Abstract
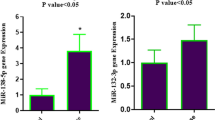
Modulation of nuclear factor KappaB (NF-κB) activation may play a role in regulating inflammatory conditions associated with coronary artery disease (CAD). MicroRNA-146a (miR-146a) primarily targets interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK-1) and tumour necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6 (TRAF-6), which results in inhibition of NF-κB via the TLR pathway. This study investigated the influence of the miR-146a GC rs2910164 on miR-146a expression in young South African Indians with CAD. CAD patients and controls were genotyped by PCR–RFLP and miRNA-146a levels were measured by qPCR. IRAK-1, TRAF-6 and NF-κB expression was determined by Western blot. No differences in genotypic frequency was found (GG: 45 vs. 47 %, GC: 46 vs. 41 %, CC: 9 vs. 12 %) in controls and patients respectively (odds ratio = 1.025; 95 % confidence interval 0.6782–1.550; p = 0.9164). Significantly higher levels of miR-146a was associated with CAD patients with the CC genotype (6.25-fold increase relative to controls and patients with the wildtype variant, p < 0.0001). Significantly lower levels of IRAK-1 (0.38 ± 0.02; p = 0.0072) and TRAF-6 (0.44 ± 0.02; p = 0.0146) was found in CAD patients with the CC genotype. The lowest levels of NF-κB and C-reactive protein were found in patients with the homozygous C allele compared to the heterozygous GC and wildtype variants. We propose a role for miR-146a in TLR signalling through a negative feedback mechanism involving the attenuation of NF-κB by down-regulation of IRAK-1 and TRAF-6. Our observations implicate miR-146a as a target for lowering inflammation in CAD patients.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hung, P. S., Chang, K. W., Kao, S. Y., Chu, T. H., Liu, C. J., & Lin, S. C. (2012). Association between the rs2910164 polymorphism in pre-mir-146a and oral carcinoma progression. Oral Oncology, 48, 404–408.
Takahashi, Y., Satoh, M., Minami, Y., Tabuchi, T., Itoh, T., & Nakamura, M. (2010). Expression of miR-146a/b is associated with the Toll-like receptor 4 signal in coronary artery disease: Effect of renin-angiotensin system blockade and statins on miRNA-146a/b and Toll-like receptor 4 levels. Clinical Science, 119, 395–405.
Zorc, M., Jevsinek Skok, D., Godnic, I., Calin, G. A., Horvat, S., Jiang, Z., et al. (2012). Catalog of microRNA seed polymorphisms in vertebrates. PLoS ONE, 7(1), e30737.
Ellwanger, D. C., Buttner, F. A., Mewes, H. W., & Stumpflen, V. (2011). The sufficient minimal set of miRNA seed types. Bioinformatics, 27(10), 1346–1350.
Hu, Z., Liang, J., Wang, Z., Tian, T., Zhou, X., Chen, J., et al. (2008). Common genetic variants in pre-microRNAs were associated with increased risk of breast cancer in Chinese women. Human Mutation, 30(1), 79–84.
Mittal, R. D., Gangwar, R., George, G. P., Mittal, T., & Kapoor, R. (2011). Investigative role of pre-microRNAs in bladder cancer patients: A case-control study in North India. DNA and Cell Biology, 30(6), 401–406.
Li, L., Chen, X., & Li, Y. (2010). MicroRNA-146a and human disease. Scandinavian Journal of Immunology, 71, 227–231.
Yang, B., Chen, J., Li, Y., Zhang, J., Li, D., Huang, Z., et al. (2012). Association of polymorphisms in pre-miRNA with inflammatory biomarkers in rheumatoid arthritis in the Chinese Han population. Human Immunology, 73, 101–106.
Xu, T., Zhu, Y., Wei, Q., Yuan, Y., Zhou, F., Ge, Y., et al. (2008). A functional polymorphism in the miR-146a gene is associated with the risk for hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis, 29(11), 2126–2131.
Li, D., Wang, T., Song, X., Qucuo, M., Yang, B., Zhang, J., et al. (2011). Genetic study of two single nucleotide polymorphisms within corresponding microRNAs and susceptibility to tuberculosis in a Chinese Tibetan and Han population. Human Immunology, 72, 598–602.
Raitoharju, E., Lyytikainen, L. P., Levula, M., Oksala, N., Mennander, A., Tarkka, M., et al. (2011). miR-21, miR-210, miR-34a, and miR-146a/b are up-regulated in human atherosclerotic plaques in the Tampere Vascular Study. Atherosclerosis, 219, 211–217.
