Abstract
Introduction
Liver cirrhosis (LC) is an advanced liver disease that can develop into hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is one of the main causes of LC. Therefore, there is an urgent need for developing a new method to monitor the progression of HBV-related LC (HBV-LC).
Objectives
In this study, we attempted to examine serum metabolic changes in healthy individuals as well as patients with HBV and HBV-LC. Furthermore, potential metabolite biomarkers were identified to evaluate patients progressed from health to HBV-LC.
Methods
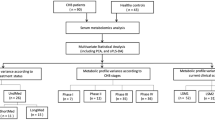
Metabolic profiles in the serum of healthy individuals as well as patients with HBV and HBV-LC were detected using an NMR-based metabolomic approach. Univariate and multivariate analyses were conducted to analyze serum metabolic changes during HBV-LC progression. Moreover, potential metabolite biomarkers were explored by receiver operating characteristic curve analysis.
Results
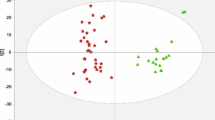
Serum metabolic changes were closely associated with the progression of HBV-LC, mainly involving energy metabolism, protein metabolism, lipid metabolism and microbial metabolism. Serum histidine was identified as a potential biomarker for HBV patients. Acetate, formate, pyruvate and glutamine in the serum were identified as a potential biomarker panel for patients progressed from HBV to HBV-LC. In addition, phenylalanine, unsaturated lipid, n-acetylglycoprotein and acetone in the serum could be considered as a potential common biomarkers panel for these patients.
Conclusion
NMR-based serum metabolomic approach could be a promising tool to monitor the progression of liver disease. Different metabolites may reflect different stages of liver disease.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amathieu, R., Nahon, P., Triba, M., Bouchemal, N., Trinchet, J. C., Beaugrand, M., et al. (2011). Metabolomic approach by 1H NMR spectroscopy of serum for the assessment of chronic liver failure in patients with cirrhosis. Journal of Proteome Research, 10(7), 3239–3245.
Arain, S. Q., Talpur, F. N., Channa, N. A., Ali, M. S., & Afridi, H. I. (2017). Serum lipid profile as a marker of liver impairment in hepatitis B Cirrhosis patients. Lipids in Health and Disease, 16(1), 51.
Askgaard, G., Grønbæk, M., Kjær, M. S., Tjønneland, A., & Tolstrup, J. S. (2015). Alcohol drinking pattern and risk of alcoholic liver cirrhosis: A prospective cohort study. Journal of Hepatology, 62(5), 1061–1067.
Bialecki, E. S., & Di Bisceglie, A. M. (2005). Clinical presentation and natural course of hepatocellular carcinoma. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 17(5), 485–489.
Callewaert, N., Van Vlierberghe, H., Van Hecke, A., Laroy, W., Delanghe, J., & Contreras, R. (2004). Noninvasive diagnosis of liver cirrhosis using DNA sequencer–based total serum protein glycomics. Nature Medicine, 10(4), 429–434.
Cao, H., Huang, H., Xu, W., Chen, D., Yu, J., Li, J., et al. (2011). Fecal metabolome profiling of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma patients by ultra performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Analytica Chimica Acta, 691(1), 68–75.
Chen, Y. J., Zhu, J. M., Wu, H., Fan, J., Zhou, J., Hu, J., et al. (2013). Circulating microRNAs as a fingerprint for liver cirrhosis. PLoS ONE, 8(6), e66577.
Chrostek, L., Supronowicz, L., Panasiuk, A., Cylwik, B., Gruszewska, E., & Flisiak, R. (2014). The effect of the severity of liver cirrhosis on the level of lipids and lipoproteins. Clinical and Experimental Medicine, 14(4), 417–421.
Embade, N., Mariño, Z., Diercks, T., Cano, A., Lens, S., Cabrera, D., et al. (2016). Metabolic characterization of advanced liver fibrosis in HCV patients as studied by serum 1H-NMR spectroscopy. PLoS ONE, 11(5), e0155094.
Fattovich, G., Stroffolini, T., Zagni, I., & Donato, F. (2004). Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: Incidence and risk factors. Gastroenterology, 127(5), S35-S50.
Gao, H., Lu, Q., Liu, X., Cong, H., Zhao, L., Wang, H., et al. (2009). Application of 1H NMR-based metabonomics in the study of metabolic profiling of human hepatocellular carcinoma and liver cirrhosis. Cancer Science, 100(4), 782–785.
Holecek, M. (2010). Three targets of branched-chain amino acid supplementation in the treatment of liver disease. Nutrition (Burbank, Los Angeles County, Calif.), 26(5), 482–490.
Holmes, E., Wilson, I. D., & Nicholson, J. K. (2008). Metabolic phenotyping in health and disease. Cell, 134(5), 714–717.
Huisman, E. J., Trip, E. J., Siersema, P. D., van Hoek, B., & van Erpecum, K. J. (2011). Protein energy malnutrition predicts complications in liver cirrhosis. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 23(11), 982–989.
Longo, N., Ardon, O., Vanzo, R., Schwartz, E., & Pasquali, M. (2011). Disorders of creatine transport and metabolism. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part C: Seminars in Medical Genetics, 157(No. 1), 72–78.
