Abstract
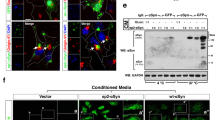
Mutations in the α-synuclein gene have been linked to rare cases of familial Parkinson's disease (PD). α-Synuclein, a 140 amino acid polypeptide, is a major component of Lewy bodies (LB), a pathological hallmark of PD. Transgenic mice, Drosophila and marmosets (Challitrix jacchus) expressing either wild type (WT) or mutant human α-synuclein develop motor deficits, LB-like inclusions in some neurons and neuronal degeneration. The effects of human α-synuclein were investigated in a neuronal rat cell line (B103). Plasmids expressing WT and mutant human α-synuclein regulated by the cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter were prepared and used for creating stably transfected neuronal rat cell lines. For localizing α-synuclein expression, stably transfected neuronal rat cell lines, expressing α-synuclein enhanced green fluorescent protein fusion proteins, regulated by either the CMV or the human platelet-derived growth factor ß promoter were generated. Over-expression of WT and A53T α-synuclein regulated by CMV promoter in stable transfectants resulted in formation of α-synuclein-immunopositive inclusion-like structures and mitochondrial alterations. Taken together, these results suggest that abnormal accumulation of α-synuclein could lead to mitochondrial alterations that might result in oxidative stress and eventually, cell death.







Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Adamczyk A, Solecka J, Strosznajder JB (2005) Expression of alpha-synuclein indifferent brain parts of adult and aged rats. J Physiol Pharmacol 56:29–37
Chartier-Harlin MC, Kachergus J, Roumier C et al (2004) Alpha-synuclein locus duplication as a cause of familial Parkinson's disease. Lancet 364:1167–1169
Coffin RS, Thomas SK, Thomas NS et al (1998) Pure populations of transduced primary human cells can be produced using GFP expressing herpes virus vectors and flow cytometry. Gene Ther 5:718–722
Conway KA, Harper JD, Lansbury PT (1998) Accelerated in vitro fibril formation by a mutant alpha-synuclein linked to early-onset Parkinson disease. Nat Med 4:1318–1320
Eslamboli A, Romero-Ramos M, Burger C et al (2007) Long-term consequences of human alpha-synuclein overexpression in the primate ventral midbrain. Brain 130:799–815
Feany MB, Bender WW (2000) A Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease. Nature 404:394–398
Galvin JE, Uryu K, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (1999) Axon pathology in Parkinson's disease and Lewy body dementia hippocampus contains alpha-, beta-, and gamma-synuclein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:13450–13455
George JM, Jin H, Woods WS, Clayton DF (1995) Characterization of a novel protein regulated during the critical period for song learning in the zebra finch. Neuron 15:361–372
Ghadially FN (1982) Ultrastructural pathology of the cell and matrix, 2nd edn. Beccles, London
Giasson BI, Uryu K, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (1999) Mutant and wild type human alpha-synucleins assemble into elongated filaments with distinct morphologies in vitro. J Biol Chem 274:7619–7622
Gozes I (2004) Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease: protein aggregations and neuroprotection. J Mol Neurosci 24:333–336
Hashimoto M, Hsu LJ, Xia Y et al (1999a) Oxidative stress induces amyloid-like aggregate formation of NACP/alpha-synuclein in vitro. Neuroreport 10:717–721
Hashimoto M, Takeda A, Hsu LJ, Takenouchi T, Masliah E (1999b) Role of cytochrome c as a stimulator of alpha-synuclein aggregation in Lewy body disease. J Biol Chem 274:28849–28852
Hsu LJ, Sagara Y, Arroyo A et al (2000) Alpha-synuclein promotes mitochondrial deficit and oxidative stress. Am J Pathol 157:401–410
Ibanez P, Bonnet AM, Debarges B et al (2004) Causal relation between alpha-synuclein gene duplication and familial Parkinson's disease. Lancet 364:1169–1171
Irizarry MC, Growdon W, Gomez-Isla T et al (1998) Nigral and cortical Lewy bodies and dystrophic nigral neurites in Parkinson's disease and cortical Lewy body disease contain alpha-synuclein immunoreactivity. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 57:334–337
Iwai A, Masliah E, Yoshimoto M et al (1995) The precursor protein of non-A beta component of Alzheimer's disease amyloid is a presynaptic protein of the central nervous system. Neuron 14:467–475
Iwai A (2000) Properties of NACP/alpha-synuclein and its role in Alzheimer's disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1502:95–109
Jakes R, Spillantini MG, Goedert M (1994) Identification of two distinct synucleins from human brain. FEBS Lett 345:27–32
Kahle PJ, Neumann M, Ozmen L et al (2000) Subcellular localization of wild-type and Parkinson's disease-associated mutant alpha-synuclein in human and transgenic mouse brain. J Neurosci 20:6365–6373
Kanda S, Bishop JF, Eglitis MA, Yang Y, Mouradian MM (2000) Enhanced vulnerability to oxidative stress by alpha-synuclein mutations and C-terminal truncation. Neurosci 97:279–284
Krüger R, Kuhn W, Muller T et al (1998) Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease. Nat Genet 18:106–108
Lee MK, Stirling W, Xu Y et al (2002) Human alpha-synuclein-harboring familial Parkinson's disease-linked Ala-53–Thr mutation causes neurodegenerative disease with alpha-synuclein aggregation in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:8968–8973
Lee VM, Giasson BI, Trojanowski JQ (2004) More than just two peas in a pod: common amyloidogenic properties of tau and alpha-synuclein in neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Neurosci 27:129–134
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Luft JH (1961) Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 9:409–414
Maries E, Dass B, Collier TJ, Kordower JH, Steece-Collier K (2003) The role of alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease: insights from animal models. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:727–738
