Abstract
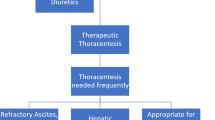
Hepatic hydrothorax (HH) is an infrequent but a well-known complication of portal hypertension in patients with end-stage liver disease. The estimated prevalence of HH is around 4–6 % in cirrhotics. Thoracentesis and pleural fluid analysis is a must for establishing the diagnosis of this transudative effusion in the absence of primary cardiopulmonary disease. Management strategies include sodium restriction, diuretics, thoracentesis, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt, pleurodesis, and video assisted thoracic surgery in selected patients. Liver transplantation remains the ultimate definitive management paradigm. Refractory HH thus warrants prompt consideration of liver transplantation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krok KL, Cardenas A. Hepatic hydrothorax. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;33(1):3–10.
Roussos A, Philippou N, Mantzaris GJ, et al. Hepatic hydrothorax: pathophysiology diagnosis and management. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;22(9):1388–93.
Cardenas A, Kelleher T, Chopra S. Review article: hepatic hydrothorax. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004;20(3):271–9.
Chen TA, Lo GH, Lai KH. Risk factors for spontaneous bacterial empyema in cirrhotic patients with hydrothorax. J Chin Med Assoc. 2003;66(10):579–86.
Ladero JM. Recurring hepatic hydrothorax: a difficult therapeutic challenge. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2001;93(9):561–5.
Gur C, Ilan Y, Shibolet O. Hepatic hydrothorax—pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment—review of the literature. Liver Int. 2004;24(4):281–4.
Garcia N Jr, Mihas AA. Hepatic hydrothorax: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2004;38(1):52–8.
Alagiakrishnan K, Patel PJ. Left-sided hepatic hydrothorax with ascites. Int J Clin Pract. 1999;53(3):225–6.
Gurung P, Goldblatt M, Huggins JT, et al. Pleural fluid analysis and radiographic, sonographic, and echocardiographic characteristics of hepatic hydrothorax. Chest. 2011;140(2):448–53.
Zenda T, Miyamoto S, Murata S, et al. Detection of diaphragmatic defect as the cause of severe hepatic hydrothorax with magnetic resonance imaging. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93(11):2288–9.
Huang PM, Chang YL, Yang CY, et al. The morphology of diaphragmatic defects in hepatic hydrothorax: thoracoscopic finding. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;130(1):141–5.
Lazaridis KN, Frank JW, Krowka MJ, et al. Hepatic hydrothorax: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Am J Med. 1999;107(3):262–7.
Strauss RM, Boyer TD. Hepatic hydrothorax. Semin Liver Dis. 1997;17(3):227–32.
Kaplan LM, Epstein SK, Schwartz SL, et al. Clinical, echocardiographic, and hemodynamic evidence of cardiac tamponade caused by large pleural effusions. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;151(3 Pt 1):904–8.
Castellote J, Gornals J, Lopez C, et al. Acute tension hydrothorax: a life-threatening complication of cirrhosis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2002;34(5):588–9.
Xiol X, Castellvi JM, Guardiola J, et al. Spontaneous bacterial empyema in cirrhotic patients: a prospective study. Hepatology. 1996;23(4):719–23.
Foschi FG, Piscaglia F, Pompili M, et al. Real-time contrast-enhanced ultrasound—a new simple tool for detection of peritoneal-pleural communications in hepatic hydrothorax. Ultraschall Med. 2008;29(5):538–42.
Nakamura A, Kojima Y, Ohmi H, et al. Peritoneal–pleural communications in hepatic hydrothorax demonstrated by thoracoscopy. Chest. 1996;109(2):579–81.
Alonso JC. Pleural effusion in liver disease. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;31(6):698–705.
Castellote J, Xiol X, Cortes-Beut R, et al. Complications of thoracentesis in cirrhotic patients with pleural effusion. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2001;93(9):566–75.
McVay PA, Toy PT. Lack of increased bleeding after paracentesis and thoracentesis in patients with mild coagulation abnormalities. Transfusion. 1991;31(2):164–71.
Xiol X, Castellote J, Cortes-Beut R, et al. Usefulness and complications of thoracentesis in cirrhotic patients. Am J Med. 2001;111(1):67–9.
Light RW. Diagnostic principles in pleural disease. Eur Respir J. 1997;10(2):476–81.
Xiol X, Castellote J, Baliellas C, et al. Spontaneous bacterial empyema in cirrhotic patients: analysis of eleven cases. Hepatology. 1990;11(3):365–70.
Abba AA, Laajam MA, Zargar SA. Spontaneous neutrocytic hepatic hydrothorax without ascites. Respir Med. 1996;90(10):631–4.
Sese E, Xiol X, Castellote J, et al. Low complement levels and opsonic activity in hepatic hydrothorax: its relationship with spontaneous bacterial empyema. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2003;36(1):75–7.
