Abstract
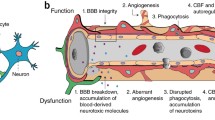
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly specialized system that controls the exchanges between the blood and the central nervous system (CNS). This barrier shields the CNS from toxic substances in the blood and provides nutrients to CNS, thus playing an essential role in the maintenance of homeostasis. The anatomical basis of the BBB is formed by the endothelial cells of brain microvasculature, with elaborated tight and adherens junctions, which together with pericytes, the basement membrane, and astrocytes, as well as neurons, microglia and oligodendrocytes form the neurovascular unit. The interaction between all these components guarantees a proper environment for neural function and a restricted permeability and transport. Pericytes were initially reported by Rouget in 1873 and since then they have been recognized as an important component of the BBB, despite the difficulty of their identification. Diverse functions have been assigned to pericytes, including a role in BBB properties, hemostasis, and angiogenesis, as well as a contractile, immune, and phagocytic function. These cells are also seen like multipotent cells and so with a great potential for therapy. Here, we review the neurovascular unit composition and the interplay between the diverse components, addressing pericytes with a particular detail.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABC:
-
ATP-binding cassette
- α-SMA:
-
α-smooth muscle actin
- Ang:
-
Angiopoietin
- AJ:
-
Adherens junction
- BBB:
-
Blood–brain barrier
- BM:
-
Basement membrane
- BMVEC:
-
Brain microvascular endothelial cell
- CAM:
-
Cell adhesion molecule
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- EC:
-
Endothelial cell
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- GFAP:
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- GLUT-1:
-
Glucose transporter-1
- ICAM-1:
-
Intercellular adhesion molecule-1
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- JAM:
-
Junctional adhesion molecule
- MHC:
-
Major histocompatibility complex
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- MRP:
-
Multidrug resistance-associated protein
- NVU:
-
Neurovascular unit
- OPC:
-
Oligodendrocyte precursor cell
- PDGF-β:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor-β
- P-gp:
-
P-glycoprotein
- RGS-5:
-
G-protein signaling-5
- TEER:
-
Transendothelial electrical resistance
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor-β
- TJ:
-
Tight junction
- VCAM-1:
-
Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- VEGFR2:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2
- ZO:
-
Zonula occludens
References
Persidsky Y, Ramirez SH, Haorah J, Kanmogne GD (2006) Blood–brain barrier: structural components and function under physiologic and pathologic conditions. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 1(3):223–236
Abbott NJ, Ronnback L, Hansson E (2006) Astrocyte–endothelial interactions at the blood–brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci 7(1):41–53
Abbott NJ, Patabendige AA, Dolman DE, Yusof SR, Begley DJ (2010) Structure and function of the blood–brain barrier. Neurobiol Dis 37(1):13–25
Cardoso FL, Brites D, Brito MA (2010) Looking at the blood–brain barrier: molecular anatomy and possible investigation approaches. Brain Res Rev 64(2):328–363
Ehrlich P (1885) Das sauerstoff-bedürfnis des organismus. EineFarbenanalytische Studie. Habilitation thesis, Berlin
Goldmann E (1913) Vitalfarbung am zentralnervensystem. Abhandl Konigl preuss Akad Wiss 1:1–60
Lewandowsky M (1900) Zur lehre der cerebrospinalflussigkeit. Z Klin Med 40:480–494
Reese TS, Karnovsky MJ (1967) Fine structural localization of a blood–brain barrier to exogenous peroxidase. J Cell Biol 34(1):207–217
Zlokovic BV (2008) The blood–brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron 57(2):178–201
Ballabh P, Braun A, Nedergaard M (2004) The blood–brain barrier: an overview: structure, regulation, and clinical implications. Neurobiol Dis 16(1):1–13
Joó F, Karnushina I (1973) A procedure for the isolation of capillaries from rat brain. Cytobios 8(29):41–48
Hawkins BT, Egleton RD (2006) Fluorescence imaging of blood–brain barrier disruption. J Neurosci Methods 151(2):262–267
