Abstract
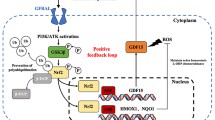
Stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 ligand-receptor axis is widely recommended as an attractive target for cancer therapy. Meanwhile, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process is linked to disease pathophysiology. As one of inhibitors of apoptosis proteins, survivin is implicated in the onset and development of cancer. In the present study, we tried to determine the cause-effect associations between SDF-1/CXCR4 axis and survivin expression in glioblastoma U-251 cell line. Survivin activation and inhibition were induced with exogenous SDF-1 and survivin small interfering RNA (survivin siRNA), respectively. Western blot was used to detect relevant proteins in SDF-1/CXCR4 axis. Western blot analysis revealed that survivin expression in U-251 increased in a dose- and time-dependent manner in response to SDF-1 treatment. However, the interference with MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathway prohibited SDF-1-induced survivin up-regulation. Importantly, survivin knockdown abrogated cell cycle progression and the expression of snail and N-cadherin, compared with non-transfectants. In conclusion, the present study shows that SDF-1 up-regulates survivin via MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathway, leading to cell cycle progression and EMT occurrence dependent on survivin. The blockade of survivin will allow for the treatment of glioblastoma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buckner JC (2003) Factors influencing survival in high-grade gliomas. Semin Oncol 30(6 Suppl 19):10–14
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO, European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumor and Radiotherapy Groups; National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352(10):987–996
Woodworth GF, Dunn GP, Nance EA, Hanes J, Brem H (2014) Emerging insights into barriers to effective brain tumor therapeutics. Front Oncol 4:126
Walker MD, Alexander E Jr, Hunt WE, MacCarty CS, Mahaley MS Jr, Mealey J Jr, Norrell HA, Owens G, Ransohoff J, Wilson CB, Gehan EA, Strike TA (1978) Evaluation of BCNU and/or radiotherapy in the treatment of anaplastic gliomas. A cooperative clinical trial. J Neurosurg 49(3):333–343
Moustakas A, Heldin P (2014) TGFβ and matrix-regulated epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Biochim Biophys Acta 1840(8):2621–2634
Lamouille S, Xu J, Derynck R (2014) Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15(3):178–196
Nieto MA (2013) Epithelial plasticity: a common theme in embryonic and cancer cells. Science 342(6159):1234850
Li Y, Ma J, Qian X, Wu Q, Xia J, Miele L, Sarkar FH, Wang Z (2013) Regulation of EMT by Notch signaling pathway in tumor progression. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 13(9):957–962
Balogh P, Katz S, Kiss AL (2013) The role of endocytic pathways in TGF-β signaling. Pathol Oncol Res 19(2):141–148
Fuxe J, Karlsson MC (2012) TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition: a link between cancer and inflammation. Semin Cancer Biol 22(5–6):455–461
Gao D, Vahdat LT, Wong S, Chang JC, Mittal V (2012) Microenvironmental regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in cancer. Cancer Res 72(19):4883–4889
Dave B, Mittal V, Tan NM, Chang JC (2012) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition, cancer stem cells and treatment resistance. Breast Cancer Res 14(1):202
Roy I, Evans DB, Dwinell MB (2014) Chemokines and chemokine receptors: Update on utility and challenges for the clinician. Surgery 155(6):961–973
Yoshie O (2013) Chemokine receptors as therapeutic targets. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi 36(4):189–196
Li W, Chen YQ, Shen YB, Shu HM, Wang XJ, Zhao CL, Chen CJ (2013) HIF-1α knockdown by miRNA decreases survivin expression and inhibits A549 cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Int J Mol Med 32(2):271–280
Guha M, Altieri DC (2009) Survivin as a global target of intrinsic tumor suppression networks. Cell Cycle 8(17):2708–2710
