Abstract
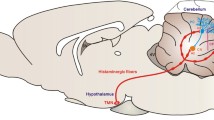
Insights into function of central histaminergic system, a general modulator originating from the hypothalamus for whole brain activity, in motor control are critical for understanding the mechanism underlying somatic-nonsomatic integration. Here, we show a novel selective role of histamine in the cerebellar nuclei, the final integrative center and output of the cerebellum. Histamine depolarizes projection neurons but not interneurons in the cerebellar nuclei via the hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels coupled to histamine H2 receptors, which are exclusively expressed on glutamatergic and glycinergic projection neurons. Furthermore, blockage of HCN channels to block endogenous histaminergic afferent inputs in the cerebellar nuclei significantly attenuates motor balance and coordination. Therefore, through directly and quickly modulation on projection neurons but not interneurons in the cerebellar nuclei, central histaminergic system may act as a critical biasing force to not only promptly regulate ongoing movement but also realize a rapid integration of somatic and nonsomatic response.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu JN, Yung WH, Kwok-Chong Chow B, Chan YS, Wang JJ (2006) The cerebellar-hypothalamic circuits: potential pathways underlying cerebellar involvement in somatic-visceral integration. Brain Res Rev 52(1):93–106
Zhang J, Li B, Yu L, He YC, Li HZ, Zhu JN, Wang JJ (2011) A role for orexin in central vestibular motor control. Neuron 69(4):793–804
Haas H, Panula P (2003) The role of histamine and the tuberomamillary nucleus in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 4(2):121–130
Haas HL, Sergeeva OA, Selbach O (2008) Histamine in the nervous system. Physiol Rev 88(3):1183–1241
Dietrichs E (1984) Cerebellar autonomic function: direct hypothalamocerebellar pathway. Science 223(4636):591–593
Haines DE, Dietrichs E, Mihailoff GA, McDonald EF (1997) The cerebellar-hypothalamic axis: basic circuits and clinical observations. Int Rev Neurobiol 41:83–107
Panula P, Pirvola U, Auvinen S, Airaksinen MS (1989) Histamine-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the rat brain. Neuroscience 28(3):585–610
Panula P, Takagi H, Inagaki N, Yamatodani A, Tohyama M, Wada H, Kotilainen E (1993) Histamine-containing nerve fibers innervate human cerebellum. Neurosci Lett 160(1):53–56
Airaksinen MS, Panula P (1988) The histaminergic system in the guinea pig central nervous system: an immunocytochemical mapping study using an antiserum against histamine. J Comp Neurol 273(2):163–186
Arrang JM, Drutel G, Garbarg M, Ruat M, Traiffort E, Schwartz JC (1995) Molecular and functional diversity of histamine receptor subtypes. Ann N Y Acad Sci 757:314–323
Vizuete ML, Traiffort E, Bouthenet ML, Ruat M, Souil E, Tardivel-Lacombe J, Schwartz JC (1997) Detailed mapping of the histamine H2 receptor and its gene transcripts in guinea-pig brain. Neuroscience 80(2):321–343
Honrubia MA, Vilaro MT, Palacios JM, Mengod G (2000) Distribution of the histamine H(2) receptor in monkey brain and its mRNA localization in monkey and human brain. Synapse 38(3):343–354
Karlstedt K, Senkas A, Ahman M, Panula P (2001) Regional expression of the histamine H(2) receptor in adult and developing rat brain. Neuroscience 102(1):201–208
He YC, Wu GY, Li D, Tang B, Li B, Ding Y, Zhu JN, Wang JJ (2012) Histamine promotes rat motor performances by activation of H(2) receptors in the cerebellar fastigial nucleus. Behav Brain Res 228(1):44–52
Song YN, Li HZ, Zhu JN, Guo CL, Wang JJ (2006) Histamine improves rat rota-rod and balance beam performances through H(2) receptors in the cerebellar interpositus nucleus. Neuroscience 140(1):33–43
Uusisaari MY, Knopfel T (2012) Diversity of neuronal elements and circuitry in the cerebellar nuclei. Cerebellum 11(2):420–421
Manto M, Gruol D, Schmahmann J, Koibuchi N, Rossi F (2012) Handbook of the cerebellum and cerebellar disorders. Springer, New York
Ito M (2011) The cerebellum: brain for an implicit self. FT Press, New Jersey
Ito M (2006) Cerebellar circuitry as a neuronal machine. Prog Neurobiol 78(3–5):272–303
Llinás RR, Walton KD, Lang EJ (2004) Cerebellum. In: Shepherd GM (ed) The synaptic organization of the brain, 5th edn. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 271–310
Czubayko U, Sultan F, Thier P, Schwarz C (2001) Two types of neurons in the rat cerebellar nuclei as distinguished by membrane potentials and intracellular fillings. J Neurophysiol 85(5):2017–2029
Aizenman CD, Huang EJ, Linden DJ (2003) Morphological correlates of intrinsic electrical excitability in neurons of the deep cerebellar nuclei. J Neurophysiol 89(4):1738–1747
Uusisaari M, Obata K, Knopfel T (2007) Morphological and electrophysiological properties of GABAergic and non-GABAergic cells in the deep cerebellar nuclei. J Neurophysiol 97(1):901–911
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 6th edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Zhang XY, Yu L, Zhuang QX, Peng SY, Zhu JN, Wang JJ (2013) Postsynaptic mechanisms underlying the excitatory action of histamine on medial vestibular nucleus neurons in rats. Br J Pharmacol 170(1):156–169