Engelhardt B, Sorokin L (2009) The blood–brain and the blood–cerebrospinal fluid barriers: function and dysfunction. Semin Immunopathol 31(4):497–511
Veszelka S, Kittel Á, Deli MA (2011) Tools for modelling blood–brain barrier penetrability. In: Tihanyi K, Vastag M (eds) Solubility, delivery and ADME problems of drugs and drug candidates. Bentham Science, Washington, pp 166–188
Sedlakova R, Shivers RR, Del Maestro RF (1999) Ultrastructure of the blood–brain barrier in the rabbit. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol 31(1):149–161
Abbott NJ (2002) Astrocyte–endothelial interactions and blood–brain barrier permeability. J Anat 200(6):629–638
Kniesel U, Wolburg H (2000) Tight junctions of the blood–brain barrier. Cell Mol Neurobiol 20(1):57–76
Fenstermacher J, Gross P, Sposito N, Acuff V, Pettersen S, Gruber K (1988) Structural and functional variations in capillary systems within the brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci 529:21–30
de Boer AG, Gaillard PJ (2006) Blood–brain barrier dysfunction and recovery. J Neural Transm 113(4):455–462
Ribeiro MM, Pinto AR, Domingues MM, Serrano I, Heras M, Bardaji ER, Tavares I, Castanho MA (2011) Chemical conjugation of the neuropeptide kyotorphin and ibuprofen enhances brain targeting and analgesia. Mol Pharm 8(5):1929–1940
Oldendorf WH, Cornford ME, Brown WJ (1977) The large apparent work capability of the blood–brain barrier: a study of the mitochondrial content of capillary endothelial cells in brain and other tissues of the rat. Ann Neurol 1(5):409–417
Boado RJ, Pardridge WM (1993) Glucose deprivation causes posttranscriptional enhancement of brain capillary endothelial glucose transporter gene expression via GLUT1 mRNA stabilization. J Neurochem 60(6):2290–2296
Begley DJ (2004) ABC transporters and the blood–brain barrier. Curr Pharm Des 10(12):1295–1312
Tatsuta T, Naito M, Oh-hara T, Sugawara I, Tsuruo T (1992) Functional involvement of P-glycoprotein in blood–brain barrier. J Biol Chem 267(28):20383–20391
Tatsuta T, Naito M, Mikami K, Tsuruo T (1994) Enhanced expression by the brain matrix of P-glycoprotein in brain capillary endothelial cells. Cell Growth Differ 5(10):1145–1152
Mariano C, Sasaki H, Brites D, Brito MA (2011) A look at tricellulin and its role in tight junction formation and maintenance. Eur J Cell Biol 90(10):787–796
Mineta K, Yamamoto Y, Yamazaki Y, Tanaka H, Tada Y, Saito K, Tamura A, Igarashi M, Endo T, Takeuchi K, Tsukita S (2011) Predicted expansion of the claudin multigene family. FEBS Lett 585(4):606–612
Furuse M, Hirase T, Itoh M, Nagafuchi A, Yonemura S, Tsukita S (1993) Occludin: a novel integral membrane protein localizing at tight junctions. J Cell Biol 123(6 Pt 2):1777–1788
Martin-Padura I, Lostaglio S, Schneemann M, Williams L, Romano M, Fruscella P, Panzeri C, Stoppacciaro A, Ruco L, Villa A, Simmons D, Dejana E (1998) Junctional adhesion molecule, a novel member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that distributes at intercellular junctions and modulates monocyte transmigration. J Cell Biol 142(1):117–127
Aurrand-Lions M, Johnson-Leger C, Wong C, Du Pasquier L, Imhof BA (2001) Heterogeneity of endothelial junctions is reflected by differential expression and specific subcellular localization of the three JAM family members. Blood 98(13):3699–3707
Mariano C (2010) Looking at tricellulin expression in the brain. Master thesis, University of Lisbon. http://repositorio.ul.pt/handle/10451/2463
Vorbrodt AW, Dobrogowska DH (2003) Molecular anatomy of intercellular junctions in brain endothelial and epithelial barriers: electron microscopist's view. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 42(3):221–242
Niessen CM (2007) Tight junctions/adherens junctions: basic structure and function. J Invest Dermatol 127(11):2525–2532
Balabanov R, Dore-Duffy P (1998) Role of the CNS microvascular pericyte in the blood–brain barrier. J Neurosci Res 53(6):637–644
Yurchenco PD, Patton BL (2009) Developmental and pathogenic mechanisms of basement membrane assembly. Curr Pharm Des 15(12):1277–1294
Del Zoppo GJ, Milner R, Mabuchi T, Hung S, Wang X, Koziol JA (2006) Vascular matrix adhesion and the blood–brain barrier. Biochem Soc Trans 34(Pt 6):1261–1266
Dore-Duffy P, Cleary K (2011) Morphology and properties of pericytes. Methods Mol Biol 686(Part 1):49–68
