Abstract
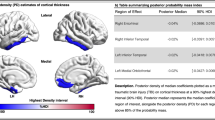
Cognitive impairment may result in significant disability in patients with Multiple Sclerosis (MS). Previous Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) studies on cognition in MS were mainly based on measures of gross brain involvement. This study, using voxel-based morphometry (VBM), aims to investigate associations between the regional distribution of grey matter (GM) damage and cognitive performance in patients with MS. Eighteen MS patients underwent an extensive neuropsychological battery and MRI, including T2-weighted scans and T1-weighted volumes. A group of 18 healthy individuals were also investigated by MRI and served as controls for the VBM. A cross-sectional analysis was first performed, to assess the pattern of regional GM atrophy in MS patients. Then, the impact of regional GM damage on patients’ neuropsychological performance was investigated by multiple regression analyses in the patient group. Correlations between global indexes of brain damage and neuropsychological measures were also assessed for comparison with previous literature. The comparison between MS patients and healthy controls revealed a widespread pattern of regional GM atrophy. Consistent with previous studies, associations were found between neuropsychological scores, and global brain atrophy and T2-lesion volumes. Critically, significant associations were found between scores on the Symbol Digit Modalities test and Long Delay Cued Recall on the California Verbal Learning Test, and regional GM volumes in well localized areas of the prefrontal, parietal, temporal, and insular cortex. This study confirms that global assessments of brain damage correlate with measures of cognitive impairment in MS. Interestingly, VBM contributes to clarify those brain regions that more likely determine the cognitive deficits observed in patients. These findings clarify the pathophysiology of cognitive impairment in MS, and propose measures which could be considered for longitudinal monitoring of patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amato, M. P., Bartolozzi, M. L., Zipoli, V., Portaccio, E., Mortilla, M., Guidi, L., et al. (2004). Neocortical volume decrease in relapsing-remitting ms patients with mild cognitive impairment. Neurology, 63(1), 89–93.
Amato, M. P., Portaccio, E., Goretti, B., Zipoli, V., Ricchiuti, L., De Caro, M. F., Patti, F., et al. (2006). The Rao’s brief repeatable battery and stroop test: Normative values with age, education and gender corrections in an Italian population. Multiple Sclerosis, 12(6), 787–793.
Arnett, P. A., Rao, S. M., Bernardin, L., Grafman, J., Yetkin, F. Z., & Lobeck, L. (1994). Relationship between frontal lobe lesions and Wisconsin Card Sorting Test performance in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology, 44(3), 420–425.
Ashburner, J., & Friston, K. J. (2000). Voxel-based morphometry-the methods. NeuroImage, 11(6), 805–821.
Ashburner, J., & Friston, K. J. (2001). Why voxel-based morphometry should be used. NeuroImage, 14(6), 1238–1243.
Ashburner, J., & Friston, K. J. (2005). Unified segmentation. NeuroImage, 26(3), 839–851.
Audoin, B., Ibarrola, D., Au Duong, M. V., Pelletier, J., Confort-Gouny, S., Malikova, I., et al. (2005). Functional MRI study of PASAT in normal subjects. Magma, 18(2), 96–102.
Baldo, J. V., Delis, D., Kramer, J., & Shimamura, A. P. (2002). Memory performance on the California Verbal Learning Test-II: Findings from patients with focal frontal lesions. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 8(4), 539–546.
Benedict, R. H., Bakshi, R., Simon, J. H., Priore, R., Miller, C., & Munschauer, F. (2002). Frontal cortex atrophy predicts cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. The Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 14(1), 44–51.
Benedict, R. H., Weinstock-Guttman, B., Fishman, I., Sharma, J., Tjoa, C. W., & Bakshi, R. (2004). Prediction of neuropsychological impairment in multiple sclerosis: Comparison of conventional magnetic resonance imaging measures of atrophy and lesion burden. Archives of Neurology, 61(2), 226–230.
