Abstract
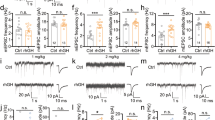
In rats, as in humans, normal aging is characterized by a decline in hippocampal-dependent learning and memory, as well as in glutamatergic function. Both growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) levels have been reported to decrease with age, and treatment with either GH or IGF-I can ameliorate age-related cognitive decline. Interestingly, acute GH and IGF-I treatments enhance glutamatergic synaptic transmission in the rat hippocampus of juvenile animals. However, whether this enhancement also occurs in old rats, when cognitive impairment is ameliorated by GH and IGF-I (des-IGF-I), remains to be determined. To address this issue, we used an in vitro CA1 hippocampal slice preparation and extracellular recording techniques to study the effects of acute application of GH and IGF-I on compound field excitatory postsynaptic potentials (fEPSPs), as well as AMPA- and NMDA-dependent fEPSPs, in young adult (10 months) and old (28 months) rats. The results indicated that both GH and IGF-I increased compound-, AMPA-, and NMDA-dependent fEPSPs to a similar extent in slices from both age groups and that this augmentation was likely mediated via a postsynaptic mechanism. Initial characterization of the signaling cascades underlying these effects revealed that the GH-induced enhancement was not mediated by the JAK2 signaling element in either young adult or old rats but that the IGF-I-induced enhancement involved a PI3K-mediated mechanism in old, but not young adults. The present findings are consistent with a role for a GH- or IGF-I-induced enhancement of glutamatergic transmission in mitigating age-related cognitive impairment in old rats.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MM, Shi L, Linville MC, Forbes ME, Long AB, Bennett C, Newton IG, Carter CS, Sonntag WE, Riddle DR, Brunso-Bechtold JK (2008) Caloric restriction and age affect synaptic proteins in hippocampal CA3 and spatial learning ability. Exp Neurol 211:141–149
Adams MM, Forbes ME, Linville MC, Riddle DR, Sonntag WE, Brunso-Bechtold JK (2009) Stability of local brain levels of insulin-like growth factor-I in two well-characterized models of decreased plasma IGF-I. Growth Factors 27(3):181–188
Alkondon M, Pereira EF, Alburquerque EX (2003) NMDA and AMPA receptors contribute to nicotinic cholinergic excitation of CA1 interneurons in the rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol 90(3):1613–1625
Ballard FJ, Wallace JC, Francis GL, Read LC, Thomas FM (1996) Des(1-3)IGF-I: a truncated form of insulin like growth factor-I. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 28(10):1085–1087
Barclay JL, Kerr LM, Arthur L, Rowland JE, Nelson CN, Ishikawa M, d’Aniello EM, White M, Noakes PG, Waters MJ (2010) In vivo targeting of the growth hormone receptor (GHR) box1 sequence demonstrates that the GHR does not signal exclusively through JAK2. Mol Endocrinol 24(1):204–217
Barnes CA (1990) Effects of aging on the dynamics of information processing and synaptic weight changes in the mammalian hippocampus. Prog Brain Res 86:89–104
Barnes CA, Rao G, Foster TC, McNaughton BL (1992) Region-specific age effects on AMPA sensitivity: electrophysiological evidence for loss of synaptic contacts in hippocampal field CA1. Hippocampus 2:457–468
Barnes CA, Rao G, Shen J (1997) Age-related decrease in the N-methyl-d-aspartate R-mediated excitatory postsynaptic potential in hippocampal region CA1. Neurobiol Aging 18:445–452
Barnes CA, Rao G, Houston FP (2000a) LTP induction threshold change in old rats at the perforant path–granule cell synapse. Neurobiol Aging 21:613–620
Barnes CA, Rao G, Orr G (2000b) Age-related decrease in the Schaffer collateral-evoked EPSP in awake, freely behaving rats. Neural Plast 7:167–178
Bauman LA, Mahle CD, Boissard CG, Gribkoff VK (1992) Age-dependence of effects of A1 adenosine receptor antagonism in rat hippocampal slices. J Neurophysiol 68:629–638