Timpl R (1989) Structure and biological activity of basement membrane proteins. Eur J Biochem 180(3):487–502
Pöschl E, Schlotzer-Schrehardt U, Brachvogel B, Saito K, Ninomiya Y, Mayer U (2004) Collagen IV is essential for basement membrane stability but dispensable for initiation of its assembly during early development. Development 131(7):1619–1628
Sixt M, Engelhardt B, Pausch F, Hallmann R, Wendler O, Sorokin LM (2001) Endothelial cell laminin isoforms, laminins 8 and 10, play decisive roles in T cell recruitment across the blood–brain barrier in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Cell Biol 153(5):933–946
Coelho NM, González-Garcia C, Salmeron-Sanchez M, Altankov G (2011) Arrangement of type IV collagen and laminin on substrates with controlled density of –OH groups. Tissue Eng Part A 17(17–18):2245–2257
McKee KK, Harrison D, Capizzi S, Yurchenco PD (2007) Role of laminin terminal globular domains in basement membrane assembly. J Biol Chem 282(29):21437–21447
Carvey PM, Hendey B, Monahan AJ (2009) The blood–brain barrier in neurodegenerative disease: a rhetorical perspective. J Neurochem 111(2):291–314
Senger DR, Davis GE (2011) Angiogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3(8):a005090
Li L, Welser JV, Dore-Duffy P, del Zoppo GJ, Lamanna JC, Milner R (2010) In the hypoxic central nervous system, endothelial cell proliferation is followed by astrocyte activation, proliferation, and increased expression of the α6β4 integrin and dystroglycan. Glia 58(10):1157–1167
Bonkowski D, Katyshev V, Balabanov RD, Borisov A, Dore-Duffy P (2011) The CNS microvascular pericyte: pericyte–astrocyte crosstalk in the regulation of tissue survival. Fluid Barriers CNS 8(1):8
Brito MA, Silva RFM, Brites D (2006) Cell response to hyperbilirubinemia: a journey along key molecular events. In: Chen FJ (ed) New trends in brain research. Nova Science, New York, pp 1–38
Grant P, Pant HC (2000) Neurofilament protein synthesis and phosphorylation. J Neurocytol 29(11–12):843–872
del Zoppo GJ (2009) Relationship of neurovascular elements to neuron injury during ischemia. Cerebrovasc Dis 27(Suppl 1):65–76
del Zoppo GJ (2008) Virchow's triad: the vascular basis of cerebral injury. Rev Neurol Dis 5(Suppl 1):S12–S21
Cohen Z, Molinatti G, Hamel E (1997) Astroglial and vascular interactions of noradrenaline terminals in the rat cerebral cortex. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17(8):894–904
Cohen Z, Bonvento G, Lacombe P, Hamel E (1996) Serotonin in the regulation of brain microcirculation. Prog Neurobiol 50(4):335–362
Tong XK, Hamel E (1999) Regional cholinergic denervation of cortical microvessels and nitric oxide synthase-containing neurons in Alzheimer's disease. Neuroscience 92(1):163–175
Vaucher E, Tong XK, Cholet N, Lantin S, Hamel E (2000) GABA neurons provide a rich input to microvessels but not nitric oxide neurons in the rat cerebral cortex: a means for direct regulation of local cerebral blood flow. J Comp Neurol 421(2):161–171
Tontsch U, Bauer HC (1991) Glial cells and neurons induce blood–brain barrier related enzymes in cultured cerebral endothelial cells. Brain Res 539(2):247–253
Minami M (2011) Neuro-glio-vascular interaction in ischemic brains. Yakugaku Zasshi 131(4):539–544
Zlokovic BV (2011) Neurovascular pathways to neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease and other disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 12(12):723–738
Rosenberg GA (2012) Neurological diseases in relation to the blood–brain barrier. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2011.197
Oberheim NA, Wang X, Goldman S, Nedergaard M (2006) Astrocytic complexity distinguishes the human brain. Trends Neurosci 29:547–553
Lai CH, Kuo KH (2005) The critical component to establish in vitro BBB model: pericyte. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 50(2):258–265
Tao-Cheng JH, Brightman MW (1988) Development of membrane interactions between brain endothelial cells and astrocytes in vitro. Int J Dev Neurosci 6(1):25–37
Siddharthan V, Kim YV, Liu S, Kim KS (2007) Human astrocytes/astrocyte-conditioned medium and shear stress enhance the barrier properties of human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Brain Res 1147:39–50
Malina KC-K, Cooper I, Teichberg VI (2009) Closing the gap between the in-vivo and in-vitro blood–brain barrier tightness. Brain Res 1284:12–21
