanowski C, Paluch R, Kogut-Bossler B. Cost-effectiveness of group and mixed family-based treatment for childhood obesity. Int J Obes. 2001;25(12):1843–1849
Yalom ID. The theory and practice of group psychotherapy. 3rd ed. New York: Basic Books, Inc.; 1985.
Salvy S-J, Bowker JW, Roemmich JN, Romero N, Kieffer E, Paluch R, et al. Peer influence on children’s physical activity: an experience sampling study. J Pediatr Psychol. 2008;33(1):39–49.
Salvy S-J, Coelho JS, Kieffer E, Epstein LH. Effects of social contexts on overweight and normal-weight children’s food intake. Physiol Behav. 2007;92(5):840–6.
Salvy S-J, Kieffer E, Epstein LH. Effects of social context on overweight and normal-weight children’s food selection. Eat Behav. 2008;9(2):190–6.
Barkley JE, Salvy S-J, Roemmich JN. The effect of simulated ostracism on physical activity behavior in children. Pediatrics. 2012;129(3):e659–66.
Jelalian E, Sato A, Hart CN. The effect of group-based weight-control intervention on adolescent psychosocial outcomes: Perceived peer rejection, social anxiety, and self-concept. Child Health Care. 2011;40(3):197–211.
Wilfley DE, Stein RI, Saelens BE, Mockus DS, Matt GE, Hayden-Wade HA, et al. Efficacy of maintenance treatment approaches for childhood overweight: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2007;298(14):1661–73.
Brownell KD, Kelman JH, Stunkard AJ. Treatment of obese children with and without their mothers: changes in weight and blood pressure. Pediatrics. 1983;71(4):515–23.
Saelens BE, Lozano P, Scholz K. A randomized clinical trial comparing delivery of behavioral pediatric obesity treatment using standard and enhanced motivational approaches. J Pediatr Psychol. 2013;38(9):954–964.
Berry D, Schwartz T, McMurray R, Skelly A, Neal M, Hall E, et al. The family partners for health study: a cluster randomized controlled trial for child and parent weight management. Nutr Diabetes. 2014;4(1):e101.
Bloom T, Sharpe L, Mullan B, Zucker N. A pilot evaluation of appetite-awareness training in the treatment of childhood overweight and obesity: a preliminary investigation. Int J Eat Disord. 2013;46(1):47–51.
Bocca G, Corpeleijn E, van den Heuvel ER, Stolk RP, Sauer PJ. Three-year follow-up of 3-year-old to 5-year-old children after participation in a multidisciplinary or a usual-care obesity treatment program. Clin Nutr. 2013.
Boutelle KN, Zucker N, Peterson CB, Rydell S, Carlson J, Harnack LJ. An intervention based on Schachter’s externality theory for overweight children: The regulation of cues pilot. J Pediatr Psychol. 2014:jst142.
Davis AM, Sampilo M, Gallagher KS, Landrum Y, Malone B. Treating rural pediatric obesity through telemedicine: Outcomes from a small randomized controlled trial. J Pediatr Psychol. 2013:jst005.
Esfarjani F, Khalafi M, Mohammadi F, Mansour A, Roustaee R, Zamani-Nour N, et al. Family-based intervention for controlling childhood obesity: an experience among Iranian children. Int J Prev Med. 2013;4(3):358.
Hofsteenge G, Chinapaw M, Delemarre-van de Waal H, Weijs P. Long-term effect of the Go4it group treatment for obese adolescents: a randomised controlled trial. Clin Nutr. 2014;33(3):385–91.
Lochrie AS, Wysocki T, Hossain J, Milkes A, Antal H, Buckloh L, et al. The effects of a family-based intervention (FBI) for overweight/obese children on health and psychological functioning. Clin Pract Pediatr Psychol. 2013;1(2):159. Saelens et al. (2013) produced the largest weight changes in the middle childhood population with both a standard intervention that utilized uniform behavioral skills and interventionist goal assignment and a similar intervention with an adjunct motivational and autonomy-enhancing intervention. Both groups lost more than 0.3 zBMI points and within-group intervention effects were large (0.8 and 0.83), suggesting the efficacy of both intervention designs.
