Summary
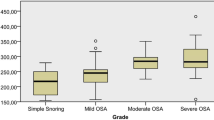
To explore the relationship between the serum vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) level and the severity of obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS), the concentrations of serum VEGF in 40 OSAHS patients and 9 healthy controls were measured by using ELISA method. Meanwhile the correlation between the concentration of VEGF and parameters of polysomnography (PSG) was examined. Our results showed that the concentrations of VEGF were significantly higher in OSAHS patients with severe hypoxia (536.8±334.7 pg/mL) than in those with mild hypoxia (329.2±174.7 pg/mL) and healthy controls (272. 8±211.0 pg/mL) (P<0.05 for both). The concentrations of VEGF were also significantly higher in OSAHS patients with hypertension (484.5±261.4 pg/mL) than in those without hypertension (311.0±158.4 pg/mL) and healthy controls (272. 8±211.0 pg/mL) (P<0.05 for both). There was a positive correlation between the concentration of VEGF and the apnea hypopnea index (AHI) (r=0.34, P<0.05). It is concluded that the concentration of the serum VEGF is positively related to the severity of OSAHS. The elevated serum VEGF level may be involved in the pathogenesis of the complications of obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weiss J W, Launois S H, Anand A et al. Cardiovascular morbidity in obstructive sleep apnea. Prog Cardiovasc Dis, 1999,41:367–376
Neufeld G, Cohen T, Gengrinovitch S et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptors. FASEB J, 1999,13:9–22
Ferrara N. Molecular and biological properties of vascular endothelial growth factor. J Mol Med, 1999,77:527–543
The Sleep Respiratory Disease Group of the Respiratory Branch of Chinese Medical Association. Diagnosis and Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Hypopnea Syndrome (Draft), Chin J Tuberc Respir Dis (Chinese), 2003,42:594–597
Schulz R, Hummel C, Heinemann S et al. Serum levels of vascular endothelial growth factor are elevated in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and severe nighttime hypoxia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2002,165:67–70
Lavie L, Kraiczi H, Hefetz A et al. Plasma vascular endothelial growth factor in sleep apnea syndrome: effects of nasal continuous positive air pressure treatment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2002,165:1624–1628
Gozal D, zipton A J. Circulating vascular endothelial growth factor levels in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep, 2002,25:59–65
Teramoto S, Kume H, Yamamoto H et al. Effects of oxygen administration on the circulation vascular endothelial growth factor levels in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Intern Med, 2003,42:681–685
Ziemer L L S, Koch C J, Maity A et al. Hypoxia and VEGF mRNA expression in human tumors. Neoplasia, 2001,3:500–508
Teramoto S, Kume H, Matsuse T et al. Oxygen administration improves the serum level of nitric oxide metabolites in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Med, 2003,4:403–407
Ip M S, Lam B, Chan L Y et al. Circulating nitric oxide is suppressed in obstructive sleep apnea and is reversed by nasal continuous positive airway pressure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2001,164(10, Pt 1):1197–1998
Prabhakar N R. Sleep apneas: an oxidative stress? Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2002,165(7):859–860
Michiels C, Arnould T, Remacle J. Endothelial cell responses to hypoxia: initiation of a cascade of cellular interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2000,1497:1–10
Davies R J O, Belt P J, Robers S J et al. Arterial blood pressure responses to graded transient arousal from sleep in normal humans. J Appl Physiol, 1993,74:1123–1130
Hornyak M, Cejnar M, Elam M et al. Muscle sympathetic nerve activity during sleep in man. Brain, 1991,114:1281–1295
Tharaux P L. Effect of sleep apnea syndrome on the vascular endothelium. Rev Neurol, 2003,159(11, Suppl):S102–106
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
MA Jing, female, born in 1979, Postgraduate Student
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Xu, Y., Zhang, Z. et al. Serum level of vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome. J. Huazhong Univ. Sc. Technol. 27, 157–160 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-007-0212-0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-007-0212-0