Halassa MM, Fellin T, Takano H, Dong JH, Haydon PG (2007) Synaptic islands defined by the territory of a single astrocyte. J Neurosci 27(24):6473–6477
Koehler RC, Roman RJ, Harder DR (2009) Astrocytes and the regulation of cerebral blood flow. Trends Neurosci 32(3):160–169
Salmina AB (2009) Neuron-glia interactions as therapeutic targets in neurodegeneration. J Alzheimers Dis 16(3):485–502
Georg WK (1996) Microglia: a sensor for pathological events in the CNS. Trends Neurosci 19(8):312–318
Kim SU, de Vellis J (2005) Microglia in health and disease. J Neurosci Res 81(3):302–313
Silva SL, Vaz AR, Barateiro A, Falcão AS, Fernandes A, Brito MA, Silva RFM, Brites D (2010) Features of bilirubin-induced reactive microglia: from phagocytosis to inflammation. Neurobiol Dis 40(3):663–675
Alonso A, Reinz E, Fatar M, Hennerici MG, Meairs S (2011) Clearance of albumin following ultrasound-induced blood–brain barrier opening is mediated by glial but not neuronal cells. Brain Res 1411:9–16
Willis CL (2011) Glia-induced reversible disruption of blood–brain barrier integrity and neuropathological response of the neurovascular unit. Toxicol Pathol 39(1):172–185
Nishioku T, Matsumoto J, Dohgu S, Sumi N, Miyao K, Takata F, Shuto H, Yamauchi A, Kataoka Y (2010) Tumor necrosis factor-α mediates the blood–brain barrier dysfunction induced by activated microglia in mouse brain microvascular endothelial cells. J Pharmacol Sci 112(2):251–254
Aggarwal S, Yurlova L, Simons M (2011) Central nervous system myelin: structure, synthesis and assembly. Trends Cell Biol 21(10):585–593
Watzlawik J, Warrington AE, Rodriguez M (2010) Importance of oligodendrocyte protection, BBB breakdown and inflammation for remyelination. Expert Rev Neurother 10(3):441–457
Rouget C (1873) Mémoire sur le developpement, la structure et les proprietes physiologiques des capillaires sanguins et lymphatiques. Arch Physiol Norm Path 5:603–663
Vimtrup BJ (1922) Beitrage zur Anatomie der kapillaren. Ubër contractile Elemente in der Gefäβwand der Blutcapillaren. Zeitschr Anat Entwickl 45:392–399
Krueger M, Bechmann I (2010) CNS pericytes: concepts, misconceptions, and a way out. Glia 58(1):1–10
Ribatti D, Nico B, Crivellato E (2011) The role of pericytes in angiogenesis. Int J Dev Biol 55(3):261–268
Dore-Duffy P (2008) Pericytes: pluripotent cells of the blood brain barrier. Curr Pharm Des 14(16):1581–1593
Braun A, Xu H, Hu F, Kocherlakota P, Siegel D, Chander P, Ungvari Z, Csiszar A, Nedergaard M, Ballabh P (2007) Paucity of pericytes in germinal matrix vasculature of premature infants. J Neurosci 27(44):12012–12024
Dore-Duffy P (2003) Isolation and characterization of cerebral microvascular pericytes. Methods Mol Med 89:375–382
Dalkara T, Gursoy-Ozdemir Y, Yemisci M (2011) Brain microvascular pericytes in health and disease. Acta Neuropathol 122(1):1–9
Shepro D, Morel NM (1993) Pericyte physiology. FASEB J 7(11):1031–1038
Frank RN, Dutta S, Mancini MA (1987) Pericyte coverage is greater in the retinal than in the cerebral capillaries of the rat. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 28(7):1086–1091
Frank RN, Turczyn TJ, Das A (1990) Pericyte coverage of retinal and cerebral capillaries. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 31:999–1007
Gerhardt H, Wolburg H, Redies C (2000) N-cadherin mediates pericytic–endothelial interaction during brain angiogenesis in the chicken. Dev Dyn 218(3):472–479
Fisher M (2009) Pericyte signaling in the neurovascular unit. Stroke 40(3 Suppl):S13–S15
Guillemin GJ, Brew BJ (2004) Microglia, macrophages, perivascular macrophages, and pericytes: a review of function and identification. J Leukoc Biol 75(3):388–397
Dore-Duffy P, Owen C, Balabanov R, Murphy S, Beaumont T, Rafols JA (2000) Pericyte migration from the vascular wall in response to traumatic brain injury. Microvasc Res 60(1):55–69
Bandopadhyay R, Orte C, Lawrenson JG, Reid AR, De Silva S, Allt G (2001) Contractile proteins in pericytes at the blood–brain and blood–retinal barriers. J Neurocytol 30(1):35–44
Nehls V, Drenckhahn D (1991) Heterogeneity of microvascular pericytes for smooth muscle type alpha-actin. J Cell Biol 113(1):147–154
Katyshev V, Dore-Duffy P (2012) Pericyte coculture models to study astrocyte, pericyte, and endothelial cell interactions. Methods Mol Biol 814(Part 4):467–481