Xu, J., Zhao, J., Evan, G., Xiao, C., Cheng, Y., & Xiao, J. (2012). Circulating microRNAs: Novel biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases. Journal of Molecular Medicine, 90, 865–875.
Jamaluddin, M. S., Weakly, S. M., Zhang, L., Kougias, P., Lin, P. H., Yao, Q., et al. (2011). miRNAs: Roles and clinical applications in vascular disease. Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics, 11(1), 79–89.
Zilahi, E., Tarr, T., Papp, G., Griger, Z., Sipka, S., & Zeher, M. (2011). Increased microRNA-146a/b, TRAF6 gene and decreased IRAK1 gene expressions in the peripheral mononuclear cells of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Immunology Letters, 141, 165–168.
Jazdzewski, K., Liyanarachchi, S., Swierniak, M., Pachucki, J., Ringel, M. D., Jarzab, B., et al. (2009). Polymorphic mature microRNAs from passenger strand of pre-miR-146a contribute to thyroid cancer. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 106(5), 1502–1505.
Chatzikyriakidou, A., Voulgari, P. V., Georgiou, I., & Drosos, A. A. (2010). A polymorphism in the 3′-UTR of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK1), a target gene of miR-146a, is associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. Joint Bone Spine, 77(5), 411–413.
Yue, C., Wang, M., Ding, B., Wang, W., Fu, S., Zhou, D., et al. (2011). Polymorphism of the pre-miR-146a is associated with risk of cervical cancer in a Chinese population. Gynecologic Oncology, 122, 33–37.
Curtale, G., Citarella, F., Carissimi, C., Goldoni, M., Carucci, N., Fulci, V., et al. (2010). An emerging player in the adaptive immune response: MicroRNA-146a is a modulator of IL-2 expression and activation-induced cell death in T lymphocytes. Blood, 115(2), 265–273.
Taganov, K. D., Boldin, M. P., Chang, K. J., & Baltimore, D. (2006). NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 103(33), 12481–12486.
Mohan, V., Venkatraman, J. V., & Pradeepa, R. (2010). Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: The Indian scenario. Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology, 4(1), 158–170.
Murray, C. J., & Lopez, A. D. (1997). Alternative projections of mortality and disability by cause 1990–2020: Global burden of disease study. The Lancet, 349, 1498–1504.
Reddy, K. S., & Yusuf, S. (1998). Emerging epidemic of cardiovascular disease in developing countries. Circulation, 97(6), 596–601.
Seedat, Y. K. (2005). Review: Diabetes mellitus in South African Indians. The British Journal of Diabetes & Vascular Disease, 5(5), 249–251.
Sharma, M., & Ganguly, N. (2005). Premature coronary artery disease in Indians and its associated risk factors. Vascular Health and Risk Management, 1(3), 217–225.
Norman, R., Bradshaw, D., Schneider, M., Pieterse, D., & Groenwald, P. (2006). Revised burden of disease estimates for the comparative risk factor assessment, South Africa 2000. Cape Town: Medical Research Council.
Sambrook, J., & Russell, D. W. (2001). Rapid isolation of mammalian DNA in molecular cloning: A laboratory manual (3rd ed.). New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Livak, K. J., & Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods, 25(4), 402–408.
Takeda, K., & Akira, S. (2004). TLR signalling pathways. Seminars in Immunology, 16, 3–9.
Pauley, K. M., Satoh, M., Chan, A. L., Bubb, M. R., Reeves, W. H., & Chan, E. K. (2008). Upregulated miR-146a expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Research & Therapy, 10(4), 101.
Hirschfield, G. M., & Pepys, M. B. (2003). C-reactive protein and cardiovascular disease: New insights from an old molecule. QJM, 96(11), 793–807.
Shen, J., Ambrosone, C. B., DiCioccio, R., Odunsi, K., Lele, S. B., & Zhao, H. (2008). A functional polymorphism in the miR-146a gene and age of familial breast/ovarian cancer diagnosis. Carcinogenesis, 29(10), 1963–1966.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation and College of Health Science Scholarships.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramkaran, P., Khan, S., Phulukdaree, A. et al. miR-146a Polymorphism Influences Levels of miR-146a, IRAK-1, and TRAF-6 in Young Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. Cell Biochem Biophys 68, 259–266 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-013-9704-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-013-9704-7