Friedman AK, Walsh JJ, Juarez B, Ku SM, Chaudhury D, Wang J, Li X, Dietz DM, Pan N, Vialou VF, Neve RL, Yue Z, Han MH (2014) Enhancing depression mechanisms in midbrain dopamine neurons achieves homeostatic resilience. Science 344(6181):313–319
Lazarov N, Rozloznik M, Reindl S, Rey-Ares V, Dutschmann M, Gratzl M (2006) Expression of histamine receptors and effect of histamine in the rat carotid body chemoafferent pathway. Eur J Neurosci 24(12):3431–3444
Zhang CZ, Zhuang QX, He YC, Li GY, Zhu JN, Wang JJ (2014) 5-HT receptor-mediated excitation on cerebellar fastigial nucleus neurons and promotion of motor behaviors in rats. Pflugers Arch 466:1259–1271
Aizenman CD, Linden DJ (1999) Regulation of the rebound depolarization and spontaneous firing patterns of deep nuclear neurons in slices of rat cerebellum. J Neurophysiol 82(4):1697–1709
de Zeeuw CI, Holstege JC, Ruigrok TJ, Voogd J (1989) Ultrastructural study of the GABAergic, cerebellar, and mesodiencephalic innervation of the cat medial accessory olive: anterograde tracing combined with immunocytochemistry. J Comp Neurol 284(1):12–35
Schwarz C, Schmitz Y (1997) Projection from the cerebellar lateral nucleus to precerebellar nuclei in the mossy fiber pathway is glutamatergic: a study combining anterograde tracing with immunogold labeling in the rat. J Comp Neurol 381(3):320–334
Bagnall MW, Zingg B, Sakatos A, Moghadam SH, Zeilhofer HU, du Lac S (2009) Glycinergic projection neurons of the cerebellum. J Neurosci 29(32):10104–10110
Altman J, Bayer SA (1978) Prenatal development of the cerebellar system in the rat. I. Cytogenesis and histogenesis of the deep nuclei and the cortex of the cerebellum. J Comp Neurol 179(1):23–48
Pugh JR, Raman IM (2008) Mechanisms of potentiation of mossy fiber EPSCs in the cerebellar nuclei by coincident synaptic excitation and inhibition. J Neurosci 28(42):10549–10560
Raman IM, Bean BP (1999) Ionic currents underlying spontaneous action potentials in isolated cerebellar Purkinje neurons. J Neurosci 19(5):1663–1674
Haas HL, Konnerth A (1983) Histamine and noradrenaline decrease calcium-activated potassium conductance in hippocampal pyramidal cells. Nature 302(5907):432–434
Sastry BR, Morishita W, Yip S, Shew T (1997) GABA-ergic transmission in deep cerebellar nuclei. Prog Neurobiol 53(2):259–271
Edgerton JR, Reinhart PH (2003) Distinct contributions of small and large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels to rat Purkinje neuron function. J Physiol 548(Pt 1):53–69
Inoue I, Yanai K, Kitamura D, Taniuchi I, Kobayashi T, Niimura K, Watanabe T, Watanabe T (1996) Impaired locomotor activity and exploratory behavior in mice lacking histamine H1 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93(23):13316–13320
Onodera K, Yamatodani A, Watanabe T, Wada H (1994) Neuropharmacology of the histaminergic neuron system in the brain and its relationship with behavioral disorders. Prog Neurobiol 42(6):685–702
Toyota H, Dugovic C, Koehl M, Laposky AD, Weber C, Ngo K, Wu Y, Lee DH, Yanai K, Sakurai E, Watanabe T, Liu C, Chen J, Barbier AJ, Turek FW, Fung-Leung WP, Lovenberg TW (2002) Behavioral characterization of mice lacking histamine H(3) receptors. Mol Pharmacol 62(2):389–397
Husson Z, Rousseau CV, Broll I, Zeilhofer HU, Dieudonne S (2014) Differential GABAergic and glycinergic inputs of inhibitory interneurons and Purkinje cells to principal cells of the cerebellar nuclei. J Neurosci 34(28):9418–9431
Pape HC (1996) Queer current and pacemaker: the hyperpolarization-activated cation current in neurons. Annu Rev Physiol 58:299–327
Uusisaari M, Knopfel T (2010) GlyT2+ neurons in the lateral cerebellar nucleus. Cerebellum 9(1):42–55
Li B, Zhu JN, Wang JJ (2014) Histaminergic afferent system in the cerebellum: structure and function. Cerebellum Ataxias 1:5
Korotkova TM, Haas HL, Brown RE (2002) Histamine excites GABAergic cells in the rat substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area in vitro. Neurosci Lett 320(3):133–136
Munakata M, Akaike N (1994) Regulation of K+ conductance by histamine H1 and H2 receptors in neurones dissociated from rat neostriatum. J Physiol 480(Pt 2):233–245
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr Rob Leurs (VU University Amsterdam, Amsterdam, the Netherlands) for his generous gifts of histamine H4 receptor agonist and antagonist. The work was supported by grants 31070959, 31071021, 31171050, 31330033, 91332124, 31471112 and NSFC/RGC Joint Research Scheme 31461163001 from the National Natural Science Foundation of China; SRFDP/RGC ERG grant 20130091140003 and NCET Program from the State Educational Ministry of China; grants BK2011014 and BK20140599 from the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China; and grant 2013T60520 from the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Jun Zhang, Qian-Xing Zhuang and Bin Li contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
(DOC 2322 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Zhuang, QX., Li, B. et al. Selective Modulation of Histaminergic Inputs on Projection Neurons of Cerebellum Rapidly Promotes Motor Coordination via HCN Channels. Mol Neurobiol 53, 1386–1401 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9096-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9096-3