Abstract
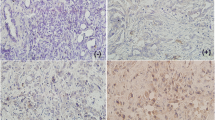
The expression levels of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1α) and HIF-2α in pancreatic cancer (PC) and their association with clinicopathologic characteristics were investigated in order to elucidate their roles in the development of PC. HIF-1α and HIF-2α mRNA levels in 20 patients with PC were detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. The expression of HIF-1α and HIF-2α protein in samples from other 90 patients with PC was measured by immunohistochemistry. Correlations between the expression of HIF-1α or HIF-2α and clinicopathologica features and prognosis were analyzed. The expression of both HIF-1α and HIF-2α mRNA was up-regulated in most cancer tissues (P<0.05). HIF-1α staining was weakly positive in most cancer tissues and strongly positive in adjacent pancreas tissues (P<0.05). Clinicopathologic analysis revealed that relatively strong HIF-1α expression in cancer tissues was related to greater invasion (P<0.05), higher tumor pathologic stage (P<0.05), higher American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stage (P<0.05) and shorter overall survival time (P<0.05). Conversely, HIF-2α staining was strongly positive in most cancer tissues and weakly positive in adjacent pancreas tissues. Clinicopathologic analysis revealed that relatively strong HIF-2α expression in cancer tissues was related to less invasion (P<0.05), lower tumor pathologic stage (P<0.05), lower AJCC stage (P<0.05) and longer overall survival time (P<0.05). Moreover, the HIF-1αhigh/HIF-2αlow group showed a shorter survival time than the HIF-1αlow/HIF-2αhigh group. In conclusion, although HIF-1α and HIF-2α mRNA expression patterns are the same, their protein expression patterns are significantly different and they play different roles in PC. Combined analysis of HIF-1α and HIF-2α expression might be useful to predict the prognosis of patients with PC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin, 2015,65(1):5–29
Megibow AJ. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma: designing the examination to evaluate the clinical questions. Radiology, 1992,183(2):297–303
Koong AC, Mehta VK, Le QT, et al. Pancreatic tumors show high levels of hypoxia. Int J Radia Oncol Biol Physics, 2000,48(4):919–922
Aravalli RN, Cressman EN, Steer CJ. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Arch Toxicol, 2013,87(2):227–247
Semenza GL. Regulation of mammalian O2 homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol, 1999,15:551–578
Wenger RH, Stiehl DP, Camenisch G. Integration of oxygen signaling at the consensus HRE. Sci STKE, 2005,2005(306):re12
Haase VH. The VHL tumor suppressor: master regulator of HIF. Curr Pharm Des, 2009,15(33):3895–3903
Majmundar AJ, Wong WJ, Simon1 MC. Hypoxia inducible factors and the response to hypoxic stress. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2010,40(2):294–309
Semenza GL. Hypoxia-inducible factors: mediators of cancer progression and targets for cancer therapy. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2012,33(4):207–214
Kitada T, Seki S, Sakaguchi H, et al. Clinicopathological significance of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression in human pancreatic carcinoma. Histopathology, 2003, 43(6):550–555
Miyake K, Yoshizumi T, Imura S, et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, histone deacetylase 1, and metastasis-associated protein 1 in pancreatic carcinoma: correlation with poor prognosis with possible regulation. Pancreas, 2008,36(3):e1–9
Shibaji T, Nagao M, Ikeda N, et al. Prognostic significance of HIF-1 alpha overexpression in human pancreatic cancer. Anticancer Res, 2003,23(6C):4721–4727
Sun HC, Qiu ZJ, Liu J, et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and associated proteins in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and their impact on prognosis. Int J Oncol, 2007,30(6):1359–1367
Zhao X, Gao S, Ren H, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma invasion and metastasis by activating transcription of the actin-bundling protein fascin. Cancer Res, 2014,74(9):2455–2464
Hu CJ, Wang LY, Chodosh LA, et al. Differential roles of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) and HIF-2 in hypoxic gene regulation. Mol Cell Biol, 2003,23(24):9361–9374
Wang V, Davis DA, Haque M, et al. Differential gene up-regulation by hypoxia-inducible factor-1A and hypoxia-inducible factor-2A in HEK293T cells. Am Assoc Cancer Res, 2005,65(8):3299–3306
Hu CJ, Iyer S, Sataur A, et al. Differential regulation of the transcriptional activities of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1alpha) and HIF-2alpha in stem cells. Mol Cell Biol, 2006,26(9):3514–3526
Warnecke C, Zaborowska Z, Kurreck J, et al. Differentiating the functional role of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1a and HIF-2a (EPAS-1) by the use of RNA interference: erythropoietin is a HIF-2a target gene in Hep3B and Kelly cells. FASEB J, 2004,18(12):1462–1464
Carroll VA, Ashcroft M. Role of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha versus HIF-2alpha in the regulation of HIF target genes in response to hypoxia, insulin-like growth factor-I, or loss of von Hippel-Lindau function: implications for targeting the HIF pathway. Cancer Res, 2006,66(12):6264–6270
Sowter HM, Raval RR, Moore JW, et al. Predominant role of hypoxia-inducible transcription factor(Hif)-1a versus Hif-2a in regulation of the transcriptional response to hypoxia. Cancer Res, 2003,63(19):6130–6134
Imamura T, Kikuchi H, Herraiz MT, et al. HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha have divergent roles in colon cancer. Int J Cancer, 2009,124(4):763–771
Unruh A, Ressel A, Mohamed HG, et al. The hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha is a negative factor for tumor therapy. Oncogene, 2003,22(21):3213–3220
Griffiths EA, Pritchard SA, Valentine HR, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression in the gastric carcinogenesis sequence and its prognostic role in gastric and gastro-oesophageal adenocarcinomas. Br J Cancer, 2007,96(1):95–103
Bangoura G, Liu ZS, Qian Q, et al. Prognostic significance of HIF-2alpha/EPAS1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol, 2007,13(23):3176–3182
Sun HX, Xu Y, Yang XR, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor 2 alpha inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth through the transcription factor dimerization partner 3/E2F transcription factor 1-dependent apoptotic pathway. Hepatology, 2013,57(3):1088–1097
Yang SL, Liu LP, Jiang JX, et al. The correlation of expression levels of HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha in hepatocellular carcinoma with capsular invasion, portal vein tumor thrombi and patients’clinical outcome. Jpn J Clin Oncol, 2014,44(2):159–167
Keith B, Johnson RS, Simon MC. HIF1a and HIF2a: sibling rivalry in hypoxic tumor growth and progression. Nat Rev Cancer, 2012,12(1):9–22
Hara S, Hamada J, Kobayashi C, et al. Expression and characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-3alpha in human kidney: suppression of HIF-mediated gene expression by HIF-3alpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2001,287(4):808–813
Zhang P, Yao Q, Lu L, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 3 is an oxygen-dependent transcription activator and regulates a distinct transcriptional response to hypoxia. Cell Reports, 2014,6(6):1110–1121
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81160311 and No. 81101621), the Outstanding Young Training Project of Science and Education of Guizhou Province, China (No. [2012] 177) and the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (No. 2013M531983).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Chen, My., Guo, Xj. et al. Expression and significance of HIF-1α and HIF-2α in pancreatic cancer. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 35, 874–879 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-015-1521-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-015-1521-3