Benedict, R. H., Carone, D. A., & Bakshi, R. (2004). Correlating brain atrophy with cognitive dysfunction, mood disturbances, and personality disorder in multiple sclerosis. Journal of Neuroimaging, 14(Suppl 3), 36S–45S.
Benedict, R. H., Zivadinov, R., Carone, D. A., Weinstock-Guttman, B., Gaines, J., Maggiore, C., et al. (2005). Regional lobar atrophy predicts memory impairment in multiple sclerosis. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 26(7), 1824–1831.
Benedict, R. H., Bruce, J. M., Dwyer, M. G., Abdelrahman, N., Hussein, S., Weinstock-Guttman, B., et al. (2006). Neocortical atrophy, third ventricular width, and cognitive dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. Archives of Neurology, 63(9), 301–306.
Benton, A. L., Varney, N. R., & Hamsher, K. D. (1978). Visuospatial judgment. A clinical test. Archives of Neurology, 35(6), 364–367.
Bermel, R. A., & Bakshi, R. (2006). The measurement and clinical relevance of brain atrophy in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurology, 5(2), 158–170.
Borkowsky, J. G., Benton, A. L., & Spreen, O. (1967). Word fluency and brain damage. Neuropsychologia, 5, 135–140.
Brass, S. D., Benedict, R. H., Weinstock-Guttman, B., Munschauer, F., & Bakshi, R. (2006). Cognitive impairment is associated with subcortical magnetic resonance imaging grey matter T2 hypointensity in multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis, 12(4), 437–444.
Cabeza, R. (2008). Role of parietal regions in episodic memory retrieval: The dual attentional processes hypothesis. Neuropsychologia, 46(7), 1813–1827.
Camp, S. J., Stevenson, V. L., Thompson, A. J., Miller, D. H., Borras, C., Auriacombe, S., et al. (1999). Cognitive function in primary progressive and transitional progressive multiple sclerosis: A controlled study with MRI correlates. Brain, 122(7), 1341–1348.
Carlesimo, G. A., Caltagirone, C., & Gainotti, G. (1996). The mental deterioration battery: Normative data, diagnostic reliability and qualitative analyses of cognitive impairment. The group for the standardization of the mental deterioration battery. European Neurology, 36(6), 378–384.
Carlesimo, G. A., Buccione, I., Fadda, L., Graceffa, A., Mauri, M., Lorusso, S., Bevilacqua, G., et al. (2002). Standardizzazione di due test di memoria per uso clinico: Breve Racconto e Figura di Rey. Nuova Rivista di Neurologia, 12, 1–13.
Ceccarelli, A., Rocca, M. A., Pagani, E., Colombo, B., Martinelli, V., Comi, G., & Filippi, M. (2008). A voxel-based morphometry study of grey matter loss in ms patients with different clinical phenotypes. NeuroImage, 42(1), 315–322.
Chiaravalloti, N. D., & DeLuca, J. (2008). Cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurology, 7(12), 1139–115.
Chiaravalloti, N. D., Wylie, G. R., Leavitt, V. M., DeLuca, J. (Published online, 2012). Increased cerebral activation after behavioral treatment for memory deficits in MS. Journal of Neurology.
Christodoulou, C., Krupp, L. B., Liang, Z., Huang, W., Melville, P., Roque, C., et al. (2003). Cognitive performance and MR markers of cerebral injury in cognitively impaired MS patients. Neurology, 60(11), 1793–1798.
Cutter, G. R., Baier, M. L., Rudick, R. A., Cookfair, D. L., Fischer, J. S., Petkau, J., et al. (1999). Development of a multiple sclerosis functional composite as a clinical trial outcome measure. Brain, 122(5), 871–882.
Delis, D. C., Kramer, J. H., Kaplan, E., & Ober, B. A. (2000). California verbal learning test manual: Second edition, adult version. San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation.
Fink, F., Eling, P., Rischkau, E., Beyer, N., Tormadl, B., Klein, J., & Hildebrandt, H. (2010). The association between California Verbal Learning Test performance and fibre impairment in multiple sclerosis: Evidence from diffusion tensor imaging. Multiple Sclerosis, 16(3), 332–341.
