Abstract
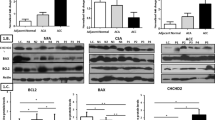
Although the effect of the central clock system on adrenal function has been extensively studied, the role of the peripheral clock system in adrenal tumorigenesis remains largely unexplored. In this study we investigated the expression of clock-related genes in normal adrenocortical tissue and adrenocortical tumors. Twenty-seven fresh frozen human adrenal tissues including 13 cortisol secreting adenomas (CSA), seven aldosterone producing adenomas (APA), and seven adrenocortical carcinomas (ACC) were collected. CLOCK, BMAL1, PER1, CRY1, Rev-ERB, and RORα mRNA and protein expression were determined by qPCR and immunoblotting in pathological tissues and compared with the adjacent normal adrenal tissues. A significant downregulation of PER1, CRY1, and Rev-ERB compared with their normal tissue was demonstrated in CSA. All clock-related genes were overexpressed in APA compared with their normal tissue, albeit not significantly. A significant upregulation of CRY1 and PER1 and downregulation of BMAL1, RORα, and Rev-ERB compared with normal adrenal tissue was observed in ACC. BMAL1 and PER1 were significantly downregulated in APA compared with CSA. CLOCK, CRY1, and PER1 were upregulated, whereas BMAL1, RORα, and Rev-ERB were downregulated in ACC compared with CSA. Our study demonstrated the expression of CLOCK, BMAL1, PER1, CRY1, Rev-ERB, and RORα in normal and pathological human adrenal tissues. Adrenal tumors exhibited altered expression of these genes compared with normal tissue, with specific differences between benign and malignant lesions and between benign tumors arising from glomerulosa vs fasciculata zone. Further studies should clarify whether these alterations could be implicated in adrenocortical tumorigenesis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Torres-Farfan, F.J. Valenzuela, R. Ebensperger, N. Méndez, C. Campino, H.G. Richter, G.J. Valenzuela, M. Serón-Ferré, Circadian cortisol secretion and circadian adrenal responses to ACTH are maintained in dexamethasone suppressed Capuchin Monkeys (Cebus Apella). Am. J. Primatol. 70(1), 93–100 (2008)
C. Campino, F.J. Valenzuela, C. Torres-Farfan, H.E. Reynolds, L. Abarzua-Catalan, E. Arteaga, C. Trucco, S. Guzmán, G.J. Valenzuela, M. Seron-Ferre, Melatonin exerts direct inhibitory actions on ACTH responses in the human adrenal gland. Horm. Metab. Res. 43(5), 337–342 (2011)
R.V. Andrews, G.E. Folk, Circadian metabolic patterns in cultured hamster adrenal glands. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 11, 393–409 (1964)
M.J. O’Hare, P.J. Hornsby, Absence of a circadian rhythm of corticosterone secretion in monolayer cultures of adult rat adrenocortical cells. Experientia 31(3), 378–380 (1975)
H. Oster, S. Damerow, S. Kiessling, V. Jakubcakova, D. Abraham, J. Tian, M.W. Hoffmann, G. Eichele, The circadian rhythm of glucocorticoids is regulated by a gating mechanism residing in the adrenal cortical clock. Cell Metab. 4(2), 163–173 (2006)
A. Ishida, T. Mutoh, T. Ueyama, H. Bando, S. Masubuchi, D. Nakahara, G. Tsujimoto, H. Okamura, Light activates the adrenal gland: timing of gene expression and glucocorticoid release. Cell Metab. 2(5), 297–307 (2005)
M.S. Jasper, W.C. Engeland, Splanchnic neural activity modulates ultradian and circadian rhythms in adrenocortical secretion in awake rats. Neuroendocrinology 59(2), 97–109 (1994)
J.E. Ottenweller, A.H. Meier, Adrenal innervation may be an extrapituitary mechanism able to regulate adrenocortical rhythmicity in rats. Endocrinology 111(4), 1334–1338 (1982)
Y.M. Ulrich-Lai, M.M. Arnhold, W.C. Engeland, Adrenal splanchnic innervation contributes to the diurnal rhythm of plasma corticosterone in rats by modulating adrenal sensitivity to ACTH. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 290(4), R1128–R1135 (2006)
C.H. Ko, J.S. Takahashi, Molecular components of the mammalian circadian clock. Hum. Mol. Genet. 15, Spec No R271–7 (2006)
N. Nader, G.P. Chrousos, T. Kino, Interactions of the circadian CLOCK system and the HPA axis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 21(5), 277–286 (2010)
A. Angelousi, E. Kassi, N. Nasiri-Ansari, H.S. Randeva, G.A. Kaltsas, G.P. Chrousos, Clock genes and cancer development in particular in endocrine tissues. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 26, R305–R317 (2019)
A. Angelousi, N. Nasiri-Ansari, E. Spilioti, E. Mantzou, V. Kalotyxou, G. Chrousos, G. Kaltsas, E. Kassi, Altered expression of circadian clock genes in polyglandular autoimmune syndrome type III. Endocrine 59(1), 109–119 (2018)
K.J. Livak, T.D. Schmittgen, Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−ΔΔC(T)) method. Methods 25(4), 402–408 (2001)