Martínez-Andrade GO, Cespedes EM, Rifas-Shiman SL, Romero-Quechol G, González-Unzaga MA, Benítez-Trejo MA, et al. Feasibility and impact of Creciendo Sanos, a clinic-based pilot intervention to prevent obesity among preschool children in Mexico City. BMC Pediatr. 2014;14(1):77.
Mazzeo SE, Kelly NR, Stern M, Gow RW, Cotter EW, Thornton LM, et al. Parent skills training to enhance weight loss in overweight children: evaluation of NOURISH. Eat Behav. 2014;15(2):225–9.
Morgan PJ, Collins CE, Plotnikoff RC, Callister R, Burrows T, Fletcher R, et al. The ‘Healthy Dads, Healthy Kids’ community randomized controlled trial: a community-based healthy lifestyle program for fathers and their children. Prev Med. 2014;61:90–9.
Kalarchian MA, Levine MD, Marcus MD. Structured dietary interventions in the treatment of severe pediatric obesity: a pilot study. Bariatr Surg Pract Patient Care. 2013;8(2):58–60.
Trost SG, Sundal D, Foster GD, Lent MR, Vojta D. Effects of a pediatric weight management program with and without active video games: a randomized trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2014.
Patrick K, Norman GJ, Davila EP, Calfas KJ, Raab F, Gottschalk M, et al. Outcomes of a 12-month technology-based intervention to promote weight loss in adolescents at risk for type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2013;7(3):759–70.
Quattrin T, Roemmich JN, Paluch R, Yu J, Epstein LH, Ecker MA. Treatment outcomes of overweight children and parents in the medical home. Pediatrics. 2014;134(2):290–7.
Stark LJ, Clifford LM, Towner EK, Filigno SS, Zion C, Bolling C, et al. A pilot randomized controlled trial of a behavioral family-based intervention with and without home visits to decrease obesity in preschoolers. J Pediatr Psychol. 2014;39(9):1001–12.
Berkowitz RI, Rukstalis MR, Bishop-Gilyard CT, Moore RH, Gehrman CA, Xanthopoulos MS, et al. Treatment of adolescent obesity comparing self-guided and group lifestyle modification programs: a potential model for primary care. J Pediatr Psychol. 2013;38(9):978–86.
Hystad HT, Steinsbekk S, Ødegård R, Wichstrøm L, Gudbrandsen OA. A randomised study on the effectiveness of therapist-led v. self-help parental intervention for treating childhood obesity. Br J Nutr. 2013;110(06):1143–50. Quattrin et al. (2014) assesses two relatively recent areas of interest in the treatment of childhood obesity, specifically treatment within a primary care setting and treatment of young children. Intensive treatment over 12 months demonstrated significant reductions in zBMI and percent overBMI that were maintained at a 24 month follow-up, thus intensive early intervention within a primary care setting may be beneficial for the treatment of childhood obesity.
Kokkvoll A, Grimsgaard S, Ødegaard R, Flægstad T, Njølstad I. Single versus multiple-family intervention in childhood overweight—Finnmark Activity School: a randomised trial. Arch Dis Child. 2013:archdischild-2012-303571.
Mirza NM, Palmer MG, Sinclair KB, McCarter R, He J, Ebbeling CB, et al. Effects of a low glycemic load or a low-fat dietary intervention on body weight in obese Hispanic American children and adolescents: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013;97(2):276–85.
Lakens D. Calculating and reporting effect sizes to facilitate cumulative science: a practical primer for t-tests and ANOVAs. Front Psychol. 2013;4:863.
Wilfley DE, Tibbs TL, Van Buren D, Reach KP, Walker MS, Epstein LH. Lifestyle interventions in the treatment of childhood overweight: a meta-analytic review of randomized controlled trials. Health Psychol. 2007;26(5):521.
Cohen J. A power primer. Psychol Bull. 1992;112(1):155.