Fischer, J. S., Rudick, R. A., Cutter, G. R., & Reingold, S. C. (1999). The multiple sclerosis functional composite measure (MSFC): An integrated approach to MS clinical outcome assessment. National ms society clinical outcomes assessment task force. Multiple Sclerosis, 5(4), 244–250.
Forn, C., Belenguer, A., Belloch, V., Sanjuan, A., Parcet, M. A., & Avila, C. (2011). Anatomical and functional differences between the paced auditory serial addition test and the symbol digit modalities test. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 33(1), 42–50.
Fulton, J. C., Grossman, R. I., Udupa, J., Mannon, L. J., Grossman, M., Wei, L., et al. (1999). MR lesion load and cognitive function in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 20(10), 1951–1955.
Good, C. D., Johnsrude, I. S., Ashburner, J., Henson, R. N., Friston, K. J., & Frackowiak, R. S. (2001). A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. NeuroImage, 14(1), 21–36.
Hester, R., Fassbender, C., & Garavan, H. (2004). Individual differences in error processing: A review and reanalysis of three event-related fMRI studies using the GO/NOGO task. Cerebral Cortex, 14(9), 986–994.
Heun, R., Klose, U., Jessen, F., Erb, M., Papassotiropoulos, A., Lotze, M., & Grodd, W. (1999). Functional MRI of cerebral activation during encoding and retrieval of words. Human Brain Mapping, 8, 157–169.
Hildebrandt, H., Lanz, M., Hahn, H. K., Hoffmann, E., Schwarze, B., Schwendemann, G., et al. (2007). Cognitive training in MS: effects and relation to brain atrophy. Restor Neurol Neurosci 25(1), 33–43.
Hohol, M. J., Guttmann, C. R., Orav, J., Mackin, G. A., Kikinis, R., Khoury, S. J., et al. (1997). Serial neuropsychological assessment and magnetic resonance imaging analysis in multiple sclerosis. Archives of Neurology, 54(8), 1018–1025.
Kurtzke, J. F. (1983). Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: An expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology, 33(11), 1444–1452.
Lanzeron, R. H., Rombouts, S. A., de Sonneville, L., Barkhof, F., & Scheltens, P. (2003). A paced visual serial addition test for fMRI. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 213(1–2), 29–34.
Litvan, I., Grafman, J., Vendrell, P., & Martinez, J. M. (1988). Slowed information processing in multiple sclerosis. Archives of Neurology, 45(3), 281–285.
Lockwood, A. H., Linn, R. T., Szymanski, H., Coad, M. L., & Wack, D. S. (2004). Mapping the neural systems that mediate the Paced Auditory Serial Addition Task (PASAT). Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 10(1), 26–34.
Lublin, F. D., & Reingold, S. C. (1996). Defining the clinical course of multiple sclerosis: Results of an international survey. National multiple sclerosis society (USA) advisory committee on clinical trials of new agents in multiple sclerosis. Neurology, 46(4), 907–911.
Mainero, C., Caramia, F., Pozzilli, C., Pisani, A., Pestalozza, I., Borriello, G., Bozzao, L., & Pantano, P. (2004). fMRI evidence of brain reorganization during attention and memory task in multiple sclerosis. NeuroImage, 21(3), 858–867.
McDonald, W. I., Compstonm, A., Edanm, G., Goodkinm, D., Hartung, H. P., Lublin, F. D., et al. (2001). Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: Guidelines from the international panel on the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Annals of Neurology, 50(1), 121–127.
Mesaros, S., Rocca, M. A., Absinta, M., Ghezzi, A., Milani, N., Moiola, L., et al. (2008). Evidence of thalamic gray matter loss in pediatric multiple sclerosis. Neurology, 70, 1107–1112.
Morgen, K., Sammer, G., Courtney, S. M., Wolters, T., Melchior, H., Blecker, C. R., et al. (2006). Evidence for a direct association between cortical atrophy and cognitive impairment in relapsing-remitting MS. NeuroImage, 30(3), 891–898.