Chen CH, Shih CM, Chou JW, et al. Outcome predictors of cirrhotic patients with spontaneous bacterial empyema. Liver Int. 2011;31(3):417–24.
Tu CY, Chen CH. Spontaneous bacterial empyema. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2012;18(4):355–8.
Gines P, Cardenas A, Arroyo V, et al. Management of cirrhosis and ascites. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(16):1646–54.
Runyon BA. Management of adult patients with ascites due to cirrhosis: an update. Hepatology. 2009;49(6):2087–107.
Kiafar C, Gilani N. Hepatic hydrothorax: current concepts of pathophysiology and treatment options. Ann Hepatol. 2008;7(4):313–20.
Tsiaousi ET, Hatzitolios AI, Trygonis SK, et al. Malnutrition in end stage liver disease: recommendations and nutritional support. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;23(4):527–33.
Sherman SC. Reexpansion pulmonary edema: a case report and review of the current literature. J Emerg Med. 2003;24(1):23–7.
Orman ES, Lok AS. Outcomes of patients with chest tube insertion for hepatic hydrothorax. Hepatol Int. 2009;3(4):582–6.
Sanyal AJ, Genning C, Reddy KR, et al. The North American study for the treatment of refractory ascites. Gastroenterology. 2003;124(3):634–41.
Gordon FD, Anastopoulos HT, Crenshaw W, et al. The successful treatment of symptomatic, refractory hepatic hydrothorax with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Hepatology. 1997;25(6):1366–9.
Siegerstetter V, Deibert P, Ochs A, et al. Treatment of refractory hepatic hydrothorax with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: long-term results in 40 patients. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001;13(5):529–34.
Rossle M, Gerbes AL. TIPS for the treatment of refractory ascites, hepatorenal syndrome and hepatic hydrothorax: a critical update. Gut. 2010;59(7):988–1000.
Spencer EB, Cohen DT, Darcy MD. Safety and efficacy of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation for the treatment of hepatic hydrothorax. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002;13(4):385–90.
Salerno F, Merli M, Cazzaniga M, et al. MELD score is better than Child–Pugh score in predicting 3-month survival of patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. J Hepatol. 2002;36(4):494–500.
Wilputte JY, Goffette P, Zech F, et al. The outcome after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) for hepatic hydrothorax is closely related to liver dysfunction: a long-term study in 28 patients. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2007;70(1):6–10.
Dhanasekaran R, West JK, Gonzales PC, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for symptomatic refractory hepatic hydrothorax in patients with cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105(3):635–41.
Mouroux J, Perrin C, Venissac N, et al. Management of pleural effusion of cirrhotic origin. Chest. 1996;109(4):1093–6.
Milanez de Campos JR, Filho LO, de Campos Werebe E, et al. Thoracoscopy and talc poudrage in the management of hepatic hydrothorax. Chest. 2000;118(1):13–7.
Takayama T, Kurokawa Y, Kaiwa Y, et al. A new technique of thoracoscopic pleurodesis for refractory hepatic hydrothorax. Surg Endosc. 2004;18(1):140–3.
Ferrante D, Arguedas MR, Cerfolio RJ, et al. Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery with talc pleurodesis in the management of symptomatic hepatic hydrothorax. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97(12):3172–5.
Northup PG, Harmon RC, Pruett TL, et al. Mechanical pleurodesis aided by peritoneal drainage: procedure for hepatic hydrothorax. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;87(1):245–50.
Drouhin F, Fischer D, Law Koune JD, et al. Treatment of hydrothorax in liver cirrhosis with chemical pleurodesis associated with continuous positive airway pressure ventilation. Preliminary results. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1991;15(3):271–2.
Lee WJ, Kim HJ, Park JH, et al. Chemical pleurodesis for the management of refractory hepatic hydrothorax in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis. Korean J Hepatol. 2011;17(4):292–8.
Medford AR, Bennett JA, Free CM, et al. Current status of medical pleuroscopy. Clin Chest Med. 2010;31(1):165–72. (Table of Contents).
Shaw P, Agarwal R. Pleurodesis for malignant pleural effusions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;1:CD002916.
Lin DJ, Zhang M, Gao GX, et al. Thoracoscopy for diagnosis and management of refractory hepatic hydrothorax. Chin Med J (Engl). 2006;119(5):430–4.
Xiol X, Tremosa G, Castellote J, et al. Liver transplantation in patients with hepatic hydrothorax. Transpl Int. 2005;18(6):672–5.
Serste T, Moreno C, Francoz C, et al. The impact of preoperative hepatic hydrothorax on the outcome of adult liver transplantation. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;22(2):207–12.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Sarin, S.K. Paradigms in the management of hepatic hydrothorax: past, present, and future. Hepatol Int 7, 80–87 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-012-9398-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-012-9398-8