Ford AL, Hunt LP, Cooper A, Shield JP. What reduction in BMI SDS is required in obese adolescents to improve body composition and cardiometabolic health? Arch Dis Child. 2010;95(4):256–61.
Kolsgaard ML, Joner G, Brunborg C, Anderssen SA, Tonstad S, Andersen LF. Reduction in BMI z-score and improvement in cardiometabolic risk factors in obese children and adolescents. The Oslo Adiposity Intervention Study-a hospital/public health nurse combined treatment. BMC Pediatr. 2011;11(1):47.
Reinehr T, Andler W. Changes in the atherogenic risk factor profile according to degree of weight loss. Arch Dis Child. 2004;89(5):419–22.
Reinehr T, Kiess W, Kapellen T, Andler W. Insulin sensitivity among obese children and adolescents, according to degree of weight loss. Pediatrics. 2004;114(6):1569–73.
Marcus MD, Kalarchian MA. Binge eating in children and adolescents. Int J Eat Disord. 2003;34(S1):S47–57.
Boutelle KN, Zucker NL, Peterson CB, Rydell SA, Cafri G, Harnack L. Two novel treatments to reduce overeating in overweight children: a randomized controlled trial. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2011;79(6):759.
Danielsson P, Kowalski J, Ekblom Ö, Marcus C. Response of severely obese children and adolescents to behavioral treatment. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2012;166(12):1103–8.
Staiano AE, Abraham AA, Calvert SL. Adolescent exergame play for weight loss and psychosocial improvement: a controlled physical activity intervention. Obesity. 2013;21(3):598–601.
Epstein LH, Paluch RA, Roemmich JN, Beecher MD. Family-based obesity treatment, then and now: twenty-five years of pediatric obesity treatment. Health Psychol. 2007;26(4):381.
Caprio S. Treating child obesity and associated medical conditions. Futur Child. 2006;16(1):209–24.
Altman MW, Wilfley DE. Evidence update on the treatment of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2014;12:1–17
Goldschmidt AB, Best JR, Stein RI, Saelens BE, Epstein LH, Wilfley DE. Predictors of child weight loss and maintenance among family-based treatment completers. 2014;82(6):1140
Nguyen B, Kornman K, Baur L. A review of electronic interventions for prevention and treatment of overweight and obesity in young people. Obes Rev. 2011;12(5):e298–314.
An J-Y, Hayman LL, Park Y-S, Dusaj TK, Ayres CG. Web‐based weight management programs for children and adolescents: a systematic review of randomized controlled trial studies. Adv Nurs Sci. 2009;32(3):222–40.
Turner-McGrievy GM, Tate DF. Weight loss social support in 140 characters or less: use of an online social network in a remotely delivered weight loss intervention. Transl Behav Med. 2013;3(3):287–94.
Kulik NL, Fisher EB, Ward DS, Ennett ST, Bowling JM, Tate DF. Peer support enhanced social support in adolescent females during weight loss. Am J Health Behav. 2014;38(5):789–800.
Wilfley D, Frank M, Welch R, Spurrell E, Rounsaville B. Adapting interpersonal psychotherapy to a group format (IPT-G) for binge eating disorder: toward a model for adapting empirically supported treatments. Psychother Res. 1998;8(4):379–91.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Conflict of Interest
Jacqueline Hayes, Myra Altman, and Jackson Coppock have no conflicts of interest. Andrea Goldschmidt received a grant from the National Center for Research Resources. Denise Wilfley was a consultant for Shire Pharmaceuticals; Wilfley is a member of Psychosocial Risk and Disease Prevention Study Section of the Center for Scientific Review. Wilfley received a grant from the NIH/NHLBI, honoraria from the Healthy Youth Partnership Presentation, and travel accommodations as a consultant from the Parents as the Agent of Change for Childhood Obesity Principal Investigator, Kerri Boutelle, PhD.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Obesity + Diet
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayes, J.F., Altman, M., Coppock, J.H. et al. Recent Updates on the Efficacy of Group-Based Treatments for Pediatric Obesity. Curr Cardiovasc Risk Rep 9, 16 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12170-015-0443-8
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12170-015-0443-8