Bernas MJ, Cardoso FL, Daley SK et al (2010) Establishment of primary cultures of human brain microvascular endothelial cells to provide an in vitro cellular model of the blood–brain barrier. Nat Protoc 5(7):1265–1272
Nakagawa S, Deli MA, Kawaguchi H, Shimizudani T, Shimono T, Kittel A, Tanaka K, Niwa M (2009) A new blood–brain barrier model using primary rat brain endothelial cells, pericytes and astrocytes. Neurochem Int 54(3-4):253–263
Nishioku T, Dohgu S, Takata F, Eto T, Ishikawa N, Kodama KB, Nakagawa S, Yamauchi A, Kataoka Y (2009) Detachment of brain pericytes from the basal lamina is involved in disruption of the blood–brain barrier caused by lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis in mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29(3):309–316
DeRuiter MC, Poelmann RE, VanMunsteren JC, Mironov V, Markwald RR, Gittenberger-de Groot AC (1997) Embryonic endothelial cells transdifferentiate into mesenchymal cells expressing smooth muscle actins in vivo and in vitro. Circ Res 80:444–451
Oishi K, Kamiyashiki T, Ito Y (2007) Isometric contraction of microvascular pericytes from mouse brain parenchyma. Microvasc Res 73(1):20–28
Ozerdem U, Grako KA, Dahlin-Huppe K, Monosov E, Stallcup WB (2001) NG2 proteoglycan is expressed exclusively by mural cells during vascular morphogenesis. Dev Dyn 222(2):218–227
Winkler EA, Bell RD, Zlokovic BV (2010) Pericyte-specific expression of PDGF beta receptor in mouse models with normal and deficient PDGF beta receptor signaling. Mol Neurodegener 5:32
Covas DT, Panepucci RA, Fontes AM, Silva WA Jr, Orellana MD, Freitas MC, Neder L, Santos AR, Peres LC, Jamur MC, Zago MA (2008) Multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells obtained from diverse human tissues share functional properties and gene-expression profile with CD146+ perivascular cells and fibroblasts. Exp Hematol 36:642–654
Crisan M, Yap S, Casteilla L, Chen CW, Corselli M, Park TS, Andriolo G, Sun B, Zheng B, Zhang L, Norotte C, Teng PN, Traas J, Schugar R, Deasy BM, Badylak S, Buhring HJ, Giacobino JP, Lazzari L, Huard J, Peault B (2008) A perivascular origin for mesenchymal stem cells in multiple human organs. Cell Stem Cell 3(3):301–313
Vandenhaute E, Dehouck L, Boucau MC, Sevin E, Uzbekov R, Tardivel M, Gosselet F, Fenart L, Cecchelli R, Dehouck MP (2011) Modelling the neurovascular unit and the blood–brain barrier with the unique function of pericytes. Curr Neurovasc Res 8(4):258–269
Rhodin JA, Fujita H (1989) Capillary growth in the mesentery of normal young rats. Intravital video and electron microscope analyses. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol 21(1):1–34
Hess DC, Abe T, Hill WD, Studdard AM, Carothers J, Masuya M, Fleming PA, Drake CJ, Ogawa M (2004) Hematopoietic origin of microglial and perivascular cells in brain. Exp Neurol 186(2):134–144
Dore-Duffy P, Katychev A, Wang X, Van Buren E (2006) CNS microvascular pericytes exhibit multipotential stem cell activity. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26(5):613–624
Cuevas P, Gutierrez-Diaz JA, Reimers D, Dujovny M, Diaz FG, Ausman JI (1984) Pericyte endothelial gap junctions in human cerebral capillaries. Anat Embryol (Berl) 170(2):155–159
Rucker HK, Wynder HJ, Thomas WE (2000) Cellular mechanisms of CNS pericytes. Brain Res Bull 51(5):363–369
Dohgu S, Takata F, Yamauchi A, Nakagawa S, Egawa T, Naito M, Tsuruo T, Sawada Y, Niwa M, Kataoka Y (2005) Brain pericytes contribute to the induction and up-regulation of blood–brain barrier functions through transforming growth factor-β production. Brain Res 1038(2):208–215
Nakagawa S, Deli MA, Nakao S, Honda M, Hayashi K, Nakaoke R, Kataoka Y, Niwa M (2007) Pericytes from brain microvessels strengthen the barrier integrity in primary cultures of rat brain endothelial cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 27(6):687–694
Nakamura K, Kamouchi M, Kitazono T, Kuroda J, Matsuo R, Hagiwara N, Ishikawa E, Ooboshi H, Ibayashi S, Iida M (2008) Role of NHE1 in calcium signaling and cell proliferation in human CNS pericytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 294(4):H1700–H1707
Al Ahmad A, Taboada CB, Gassmann M, Ogunshola OO (2011) Astrocytes and pericytes differentially modulate blood–brain barrier characteristics during development and hypoxic insult. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31(2):693–705