H. Guo, H. Guo, J.M. Brewer, M.N. Lehman, E.L. Bittman, Suprachiasmatic regulation of circadian rhythms of gene expression in hamster peripheral organs: effects of transplanting the pacemaker. J. Neurosci. 26(24), 6406–6412 (2006)
F.J. Valenzuela, C. Torres-Farfan, H.G. Richter, N. Mendez, C. Campino, F. Torrealba, G.J. Valenzuela, M. Serón-Ferré, Clock gene expression in adult primate suprachiasmatic nuclei and adrenal: is the adrenal a peripheral clock responsive to melatonin? Endocrinology 149(4), 1454–1461 (2008)
W.C. Engeland, M.M. Arnhold, Neural circuitry in the regulation of adrenal corticosterone rhythmicity. Endocrine 28(3), 325–332 (2005)
A.H. Meier, Daily variation in concentration of plasma corticosteroid in hypophysectomized rats. Endocrinology 98(6), 1475–1479 (1976)
J. Fahrenkrug, J. Hannibal, B. Georg, Diurnal rhythmicity of the canonical clock genes Per1, Per2 and Bmal1 in the rat adrenal gland is unaltered after hypophysectomy. J. Neuroendocrinol. 20(3), 323–329 (2008)
R.M. Buijs, J. Wortel, J.J. Van Heerikhuize, M.G. Feenstra, G.J. Ter Horst, H.J. Romijn, A. Kalsbeek, Anatomical and functional demonstration of a multisynaptic suprachiasmatic nucleus adrenal (cortex) pathway. Eur. J. Neurosci. 11(5), 1535–1544 (1999)
C. Cailotto, J. Lei, J. van der Vliet, C. van Heijningen, C.G. van Eden, A. Kalsbeek, P. Pévet, R.M. Buijs, Effects of nocturnal light on (clock) gene expression in peripheral organs: a role for the autonomic innervation of the liver. PLoS ONE 4(5), e5650 (2009)
Z. Nagy, A. Marta, H. Butz, I. Liko, K. Racz, A. Patocs, Modulation of the circadian clock by glucocorticoid receptor isoforms in the H295R cell line. Steroids 11, 620–27 (2016)
J. Richards, K.-Y. Cheng, S. All, G. Skopis, L. Jeffers, I.J. Lynch, C.S. Wingo, M.L. Gumz, A role for the circadian clock protein Per1 in the regulation of aldosterone levels and renal Na+ retention. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 305(12), F1697–704 (2013)
D.G. Romero, S. Rilli, M.W. Plonczynski, L.L. Yanes, M.Y. Zhou, E.P. Gomez-Sanchez, C.E. Gomez-Sanchez, Adrenal transcription regulatory genes modulated by angiotensin II and their role in steroidogenesis. Physiol. Genomics 30(1), 26–34 (2007)
M. Tetti, I. Castellano, F. Venziano, C. Magnino, F. Veglio, P. Mulatero, S. Monticone, Role of cryptochrome-1 and cryptochrome-2 in aldosterone-producing adenomas and adrenocortical cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19(6), E1675 (2018)
N.C. Nicolaides, E. Charmandari, T. Kino, G.P. Chrousos, Stress-related and circadian secretion and target tissue actions of glucocorticoids: impact on health. Front. Endocrinol. 8, 70 (2017)
E. Kassi, G. Chrousos, The central CLOCK system and the stress axis in health and disease. Hormones 12(2), 172–191 (2013)
S.-M. Kim, N. Neuendorff, R.C. Alaniz, Y. Sun, R.S. Chapkin, D.J. Earnest, Shift work cycle-induced alterations of circadian rhythms potentiate the effects of high-fat diet on inflammation and metabolism. FASEB J. 32(6), 3085–3095 (2018)
M. Perelis, K.M. Ramsey, J. Bass, The molecular clock as a metabolic rheostat. Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 17, 99–105 (2015)
A. Woller, D. Gonze, Modeling clock-related metabolic syndrome due to conflicting light and food cues. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 13641 (2018)
T. Karantanos, G. Theodoropoulos, M. Gazouli, A. Vaiopoulou, C. Karantanou, M. Lymberi, D. Pektasides, Expression of clock genes in patients with colorectal cancer. Int. J. Biol. Markers 28(3), 280–285 (2013)
M. Elshazley, M. Sato, T. Hase, R. Yamashita, K. Yoshida, S. Toyokuni, F. Ishiguro, H. Osada, Y. Sekido, K. Yokoi et al. The circadian clock gene BMAL1 is a novel therapeutic target for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Int. J. Cancer 131(12), 2820–2831 (2012)
A. Shostak, Circadian clock, cell division, and cancer: from molecules to organism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18(4), E873 (2017)
S. Sahar, P. Sassone-Corsi, Metabolism and cancer: the circadian clock connection. Nat. Rev. Cancer 9(12), 886–896 (2009)
A. Sancar, L.A. Lindsey-Boltz, S. Gaddameedhi, C.P. Selby, R. Ye, Y.-Y. Chiou, M.G. Kemp, J. Hu, J.H. Lee, N. Ozturk, Circadian clock, cancer, and chemotherapy. Biochemistry 54(2), 110–123 (2015)
S. Kiessling, N. Cermakian, The tumor circadian clock: a new target for cancer therapy? Future Oncol. 13(29), 2607–2610 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Angelousi, A., Nasiri-Ansari, N., Karapanagioti, A. et al. Expression of clock-related genes in benign and malignant adrenal tumors. Endocrine 68, 650–659 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-020-02246-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-020-02246-z