Nocentini, U., Giordano, A., Di Vincenzo, S., Panella, M., & Pasqualetti, P. (2006). The symbol digit modalities test–oral version: Italian normative data. Functional Neurology, 21(2), 93–96.
Prinster, A., Quarantelli, M., Orefice, G., Lanzillo, R., Brunetti, A., Mollica, C., et al. (2006). Grey matter loss in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: A voxel-based morphometry study. NeuroImage, 29, 859–867.
Rao, S. M. (1986). Neuropsychology of multiple sclerosis: A critical review. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 8(5), 503–542.
Rao, S. M., Leo, G. J., Haughton, V. M., St Aubin-Faubert, P., & Bernardin, L. (1989). Correlation of magnetic resonance imaging with neuropsychological testing in multiple sclerosis. Neurology, 39(2, Pt 1), 161–166.
Raven, J. C. (1949). Progressive matrices (1947), sets A, Ab, B. London, Lewis: Board and Book Forms.
Rey, A. (1941). L’examen psychologique dans les cas d’encèphalopathie traumatique. Archives de Psychologie, 28, 286–340.
Rovaris, M., & Filippi, M. (2000). MRI correlates of cognitive dysfunction in multiple sclerosis patients. Journal of Neurovirology, 6(Suppl 2), S172–S175.
Rypma, B., Berger, J. S., Genova, H. M., Rebbecchi, D., & D’Esposito, M. (2005). Dissociatine age-related changes in cognitive strategy and neural efficiency using event-related fMRI. Cortex, 41(4), 582–594.
Sanfilipo, M. P., Benedict, R. H., Weinstock-Guttman, B., & Bakshi, R. (2006). Gray and white matter brain atrophy and neuropsychological impairment in multiple sclerosis. Neurology, 66(5), 685–692.
Sepulcre, J., Sastre-Garriga, J., Cercignani, M., Ingle, G. T., Miller, D. H., & Thompson, A. J. (2006). Regional gray matter atrophy in early primary progressive multiple sclerosis: A voxel-based morphometry study. Archives of Neurology, 63, 1175–1180.
Smith, A. (2000). Symbol digit modalities test, manual. Webster Psychological Services.
Solari, A., Motta, A., Mendozzi, L., Aridon, P., Bergamaschi, R., Ghezzi, A., et al. (2003). The Italian version of the Chicago multiscale depression inventory: Translation, adaptation and testing in people with multiple sclerosis. Neurological Sciences, 24(6), 371–379.
Sumowski, J. F., Chiaravalloti, N., & Deluca, J. (2009). Cognitive reserve moderates the negative effect of brain atrophy on cognitive efficiency in multiple sclerosis. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 15(4), 606–612.
Sumowski, J. F., Wylie, G. R., Chiaravalloti, N., & DeLuca, J. (2010). Intellectual enrichment lessens the effect of brain atrophy on learning and memory in multiple sclerosis. Neurology, 74(24), 1942–1945.
Swirsky-Sacchetti, T., Mitchell, D. R., Seward, J., Gonzales, C., Lublin, F., Knobler, R., & Field, H. L. (1992). Neuropsychological and structural brain lesions in multiple sclerosis: A regional analysis. Neurology, 42(7), 1291–1295.
Zakzanis, K. K. (2000). Distinct neurocognitive profiles in multiple sclerosis subtypes. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 15(2), 115–136.
Zivadinov, R., Sepcic, J., Nasuelli, D., De Masi, R., Bragadin, L. M., Tommasi, M. A., et al. (2001). A longitudinal study of brain atrophy and cognitive disturbances in the early phase of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 70(6), 773–780.
Acknowledgments
The Neuroimaging Laboratory of the Santa Lucia Foundation is supported in part by the Italian Ministry of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nocentini, U., Bozzali, M., Spanò, B. et al. Exploration of the relationships between regional grey matter atrophy and cognition in multiple sclerosis. Brain Imaging and Behavior 8, 378–386 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-012-9170-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-012-9170-7