Medina, S., Dominguez-Perles, R., Gil, J. I., Ferreres, F., & Gil-Izquierdo, A. (2014). Metabolomics and the diagnosis of human diseases-A guide to the markers and pathophysiological pathways affected. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 21(7), 823–848.
Meng, Q. H., Wang, J. H., Yu, H. W., Li, J., Feng, Y. M., Hou, W., et al. (2010). Resting energy expenditure and substrate metabolism in Chinese patients with acute or chronic hepatitis B or liver cirrhosis. Internal Medicine, 49(19), 2085–2091.
Mokdad, A. A., Lopez, A. D., Shahraz, S., Lozano, R., Mokdad, A. H., Stanaway, J., et al. (2014). Liver cirrhosis mortality in 187 countries between 1980 and 2010: A systematic analysis. BMC Medicine, 12(1), 145.
Mölleken, C., Sitek, B., Henkel, C., Poschmann, G., Sipos, B., Wiese, S., et al. (2009). Detection of novel biomarkers of liver cirrhosis by proteomic analysis. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.), 49(4), 1257–1266.
Monteiro, M. S., Carvalho, M., Bastos, M. L., & Guedes de Pinho, P. (2013). Metabolomics analysis for biomarker discovery: Advances and challenges. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 20(2), 257–271.
Moriwaki, H., Miwa, Y., Tajika, M., Kato, M., Fukushima, H., & Shiraki, M. (2004). Branched-chain amino acids as a protein-and energy-source in liver cirrhosis. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 313(2), 405–409.
Nicholson, J. K., Foxall, P. J., Spraul, M., Farrant, R. D., & Lindon, J. C. (1995). 750 MHz 1H and 1H-13C NMR spectroscopy of human blood plasma. Analytical Chemistry, 67, 793–811.
Perz, J. F., Armstrong, G. L., Farrington, L. A., Hutin, Y. J., & Bell, B. P. (2006). The contributions of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infections to cirrhosis and primary liver cancer worldwide. Journal of Hepatology, 45(4), 529–538.
Psychogios, N., Hau, D. D., Peng, J., Guo, A. C., Mandal, R., Bouatra, S., et al. (2011). The human serum metabolome. PLoS ONE, 6(2), e16957.
Qi, S., Tu, Z., Ouyang, X., Wang, L., Peng, W., Cai, A., et al. (2012). Comparison of the metabolic profiling of hepatitis B virus-infected cirrhosis and alcoholic cirrhosis patients by using 1H NMR-based metabonomics. Hepatology Research, 42(7), 677–685.
Qin, N., Yang, F., Li, A., Prifti, E., Chen, Y., Shao, L., et al. (2014). Alterations of the human gut microbiome in liver cirrhosis. Nature, 513(7516), 59–64.
Schuppan, D., & Afdhal, N. H. (2008). Liver cirrhosis. Lancet, 371(9615), 838–851.
Tajika, M., Kato, M., Mohri, H., Miwa, Y., Kato, T., Ohnishi, H., & Moriwaki, H. (2002). Prognostic value of energy metabolism in patients with viral liver cirrhosis. Nutrition (Burbank, Los Angeles County, Calif.), 18(3), 229–234.
Tsochatzis, E. A., Bosch, J., & Burroughs, A. K. (2014). Liver cirrhosis. Lancet, 383(9930), 1749–1761.
Vere, C. C., Streba, C. T., Streba, L., & Rogoveanu, I. (2012). Lipid serum profile in patients with viral liver cirrhosis. Medical Principles and Practice, 21(6), 566–568.
Wishart, D. S., Jewison, T., Guo, A. C., Wilson, M., Knox, C., Liu, Y., et al. (2012). HMDB 3.0-the human metabolome database in 2013. Nucleic Acids Research, 41, 801–807.
Xia, J., Sinelnikov, I. V., Han, B., & Wishart, D. S. (2015). MetaboAnalyst 3.0-making metabolomics more meaningful. Nucleic Acids Research, 43(W1), W251–W257.
Xie, Y., Yao, Q., Butt, A. M., Guo, J., Tian, Z., Bao, X., et al. (2014). Expression profiling of serum microRNA-101 in HBV-associated chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biology & Therapy, 15(9), 1248–1255.
Yang, J., He, J., Cao, H., Zhao, X., Fu, S., Lu, H., et al. (2012). Correlation between plasma amino acid profiles and the various stages of hepatitis B infection. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases, 31(8), 2045–2052.
Yin, P., Wan, D., Zhao, C., Chen, J., Zhao, X., Wang, W., et al. (2009). A metabonomic study of hepatitis B-induced liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma by using RP-LC and HILIC coupled with mass spectrometry. Molecular BioSystems, 5(8), 868–876.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.: 21605115, 21575105, 81573657) and the Public Welfare Technology Application Research Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No.: 2017C33066).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HCG, JSJ and HZ contributed to experimental design. MJC, SML and LCZ contributed to sample collection and NMR metabolomic analysis. HZ and HCG contributed to data analysis, result interpretation and writing. All authors have read, revised and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Lishui Central Hospital.
Informed consent
Written informed consents were obtained from all participants.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, H., Chen, M., Lu, S. et al. Metabolic characterization of hepatitis B virus-related liver cirrhosis using NMR-based serum metabolomics. Metabolomics 13, 121 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1260-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1260-5