Shimizu F, Sano Y, Maeda T, Abe MA, Nakayama H, Takahashi R, Ueda M, Ohtsuki S, Terasaki T, Obinata M, Kanda T (2008) Peripheral nerve pericytes originating from the blood–nerve barrier expresses tight junctional molecules and transporters as barrier-forming cells. J Cell Physiol 217(2):388–399
Armulik A, Genove G, Mae M, Nisancioglu MH, Wallgard E, Niaudet C, He L, Norlin J, Lindblom P, Strittmatter K, Johansson BR, Betsholtz C (2010) Pericytes regulate the blood–brain barrier. Nature 468(7323):557–561
Bell RD, Winkler EA, Sagare AP, Singh I, LaRue B, Deane R, Zlokovic BV (2010) Pericytes control key neurovascular functions and neuronal phenotype in the adult brain and during brain aging. Neuron 68(3):409–427
Thanabalasundaram G, Schneidewind J, Pieper C, Galla HJ (2011) The impact of pericytes on the blood–brain barrier integrity depends critically on the pericyte differentiation stage. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 43:1284–1293
Kamouchi M, Ago T, Kitazono T (2011) Brain pericyte: emerging concepts and functional roles in brain homeostasis. Cell Mol Neurobiol 31:175–193
Daneman R, Zhou L, Kebede AA, Barres BA (2010) Pericytes are required for blood–brain barrier integrity during embryogenesis. Nature 468(7323):562–566
Brachvogel B, Pausch F, Farlie P, Gaipl U, Etich J, Zhou Z, Cameron T, von der Mark K, Bateman JF, Pöschl E (2007) Isolated Anxa5+/Sca-1+ perivascular cells from mouse meningeal vasculature retain their perivascular phenotype in vitro and in vivo. Exp Cell Res 313(12):2730–2743
Hellström M, Gerhardt H, Kalen M, Li X, Eriksson U, Wolburg H, Betsholtz C (2001) Lack of pericytes leads to endothelial hyperplasia and abnormal vascular morphogenesis. J Cell Biol 153(3):543–553
Dore-Duffy P, Balabanov R, Beaumont T, Hritz MA, Harik SI, LaManna JC (1999) Endothelial activation following prolonged hypobaric hypoxia. Microvasc Res 57(2):75–85
Gonul E, Duz B, Kahraman S, Kayali H, Kubar A, Timurkaynak E (2002) Early pericyte response to brain hypoxia in cats: an ultrastructural study. Microvasc Res 64(1):116–119
Jain RK (2003) Molecular regulation of vessel maturation. Nat Med 9(6):685–693
Yamagishi S, Yonekura H, Yamamoto Y, Fujimori H, Sakurai S, Tanaka N, Yamamoto H (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor acts as a pericyte mitogen under hypoxic conditions. Lab Invest 79(4):501–509
Hagedorn M, Balke M, Schmidt A, Bloch W, Kurz H, Javerzat S, Rousseau B, Wilting J, Bikfalvi A (2004) VEGF coordinates interaction of pericytes and endothelial cells during vasculogenesis and experimental angiogenesis. Dev Dyn 230(1):23–33
Winkler F, Kozin SV, Tong RT, Chae SS, Booth MF, Garkavtsev I, Xu L, Hicklin DJ, Fukumura D, di Tomaso E, Munn LL, Jain RK (2004) Kinetics of vascular normalization by VEGFR2 blockade governs brain tumor response to radiation: role of oxygenation, angiopoietin-1, and matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Cell 6(6):553–563
Kale S, Hanai J, Chan B, Karihaloo A, Grotendorst G, Cantley L, Sukhatme VP (2005) Microarray analysis of in vitro pericyte differentiation reveals an angiogenic program of gene expression. FASEB J 19(2):270–271
Brito MA, Zurolo E, Pereira P, Barroso C, Aronica E, Brites D (2011) Cerebellar axon/myelin loss, angiogenic sprouting, and neuronal increase of vascular endothelial growth factor in a preterm infant with kernicterus. J Child Neurol. doi:10.1177/0883073811423975
Abramsson A, Kurup S, Busse M, Yamada S, Lindblom P, Schallmeiner E, Stenzel D, Sauvaget D, Ledin J, Ringvall M, Landegren U, Kjellen L, Bondjers G, Li JP, Lindahl U, Spillmann D, Betsholtz C, Gerhardt H (2007) Defective N-sulfation of heparan sulfate proteoglycans limits PDGF-BB binding and pericyte recruitment in vascular development. Genes Dev 21(3):316–331
Ballabh P, Xu H, Hu F, Braun A, Smith K, Rivera A, Lou N, Ungvari Z, Goldman SA, Csiszar A, Nedergaard M (2007) Angiogenic inhibition reduces germinal matrix hemorrhage. Nat Med 13(4):477–485
Paik JH, Skoura A, Chae SS, Cowan AE, Han DK, Proia RL, Hla T (2004) Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor regulation of N-cadherin mediates vascular stabilization. Genes Dev 18(19):2392–2403