Maroteaux L, Campanelli JT, Scheller RH (1988) Synuclein: a neuron-specific protein localized to the nucleus and presynaptic nerve terminal. J Neurosci 8:2804–2815
Martin LJ, Pan Y, Price AC et al (2006) Parkinson's disease alpha-synuclein transgenic mice develop neuronal mitochondrial degeneration and cell death. J Neurosci 26:41–50
Masliah E, Iwai A, Mallory M, Ueda K, Saitoh T (1996) Altered presynaptic protein NACP is associated with plaque formation and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol 148:201–210
Masliah E, Alford M, Mallory M, Rockenstein E, Moechars D, Van Leuven F (2000a) Abnormal glutamate transport function in mutant amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. Exp Neurol 163:381–387
Masliah E, Rockenstein E, Veinbergs I et al (2000b) Dopaminergic loss and inclusion body formation in alpha-synuclein mice: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Science 287:1265–1269
McLean PJ, Ribich S and Hyman BT (2000) Subcellular localization of alpha-synuclein in primary neuronal cultures: effect of missense mutations. J Neural Transm Suppl 53–63
McLean PJ, Kawamata H, Hyman BT (2001) Alpha-synuclein-enhanced green fluorescent protein fusion proteins form proteasome sensitive inclusions in primary neurons. Neurosci 104:901–912
Ostrerova-Golts N, Petrucelli L, Hardy J, Lee JM, Farer M, Wolozin B (2000) The A53T alpha-synuclein mutation increases iron-dependent aggregation and toxicity. J Neurosci 20:6048–6054
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E et al (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science 276:2045–2047
Reynolds ES (1963) Liver parenchymal cell injury in initial alterations of the cell following poisoning with carbon-tetrachloride. J Cell Biol 19:139–157
Robinson D, Ehlers U, Herken R, Herrmann F, Mayer F, Schürmann FW (1985) Präparationstechniken in der Elektronenmikroskopie, 1st edn. Springer, Berlin
Rockenstein E, Schwach G, Ingolic E et al (2005) Lysosomal pathology associated with alpha-synuclein accumulation in transgenic models using an eGFP fusion protein. J Neurosci Res 80:247–259
Saha AR, Ninkina NN, Hanger DP, Anderton BH, Davies AM, Buchman VL (2000) Induction of neuronal death by alpha-synuclein. Eur J Neurosci 12:3073–3077
Schubert D, Behl C (1993) The expression of amyloid beta protein precursor protects nerve cells from beta-amyloid and glutamate toxicity and alters their interaction with the extracellular matrix. Brain Res 629:275–282
Schubert D, Heinemann S, Carlisle W et al (1974) Clonal cell lines from the rat central nervous system. Nature 249:224–227
Shavali S, Brown-Borg HM, Ebadi M, Porter J (2008) Mitochondrial localization of alpha-synuclein protein in alpha-synuclein overexpressing cells. Neurosci. Lett. 439:125–128
Sidhu A, Wersinger C, Vernier P (2004) Does alpha-synuclein modulate dopaminergic synaptic content and tone at the synapse? FASEB J 18:637–647
Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J et al (2003) α-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson's disease. Science 320:841
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M (1997) Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388:839–840
Stefanova N, Klimaschewski L, Poewe W, Wenning GK, Reindl M (2001) Glial cell death induced by overexpression of alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci Res 65:432–438
Takeda A, Hashimoto M, Mallory M et al (1998) Abnormal distribution of the non-Abeta component of Alzheimer's disease amyloid precursor/alpha-synuclein in Lewy body disease as revealed by proteinase K and formic acid pretreatment. Lab Invest 78:1169–1177
Takenouchi T, Hashimoto M, Hsu LJ et al (2001) Reduced neuritic outgrowth and cell adhesion in neuronal cells transfected with human alpha-synuclein. Mol Cell Neurosci 17:141–150
Trimmer PA, Swerdlow RH, Parks JK et al (2000) Abnormal mitochondrial morphology in sporadic Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease cybrid cell lines. Exp Neurol 162:37–50
Ueda K, Fukushima H, Masliah E et al (1993) Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding an unrecognized component of amyloid in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:11282–11286
van der Putten PH, Wiederhold KH, Probst A et al (2000) Neuropathology in mice expressing human alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci 20:6021–6029
Yu S, Li X, Liu G et al (2007) Extensive nuclear localization of α-synuclein in normal rat brain neurons revealed by a novel monoclonal antibody. Neurosci 145:539–555
Zarranz JJ, Alegre J, Gomez-Esteban JC et al (2004) The new mutation, E46K, of alpha-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann Neurol 55:164–173
Zhang G, Gurtu V, Kain SR (1996) An enhanced green fluorescent protein allows sensitive detection of gene transfer in mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 227:707–711
Zhou W, Hurlbert MS, Schaack J, Prasad KN, Freed CR (2000) Overexpression of human alpha-synuclein causes dopamine neuron death in rat primary culture and immortalized mesencephalon-derived cells. Brain Res 866:33–43
Zhou W, Schaack J, Zawada WM, Freed CR (2002) Overexpression of human alpha-synuclein causes dopamine neuron death in primary human culture mesencephalic cells. Brain Res 926:42–50
Acknowledgments
All plasmids, but also the B103 cell line which were used in this work, were a gift of Elizer Masliah (Department of Neuroscience, University of California San Diego, La Jolla, USA). We would like to thank him for that and his laboratory for doing the Ribonuclease Protection Assay.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwach, G., Tschemmernegg, M., Pfragner, R. et al. Establishment of Stably Transfected Rat Neuronal Cell Lines Expressing α-Synuclein GFP Fusion Proteins. J Mol Neurosci 41, 80–88 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-009-9289-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-009-9289-1