Bellone C, Nicoll RA (2007) Rapid bidirectional switching of synaptic NMDA receptors. Neuron 55:779–785
Billestrub N, Bouchelouche P, Allevato G, Ilondo M, Nielsen JH (1995) Growth hormone receptor C-terminal domains required for growth hormone-induced intracellular free Ca2+ oscillations and gene transcriptions. Proc Natl Acad Sci 92(7):2725–2729
Burton KA, Kabigting EB, Clifton DK, Steiner RA (1992) Growth hormone receptor messenger ribonucleic acid distribution in the adult male rat brain and its colocalization in hypothalamic somatostatin neurons. Endocrinology 131:958–963
Cao X, Cui Z, Feng R, Tang YP, Qin Z, Mei B, Tsien JZ (2007) Maintenance of superior learning and memory function in NR2B transgenic mice during ageing. Eur J Neurosci 25:1815–1822
Carter CS, Ramsey MM, Sonntag WE (2002) A critical analysis of the role of growth hormone and IGF-1 in aging and lifespan. Trends Genet 18:295–301
Carter-Su C, King AP, Argetsinger LS, Smit LS, Vanderkuur J, Campbell GS (1996) Endocr J 43:S65–S70
Chen BS, Roche KW (2007) Regulation of NMDA receptors by phosphorylation. Neuropharmacology 53:362–368
Cittadini A, Longobardi S, Fazio S, Sacca L (1999) Growth hormone and the heart. Miner Electrolyte Metab 25:51–55
Conti E, Musumeci MB, Assenza GE, Quarta G, Autore C, Volpe M (2008) Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-1: a new cardiovascular disease treatment option? Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem 6:258–271
Costantini C, Scrable H, Puglielli L (2006) An aging pathway controls the TrkA to p75NTR receptor switch and amyloid beta-peptide generation. EMBO J 25:1997–2006
Cull-Candy S, Brickley S, Farrant M (2001) NMDA receptor subunits: diversity, development and disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11:327–335
Deupree DL, Bradley J, Turner DA (1993) Age-related alterations in potentiation in the CA1 region in F344 rats. Neurobiol Aging 14:249–258
Eckles-Smith K, Clayton D, Bickford P, Browning MD (2000) Caloric restriction prevents age-related deficits in LTP and in NMDA receptor expression. Brain research. Mol Brain Res 78:154–162
Foster TC (2002) Regulation of synaptic plasticity in memory and memory decline with aging. Prog Brain Res 138:283–303
Foster TC, McNaughton BL (1991) Long-term enhancement of CA1 synaptic transmission is due to increased quantal size, not quantal content. Hippocampus 1:79–91
Foy MR, Xu J, Xie X, Brinton RD, Thompson RF, Berger TW (1999) 17beta-estradiol enhances NMDA receptor mediated EPSPs and long-term potentiation. J Neurophysiol 81:925–929
Fraser RA, Attardo D, Harvey S (1990) Growth hormone receptors in hypothalamic and extra-hypothalamic tissues. J Mol Endocrinol 5:231–238
Frazier CJ, Buhler AV, Weiner JL, Dunwiddie TV (1998) Synaptic potentials mediated via alpha-bungarotoxin sensitive nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in rat hippocampal interneurons. J Neurosci 18(20):8228–8235
Frick KM, Baxter MG, Markowska AL, Olton DS, Price DL (1995) Age-related spatial reference and working memory deficits assessed in the water maze. Neurobiol Aging 16:149–160
Gahete MD, Duran-Prado M, Luque RM, Martinez-Fuentes AJ, Quintero A, Gutierrez-Pascual E, Cordoba-Chacon J, Malagon MM, Gracia-Navarro F, Castano JP (2009) Understanding the multifactorial control of growth hormone release by somatotropes: lessons from comparative endocrinology. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1163:137–153
Goff DC, Lamberti JS, Leon AC, Green MF, Miller AL, Patel J, Manschreck T, Freudenreich O, Johnson SA (2008) A placebo-controlled add-on trial of the Ampakine, CX516, for cognitive deficits in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:465–472
Gu Q, Korach KS, Moss RL (1999) Rapid action of 17β-estradiol on kainite-induced currents in hippocampal neurons lacking intracellular estrogen receptors. Endocrinology 140(2):660–666
