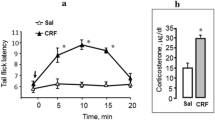
This review provides an analysis of data on the mechanisms of the analgesic action of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) on somatic pain sensitivity. Experiments on rats addressed the involvement of opioid and glucocorticoid receptors and type 2 CRF receptors in mediating the analgesic effect induced by systemic administration of CRF. The results showed that the analgesic action of CRF may involve type 2 CRF receptors; CRF analgesia can appear in two forms: opioid-dependent and opioid-independent, whose development appears to be determined by the nature of the pain stimulus and the use of anesthesia. The opioid-dependent form of analgesia may be supported by glucocorticoid hormones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. I. Bogdanov and N. I. Yarushkina, “The role of hypothamalohypophyseal-adrenocortical system hormones in the analgesic effect of corticotrophin-releasing hormone,” Ros. Fiziol. Zh., 92, No. 2, 262–270 (2006).
L. P. Filaretova, T. T. Podvigina, T. R. Bagaeva, and A. A. Filaretov, “Prolonged suppression of hypothamalo-hypophyseal-adrenocortical system function in rats,” Ros. Fiziol. Zh., 81, No. 1, 24–31 (1995).
N. I. Yarushkina, “the role of hypothamalo-hypophyseal-adrenocortical system hormones in regulating pain sensitivity,” Ros. Fiziol. Zh., 93, No. 11, 1252–1262 (2007).
N. I. Yarushkina and T. R. Bagaeva, “Mechanisms of the analgesic effect of corticotrophin-releasing factor in conscious rats,” Ros. Fiziol. Zh., 96, No. 2, 128–137 (2010).
N. I. Yarushkina, T. R. Bagaeva, and L. P. Filaretova, “The analgesic action of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) on somatic pain sensitivity: the involvement of glucocorticoids and CRF-2 receptors,” Ros. Fiziol. Zh., 94, No. 10, 1118–1125 (2008).
F. J. Ayesta and K. E. Nikolarakis, “Peripheral but not intracerebrovascular corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) produces antinociception which is not opioid mediated,” Brain Res., 503, No. 2, 219–224 (1989).
M. Bianchi, P. Sacerdote, L. Locatelli, et al., “Corticotropin-releasing hormone, interleukin-1b, and tumor necrosis factor shared characteristic of stress mediators,” Brain Res., 546, No. 1, 139–142 (1991).
R. K. Butler and D. P. Finn, “Stress-induced analgesia,” Prog. Neurobiol., 88, No. 3, 184–202 (2009).
A. Capasso and A. Loizzo, “Functional interference of dexamethasone on some morphine effects: hypothesis for the steroid-opioid interaction,” Recent Pat. CNS Drug Discov., 3, No. 2, 138–150 (2008).
A. Capasso, A. Di Giannuario, A. Loizzo, et al., “Central interaction of dexamethasone and RU-38486 on morphine antinociception in mice,” Life. Sci., 51, No. 14, 139–143 (1993).
M. S. Capeda, I. Bonney, J. Moyano, and D. B. Carr, “Corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) produces analgesia in a thermal model independent of its effect on systemic beta-endorphin and corticosterone,” Regul. Pept., 118, No. 1–2, 39–43 (2004).
L. J. Crofford, E. A. Young, N. C. Engleberg, et al., “Basal circadian and pulsatile ACTH and cortisol secretion in patients with fibromyalgia and/or chronic fatigue syndrome,” Brain Behav. Immun., 18, No. 4, 314–325 (2004).
X. Y. Cui, T. Lundeberg, and L. C. Yu, “Role of corticotropin-releasing factor and its receptor in nociceptive modulation in the central nucleus of the amygdala in rats,” Brain Res., 995, No. 1, 23–28 (2004).
M. Devor and V. Zalkind, “Reversible analgesia, atonia, and loss of consciousness on bilateral intracerebral microinjection of pentobarbital,” Pain, 94, No. 1, 101–112 (2001).
R. C. Gaillard, A. Riondel, A. F. Miller, et al., “RU 486: A steroid with antiglucocorticosteroid activity that only disinhibits the human pituitary-adrenal system at a specific time of day,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 81, 3879–3882 (1984).
K. M. Hargreaves, R. Dubner, and A. H. Costello, “Corticotrophinreleasing factor (CRF) has a peripheral site of action for antinociception,” Eur. J. Pharm., 170, No. 3, 275–279 (1989).
