Summary
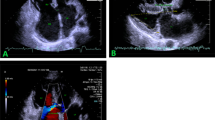
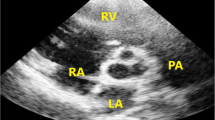
The present study evaluated the application of three dimensional echocardigraphy (3DE) in the diagnosis of atrial septal defect (ASD) and the measurement of its size by 3DE and compared the size with surgical findings. Two-dimensional and real-time three dimensional echocardiography (RT3DE) was performed in 26 patients with atrial septal defect, and the echocardiographic data were compared with the surgical findings. Significant correlation was found between defect diameter by RT3DE and that measured during surgery (r=0.77, P<0.001). The defect area changed significantly during cardiac cycle. Percentage change in defect size during cardiac cycle ranged from 6%–70%. Our study showed that the size and morphology of atrial septal defect obtained with RT3DE correlate well with surgical findings. Therefore, RT3DE is a feasible and accurate non-invasive imaging tool for assessment of atrial septal size and dynamic changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Houck RC, Cooke JE, Gill EA. Live 3D echocardiography a replacement for traditional 2D echocardiography? AJR, 2006,187:1092–1106
Cheng TO, Xie MX, Wang XF, et al. Real-time 3-Dimensional echocardiography assessing Atrial and ventricular septal defects: An echocardiographic-surgical correlative study. Am Heart J, 2004,148:617–619
Balestrinil L, Fleishman C, Kislol L, et al. Real-time-3dimensional echocardiography evaluation of congenital heart disease’s. Am Soc Echocadiogr, 2000,13:171–176
Marks GR, Fulton DR, Pandian DG, et al. Delineation of site, relative size and dynamic geometry of Atrial septal defect by real-time three dimensional echocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol, 1995,25:482–490
Acar P, Roux D, Doulac Y, et al. Transthoracic three dimensional echocardiography prior to closure of Atrial septal defect in children. Cardiol Young, 2003,13(1):58–63
Franke A, Rulands D, Kuhl HP, et al. Changes of atrial septal defect area during the cardiac cycle: evaluation of dynamic transoesophegeal three dimensional echocardiography(Abstract). Euro Heart J, 1996,17(suppl):2317
Thonopolous BD, Laskari CV, Tsaous GS, et al. Closure of Atrial septal defect with the Amplatzer occlusion device: preliminary results. J Am Coll Cardiol, 1998,8531:1110–1116
Wang XF, Deng YB, Nanda NC. Live three dimension echocardiography, imaging principle and clinical application. J CEchocardiography, 2003,20(7):593–604
Kannan BR, Francis E, Sivakumar K, et al. Transcatheter closure of very large (>25 mm) atrial septal defect using amplatzer septal occluder. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv, 2003,59:522–527
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This project was supported by a grant from the Youth Science Foundation of China (No. 30600213).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mweri, S.T., Deng, Y., Cheng, P. et al. Evaluation of atrial septal defect using real-time three-dimensional echocardiography: Comparison with surgical findings. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 29, 257–259 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-009-0225-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-009-0225-y