Guan J, Williams CE, Skinner SJ, Mallard EC, Gluckman PD (1996) The effects of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, IGF-2, and des-IGF-1 on neuronal loss after hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in adult rats: evidence for a role for IGF binding proteins. Endocrinology 137:893–898
Hamlyn E, Brand L, Shahid M, Harvey BH (2009) The ampakine, Org 26576, bolsters early spatial reference learning and retrieval in the Morris water maze: a subchronic, dose-ranging study in rats. Behav Pharmacol 20:662–667
Hampson RE, Espana RA, Rogers GA, Porrino LJ, Deadwyler SA (2009) Mechanisms underlying cognitive enhancement and reversal of cognitive deficits in nonhuman primates by the ampakine CX717. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 202:355–369
Hattori N (2009) Expression, regulation and biological actions of growth hormone (GH) and ghrelin in the immune system. Growth Horm IGF Res 19:187–197
Hull KL, Harvey S (1998) Autoregulation of growth hormone receptor and growth hormone binding protein transcripts in brain and peripheral tissues of the rat. Growth Horm IGF Res 8:167–173
Jin H, Lanning NJ, Carter-Su C (2008) JAK2, but not Src family kinases, is required for STAT, ERK, and Akt signaling in response to growth hormone in preadipocytes and hepatoma cells. Mol Endocrinol 22:1825–1841
Jovenceau A, Dutar P, Billard JM (1998) Alteration of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic responses in CA1 area of the aged rat hippocampus: contribution of GABAergic and cholinergic deficits. Hippocampus 8:627–637
Karnup S, Stelzer A (1999) Temporal overlap of excitatory and inhibitory afferent input in guinea-pig CA1 pyramidal cells. J Physiol 516:485–504
Kessels HW, Malinow R (2009) Synaptic AMPA receptor plasticity and behavior. Neuron 61:340–350
Kim B, Leventhal PS, Saltiel AR, Feldman EL (1997) Insulin-like growth factor-I-mediated neurite outgrowth in vitro requires mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J Biol Chem 272:21268–21273
Kim MT, Soussou W, Gholmieh G, Ahuja A, Taguay A, Berger TW, Brinton RD (2006) 17beta-estradiol potentiates field excitatory postsynaptic potentials within each subfield of the hippocampus with greatest potentiation of the associational/commissural afferents of CA3. Neuroscience 141(1):391–406
Kutsuwada T, Kashiwabuchi N, Mori H, Sakimura K, Kushiya E, Araki K, Meguro H, Masaki H, Kumanishi T, Arakawa M (1992) Molecular diversity of the NMDA receptor channel. Nature 358:36–41
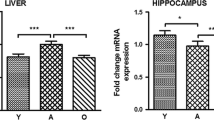
Le Grevès M, Le Grevès P, Nyberg F (2005) Age-related effects of IGF-I on the NMDA-, GH- and IGF-I receptor mRNA transcripts in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res Bull 65:369–374
Lin F, Tsien JZ (2009) Memory and NMDA receptors. N Engl J Med 361:302–303
Lin SY, Wu K, Levine ES, Mount HT, Suen PC, Black IB (1998) BDNF acutely increases tyrosine phosphorylation of the NMDA receptor subunit 2B in cortical and hippocampal postysynaptic densities. Brain Res Mol Brain 55:20–27
Lin SY, Wu K, Len GW, Xu JL, Levine ES, Suen PC, Mount HT, Black IB (1999) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhances association of protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP1D with the NMDA receptor subunit NR2B in the cortical postsynaptic density. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 70:18–25
Liu P, Smith PF, Darlington CL (2008) Glutamate receptor subunits expression in memory-associated brain structures: regional variations and effects of aging. Synapse 62:834–841
Lo HC, Ney DM (1996) GH and IGF-I differentially increase protein synthesis in skeletal muscle and jejunum of parenterally fed rats. Am J Physiol 271:E872–E878