Virgintino D, Girolamo F, Errede M, Capobianco C, Robertson D, Stallcup WB, Perris R, Roncali L (2007) An intimate interplay between precocious, migrating pericytes and endothelial cells governs human fetal brain angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 10(1):35–45
Peppiatt CM, Howarth C, Mobbs P, Attwell D (2006) Bidirectional control of CNS capillary diameter by pericytes. Nature 443(7112):700–704
Yemisci M, Gursoy-Ozdemir Y, Vural A, Can A, Topalkara K, Dalkara T (2009) Pericyte contraction induced by oxidative–nitrative stress impairs capillary reflow despite successful opening of an occluded cerebral artery. Nat Med 15(9):1031–1037
Joyce NC, Haire MF, Palade GE (1985) Contractile proteins in pericytes. I. Immunoperoxidase localization of tropomyosin. J Cell Biol 100(5):1379–1386
Joyce NC, Haire MF, Palade GE (1985) Contractile proteins in pericytes. II. Immunocytochemical evidence for the presence of two isomyosins in graded concentrations. J Cell Biol 100(5):1387–1395
Ferrari-Dileo G, Davis EB, Anderson DR (1996) Glaucoma, capillaries and pericytes. 3. Peptide hormone binding and influence on pericytes. Ophthalmologica 210(5):269–275
van Zwieten EJ, Ravid R, Swaab DF, Van de Woude T (1988) Immunocytochemically stained vasopressin binding sites on blood vessels in the rat brain. Brain Res 474(2):369–373
Yamagishi S, Hsu CC, Kobayashi K, Yamamoto H (1993) Endothelin 1 mediates endothelial cell-dependent proliferation of vascular pericytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 191(3):840–846
Hamilton NB, Attwell D, Hall CN (2010) Pericyte-mediated regulation of capillary diameter: a component of neurovascular coupling in health and disease. Front Neuroenergetics 21:2
Haefliger IO, Zschauer A, Anderson DR (1994) Relaxation of retinal pericyte contractile tone through the nitric oxide–cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 35(3):991–997
Fernández-Klett F, Offenhauser N, Dirnagl U, Priller J, Lindauer U (2010) Pericytes in capillaries are contractile in vivo, but arterioles mediate functional hyperemia in the mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:22290–22295
Verbeek MM, Westphal JR, Ruiter DJ, de Waal RM (1995) T lymphocyte adhesion to human brain pericytes is mediated via very late antigen-4/vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 interactions. J Immunol 154(11):5876–5884
Fabry Z, Fitzsimmons KM, Herlein JA, Moninger TO, Dobbs MB, Hart MN (1993) Production of the cytokines interleukin 1 and 6 by murine brain microvessel endothelium and smooth muscle pericytes. J Neuroimmunol 47(1):23–34
Esiri MM, McGee JO (1986) Monoclonal antibody to macrophages (EMB/11) labels macrophages and microglial cells in human brain. J Clin Pathol 39(6):615–621
Balabanov R, Washington R, Wagnerova J, Dore-Duffy P (1996) CNS microvascular pericytes express macrophage-like function, cell surface integrin αM, and macrophage marker ED-2. Microvasc Res 52(2):127–142
Hasan M, Glees P (1990) The fine structure of human cerebral perivascular pericytes and juxtavascular phagocytes: their possible role in hydrocephalic edema resolution. J Hirnforsch 31:237–249
Castejón OJ (2011) Ultrastructural pathology of cortical capillary pericytes in human traumatic brain oedema. Folia Neuropathol 49:162–173
Bouchard BA, Shatos MA, Tracy PB (1997) Human brain pericytes differentially regulate expression of procoagulant enzyme complexes comprising the extrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 17(1):1–9
Kim JA, Tran ND, Li Z, Yang F, Zhou W, Fisher MJ (2006) Brain endothelial hemostasis regulation by pericytes. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26(2):209–217
Corselli M, Chen CW, Crisan M, Lazzari L, Péault B (2010) Perivascular ancestors of adult multipotent stem cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 30(6):1104–1109
Farrington-Rock C, Crofts NJ, Doherty MJ, Ashton BA, Griffin-Jones C, Canfield AE (2004) Chondrogenic and adipogenic potential of microvascular pericytes. Circulation 110:2226–2232
Paquet-Fifield S, Schlüter H, Li A, Aitken T, Gangatirkar P, Blashki D, Koelmeyer R, Pouliot N, Palatsides M, Ellis S, Brouard N, Zannettino A, Saunders N, Thompson N, Li J, Kaur P (2009) A role for pericytes as microenvironmental regulators of human skin tissue regeneration. J Clin Invest 119(9):2795–2806