Lladser A, Sanhueza C, Kiessling R, Quest AF (2011) Is survivin the potential Achilles’ heel of cancer? Adv Cancer Res 111:1–37
Ravikumar G, Ananthamurthy A (2014) Cyclin D1 expression in ductal carcinoma of the breast and its correlation with other prognostic parameters. J Cancer Res Ther 10(3):671–675
Rekhi B, Motghare P (2014) Cyclin D1 and p16INK4 positive endometrial stromal sarcoma: a case report with new insights. Indian J Pathol Microbiol 57(4):606–608
Li T, Zhao X, Mo Z, Huang W, Yan H, Ling Z, Ye Y (2014) Formononetin promotes cell cycle arrest via downregulation of Akt/Cyclin D1/CDK4 in human prostate cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 34(4):1351–1358
Soppa U, Schumacher J, Florencio Ortiz V, Pasqualon T, Tejedor FJ, Becker W (2014) The Down syndrome-related protein kinase DYRK1A phosphorylates p27(Kip1) and Cyclin D1 and induces cell cycle exit and neuronal differentiation. Cell Cycle 13(13):2084–2100
Yang Y, Ma B, Li L, Jin Y, Ben W, Zhang D, Jiang K, Feng S, Huang L, Zheng J (2014) CDK2 and CDK4 play important roles in promoting the proliferation of SKOV3 ovarian carcinoma cells induced by tumor-associated macrophages. Oncol Rep 31(6):2759–2768
Kokontis JM, Lin HP, Jiang SS, Lin CY, Fukuchi J, Hiipakka RA, Chung CJ, Chan TM, Liao S, Chang CH, Chuu CP (2014) Androgen suppresses the proliferation of androgen receptor-positive castration-resistant prostate cancer cells via inhibition of Cdk2, CyclinA, and Skp2. PLoS One 9(10):e109170
Ahn SH, Jeong EH, Lee TG, Kim SY, Kim HR, Kim CH (2014) Gefitinib induces cytoplasmic translocation of the CDK inhibitor p27 and its binding to a cleaved intermediate of caspase 8 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cell Oncol (Dordr) 37(5):377–386
Xu J, Lamouille S, Derynck R (2009) TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res 19(2):156–172
Wendt MK, Allington TM, Schiemann WP (2009) Mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by TGF-beta. Futur Oncol 5(8):1145–1168
Miyazono K (2009) Transforming growth factor-beta signaling in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and progression of cancer. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci 85(8):314–323
Acknowledgments
We gratefully thank other members of Yang Lab for their critical reading of this paper and valuable suggestions.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article has been retracted at the request of the Editor-in-Chief and the Publisher per the Committee on Publication Ethics guidelines. The article shows evidence of irregularities in authorship during the submission process, there is strong reason to believe that the peer review process was compromised and the article shows similarities with the following articles which were submitted within a close timeframe:
Wenliang Chen, Xiao Zhong, Yi Wei, Yun Liu, Quan Yi, Genshui Zhang, Lishan He, Fajiang Chen, Yingping Liu, Jiandong Luo, TGF-β Regulates Survivin to Affect Cell Cycle and the Expression of EGFR and MMP9 in Glioblastoma, Molecular Neurobiology, April 2016, Volume 53, Issue 3, pp 1648–1653, DOI: 10.1007/s12035-015-9121-6 Received: 2 December 2014
Peng Yang, Gang Wang, Hongjun Huo, Qiang Li, Yan Zhao, Yuanhang Liu, SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling up-regulates survivin to regulate human sacral chondrosarcoma cell cycle and epithelial–mesenchymal transition via ERK and PI3K/AKT pathway, Med Oncol (2015) 32:377 DOI: 10.1007/s12032-014-0377-x Received: 13 November 2014
The article “SDF-1/CXCR4 Axis Regulates Cell Cycle Progression and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via Up-regulation of Survivin in Glioblastoma” was received 1 November 2014.
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0508-4.
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, A., Shi, R., Jiang, Y. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: SDF-1/CXCR4 Axis Regulates Cell Cycle Progression and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via Up-regulation of Survivin in Glioblastoma. Mol Neurobiol 53, 210–215 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-9006-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-9006-0