Lobie PE, Garcia-Aragon J, Lincoln DT, Barnard R, Wilcox JN, Waters MJ (1993) Localization and ontogeny of growth hormone receptor gene expression in the central nervous system. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 74:225–233
Lobie PE, Zhu T, Graichen R, Goh EL (2000) Growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor I and the CNS: localization, function and mechanism of action. Growth Horm IGF Res 10(Suppl B):S51–S56
Mahmoud GS, Grover LM (2006) Growth hormone enhances excitatory synaptic transmission in area CA1 of rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol 95:2962–2974
Malinow R, Malenka RC (2002) AMPA receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci 25:103–126
Markowska AL, Mooney M, Sonntag WE (1998) Insulin-like growth factor-1 ameliorates age-related behavioral deficits. Neuroscience 87:559–569
McQuiston AR (2010) Cholinergic modulation of excitatory synaptic input integration in hippocampal CA1. J Physiol 588(Pt19):3727–3742
Meguro H, Mori H, Araki K, Kushiya E, Kutsuwada T, Yamazaki M, Kumanishi T, Arakawa M, Sakimura K, Mishina M (1992) Functional characterization of a heteromeric NMDA receptor channel expressed from cloned cDNAs. Nature 357:70–74
Molina DP, Ariwodola OJ, Linville C, Sonntag WE, Weiner JL, Brunso-Bechtold JK, Adams MM (2011) Growth hormone modulates hippocampal excitatory synaptic transmission and plasticity in old rats. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.09.014; PMID:220151312
Monyer H, Burnashev N, Laurie DJ, Sakmann B, Seeburg PH (1994) Developmental and regional expression in the rat brain and functional properties of four NMDA receptors. Neuron 12:529–540
Neuman-Haefelin E, Qi W, Finkbeiner E, Walz G, Baumesister R, Hertweck M (2008) SHC-1/p52Shc targets the insulin/IGF-1 and JNK signaling pathways to modulate life span and stress response in C. elegans. Genes Dev 22(19):2721–2735
Newton IG, Forbes ME, Linville MC, Pang H, Tucker EW, Riddle DR, Brunso-Bechtold JK (2008) Effects of aging and caloric restriction on dentate gyrus synapses and glutamate receptor subunits. Neurobiol Aging 29:1308–1318
Ohlsson C, Bengtsson BA, Isaksson OG, Andreassen TT, Slootweg MC (1998) Growth hormone and bone. Endocr Rev 19:55–79
Pan W, Yu Y, Cain CM, Nyberg F, Couraud PO, Kastin AJ (2005) Permeation of growth hormone across blood-brain barrier. Endocrinology 146(12):5533–5539
Papatheodoropoulos C, Kostopoulos G (1996) Age-related changes in excitability and recurrent inhibition in the rat CA1 hippocampal region. Eur J Neurosci 8:510–520
Perrini S, Laviola L, Carreira MC, Cignarelli A, Natalicchio A, Giorgino F (2010) The GH/IGF-I axis and signaling pathways in muscle and bone: mechanisms underlying age-related skeletal muscle wasting and osteoporosis. J Endocrinol 205:201–210
Porrino LJ, Daunais JB, Rogers GA, Hampson RE, Deadwyler SA (2005) Facilitation of task performance and removal of the effects of sleep deprivation by an ampakine (CX717) in nonhuman primates. PLoS Biol 3:e299
Portera-Cailliau C, Price DL, Martin LJ (1996) N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor proteins NR2A and NR2B are differentially distributed in the developing rat central nervous system as revealed by subunit-specific antibodies. J Neurochem 66:692–700
Ramsey MM, Weiner JL, Moore TP, Carter CS, Sonntag WE (2004) Growth hormone treatment attenuates age-related changes in hippocampal short-term plasticity and spatial learning. Neuroscience 129:119–127
Ramsey MM, Adams MM, Ariwodola OJ, Sonntag WE, Weiner JL (2005) Functional characterization of des-IGF-1 action at excitatory synapses in the CA1 region of rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol 94:247–254
Richman RA, Weiss JP, Hochberg Z, Florini JR (1981) Regulation of growth hormone release: evidence against negative feedback in rat pituitary cells. Endocrinology 108:2287–2292
Rosenzweig ES, Rao G, McNaughton BL, Barnes CA (1997) Role of temporal summation in age-related long-term potentiation-induction deficits. Hippocampus 7:549–558