Yamashima T, Tonchev AB, Vachkov IH, Popivanova BK, Seki T, Sawamoto K, Okano H (2004) Vascular adventitia generates neuronal progenitors in the monkey hippocampus after ischemia. Hippocampus 14(7):861–875
Tavazoie M, Van der Veken L, Silva-Vargas V, Louissaint M, Colonna L, Zaidi B, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Doetsch F (2008) A specialized vascular niche for adult neural stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 3(3):279–288
Dore-Duffy P, Mehedi A, Wang X, Bradley M, Trotter R, Gow A (2011) Immortalized CNS pericytes are quiescent smooth muscle actin-negative and pluripotent. Microvasc Res 82(1):18–27
Montiel-Eulefi E, Nery AA, Rodrigues LC, Sánchez R, Romero F, Ulrich H (2012) Neural differentiation of rat aorta pericyte cells. Cytometry A 81(1):65–71
Dellavalle A, Sampaolesi M, Tonlorenzi R, Tagliafico E, Sacchetti B, Perani L, Innocenzi A, Galvez BG, Messina G, Morosetti R, Li S, Belicchi M, Peretti G, Chamberlain JS, Wright WE, Torrente Y, Ferrari S, Bianco P, Cossu G (2007) Pericytes of human skeletal muscle are myogenic precursors distinct from satellite cells. Nat Cell Biol 9(3):255–267
Olson LE, Soriano P (2011) PDGFRβ signaling regulates mural cell plasticity and inhibits fat development. Dev Cell 20(6):815–826
Kaur C, Ling EA (2008) Blood brain barrier in hypoxic–ischemic conditions. Curr Neurovasc Res 5(1):71–81
Correale J, Villa A (2007) The blood–brain-barrier in multiple sclerosis: functional roles and therapeutic targeting. Autoimmunity 40(2):148–160
Rosenberg GA, Yang Y (2007) Vasogenic edema due to tight junction disruption by matrix metalloproteinases in cerebral ischemia. Neurosurg Focus 22(5):E4
Desai BS, Monahan AJ, Carvey PM, Hendey B (2007) Blood–brain barrier pathology in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease: implications for drug therapy. Cell Transplant 16(3):285–299
Remy S, Beck H (2006) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of pharmacoresistance in epilepsy. Brain 129(Pt 1):18–35
Lee SW, Kim WJ, Park JA, Choi YK, Kwon YW, Kim KW (2006) Blood–brain barrier interfaces and brain tumors. Arch Pharm Res 29(4):265–275
Grieshaber MC, Flammer J (2007) Does the blood–brain barrier play a role in glaucoma? Surv Ophthalmol 52(Suppl 2):S115–S121
Kaal EC, Vecht CJ (2004) The management of brain edema in brain tumors. Curr Opin Oncol 16(6):593–600
Verbeek MM, de Waal RM, Schipper JJ, Van Nostrand WE (1997) Rapid degeneration of cultured human brain pericytes by amyloid β protein. J Neurochem 68(3):1135–1141
Kovac A, Erickson MA, Banks WA (2011) Brain microvascular pericytes are immunoactive in culture: cytokine, chemokine, nitric oxide, and LRP-1 expression in response to lipopolysaccharide. J Neuroinflammation 8:139
Eberhard A, Kahlert S, Goede V, Hemmerlein B, Plate KH, Augustin HG (2000) Heterogeneity of angiogenesis and blood vessel maturation in human tumors: implications for antiangiogenic tumor therapies. Cancer Res 60(5):1388–1393
Duz B, Oztas E, Erginay T, Erdogan E, Gonul E (2007) The effect of moderate hypothermia in acute ischemic stroke on pericyte migration: an ultrastructural study. Cryobiology 55(3):279–284
Hammes HP, Lin J, Renner O, Shani M, Lundqvist A, Betsholtz C, Brownlee M, Deutsch U (2002) Pericytes and the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 51(10):3107–3112
Szpak GM, Lewandowska E, Wierzba-Bobrowicz T, Bertrand E, Pasennik E, Mendel T, Stepień T, Leszczyńska A, Rafałowska J (2007) Small cerebral vessel disease in familial amyloid and non-amyloid angiopathies: FAD-PS-1 (P117L) mutation and CADASIL. Immunohistochemical and ultrastructural studies. Folia Neuropathol 45(4):192–204
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by PTDC/SAU-FCF/68819/2006 grant from Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT), Lisbon, Portugal (to M. A. B.) and PEst-OE/SAU/UI4013/2011 (to iMed.UL). We thank our colleagues Rui Silva, Inês Palmela, Filipa Lourenço Cardoso, and Pedro Pereira for some of the photos presented in the figures. We also thank Szilvia Veszelka, Ágnes Kittel, and Mária A. Deli for sharing with us the material presented in Fig. 2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sá-Pereira, I., Brites, D. & Brito, M.A. Neurovascular Unit: a Focus on Pericytes. Mol Neurobiol 45, 327–347 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-012-8244-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-012-8244-2