Russo VC, Werther GA (1994) Des (1-3) IGF-I potently enhances differentiated cell growth in olfactory bulb organ culture. Growth Factors 11:301–311
Schultz PE, Cook EP, Johnston D (1994) Changes in paired-pulse facilitation suggest presynaptic involvement in long-term potentiation. J Neurosci 14:5325–5337
Shi L, Adams MM, Linville MC, Newton IG, Forbes ME, Long AB, Riddle DR, Brunso-Bechtold JK (2007) Caloric restriction eliminates the aging-related decline in NMDA and AMPA receptor subunits in the rat hippocampus and induces homeostasis. Exp Neurol 206:70–79
Smit LS, Meyer DJ, Billestrup N, Norstedt G, Schwartz J, Carter-Su C (1996) The role of growth hormone receptor and JAK1 and JAK2 kinases in the activation of Stats 1,3, and 5 by GH. Mol Endocrinol 10(5):519–533
Sonntag WE, Steger RW, Forman LJ, Meites J (1980) Decreased pulsatile release of growth hormone in old male rats. Endocrinology 107:1875–1879
Sonntag WE, Bennett SA, Khan AS, Thornton PL, Xu X, Ingram RL, Brunso-Bechtold JK (2000) Age and insulin-like growth factor-1 modulate N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subtype expression in rats. Brain Res Bull 51:331–338
Sonntag WE, Carter CS, Ikeno Y, Ekenstedt K, Carlson CS, Loeser RF, Chakrabarty S, Lee S, Bennett C, Ingram R, Moore T, Ramsey M (2005) Adult-onset growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor I deficiency reduces neoplastic disease, modifies age-related pathology, and increases life span. Endocrinology 146:2920–2932
Suen PC, Wu K, Xu JL, Lin SY, Levine ES, Black IB (1998) NMDA receptor subunits in the postsynaptic density of rat brain: expression and phosphorylation by endogenous protein kinases. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 59:215–228
Sullivan KA, Kim B, Feldman EL (2008) Insulin-like growth factors in the peripheral nervous system. Endocrinology 149:5963–5971
Sun LY, Al-Regaiey K, Masternak MM, Wang J, Bartke A (2005) Local expression of GH and IGF-1 in the hippocampus of GH-deficient long-lived mice. Neurobiol Aging 26:929–937
Tang YP, Shimizu E, Dube GR, Rampon C, Kerchner GA, Zhuo M, Liu G, Tsien JZ (1999) Genetic enhancement of learning and memory in mice. Nature 401:63–69
Thornton PL, Ingram RL, Sonntag WE (2000) Chronic [D-Ala2]-growth hormone-releasing hormone administration attenuates age-related deficits in spatial memory. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 55:B106–B112
Walsh RJ, Mangurian LP, Posner BI (1990) The distribution of lactogen receptors in the mammalian hypothalamus: an in vitro autoradiographic analysis of the rabbit and rat. Brain Res 530:1–11
Zhai Q, Lai Z, Roos P, Nyberg F (1994) Characteristics of growth hormone binding sites in rat brain. Acta Paediatr Suppl 406:92–95
Zhang Q, Kohler M, Yang SN, Zhang F, Larsson O, Berggren PO (2004) Growth hormone promotes Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release in insulin-secreting cells by ryanodine receptor tyrosine phosphorylation. Mol Endocrinol 18:1658–1669
Zhu T, Ling L, Lobie PE (2002) Identification of a JAK2-independent pathway regulating growth hormone (GH)-stimulated p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase activity. GH activation of Ral and phospholipase D is Src-dependent. J Biol Chem 277:45592–45603
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH grants: NIA PO1 AG11370 and KO1 AG027828. M.M. Adams is currently supported by an Installation Grant from the European Molecular Biology Organization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Molina, D.P., Ariwodola, O.J., Weiner, J.L. et al. Growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I alter hippocampal excitatory synaptic transmission in young and old rats. AGE 35, 1575–1587 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-012-9460-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-012-9460-4