K. M. Hargreaves, C. D. Flores, and G. Mueller, “The role of pituitary β-endorphin in mediating CRF-induced antinociception,” Am. J. Physiol., 258, No. 1, E235–E242 (1990).
R. L. Hauger, V. Risbrough, O. Brauns, and F. M. Dautzenberg, “Corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) receptor signaling in the central nervous system: new molecular targets,” CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug. Targets, 5, No. 4, 453–479 (2006).
L. P. Filaretova, T. R. Bagaeva, and G. B. Makara, “Aggravation of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug gastropathy by glucocorticoid deficiency or blockade of glucocorticoid receptor in rats,” Life Sci., 71, 2457–2468 (2002).
L. Filaretova, T. Bagaeva, T. Podvigina, and G. Makara, “Various ulcerogenic stimuli are potentiated by glucocorticoids deficiency in rats,” J. Physiol. (Paris), 95, No. 1–6, 59–65 (2001).
G. Ji and V. Neugebauer, “Pro- and anti-nociceptive effects of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) in central amygdala neurons are mediated through different receptors,” J. Neurophysiol., 99, No. 3, 1201–1212 (2008).
J. E. Kelsey, W. A. Hoerman, L. Kimball, et al., “Arcuate nucleus lesions reduce opioid stress-related analgesia (SIA) and enhance non-opioid SIA in rats,” Brain Res., 382, No. 2, 278–290 (1986).
A. L. Kirchgessner, R. J. Bodnar, and G. W. Pasternak, “Naloxazone and pain-inhibitory systems: evidence for a collateral inhibition model,” Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav., 17, No. 6, 1175–1179 (1982).
Y. Kuraishi, Y. Harada, S. Aratani, et al., “Separate involvement of the spinal noradrenergic and serotonergic systems in morphine analgesia: the differences in mechanical and thermal algesic tests,” Brain Res., 273, No. 2, 245–252 (1983).
W. R. Lariviere and R. Melzack, “The role of corticotropin-releasing factor in pain and analgesia,” Pain, 84, No. 1, 1–12 (2000).
W. R. Lariviere, P. Fiorenzani, I. Ceccarelli, et al., “Central CRH administration changes formalin pain responses in male and female rats,” Brain Res., 1383, 128–134 (2011).
S. Lautenbacher, S. Roscherb, G. Kohl, et al., “Corticotropin-releasing hormone lacks analgesic properties: an experimental study in humans, using noninflammatory pain,” Pain, 83, No. 1, 1–7 (1999).
D. Le Bars, M. Gozariu, and S. W. Cadden, “Animal models of nociception,” Pharmacol. Rev., 53, No. 4, 597–652 (2001).
R. Likar, S. A. Mousa, H. Steinkellner, et al., “Involvement of intraarticular corticotropin-releasing hormone in postoperative pain modulation,” Clin. J. Pain., 23, No. 2, 136–142 (2007).
M. Lograsso, R. Nadeson, and C. S. Goodchild, “The spinal antinociceptive effects of cholinergic drugs in rats: receptor subtype specificity in different nociceptive tests,” BMC Pharmacol., 2, 20 (2002).
R. Matejec, H. Uhlich, C. Hotz, et al., “Corticotropin-releasing hormone reduces pressure pain sensitivity in humans without involvement of beta-endorphin (1-31), but does not reduce heat pain sensitivity,” Neuroendocrinology, 82, No. 3–4, 185–197 (2005).
B. S. McEwen and M. Kalia, “The role of corticosteroids and stress in chronic pain conditions,” Metab. Clin. Exp., 59, Suppl. 1, S9–S15 (2010).
G. Michaux,W. Magerl, F. Anton, and R.-D. Treede, “Experimental characterization of the effects of acute of stresslike doses of hydrocortisone in human neurogenic hyperalgesia models,” Pain, 153, No. 2, 420–428 (2012).
T. Miguel and R. Nunes-de-Souza, “Anxiogenic and antinociceptive effects of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) in injections into periaqueductal gray are modulated by CRF1 receptor in mice,” Hormones Behav., 60, No. 3, 292–300 (2011).
S. A. Mousa, C. P. Bopaiah, J. F. Richter, et al., “Inhibition of inflammatory pain by CRF at peripheral, spinal and supraspinal sites: involvement of areas coexpressing CRF receptors and opioid receptors,” Neuropsychopharmacology, 32, No. 12, 2530–2542 (2007).
D. R. Manjoshi, S. A. McErlane, N. Taepavarapruk, and P. J. Roja, “Network actions of pentobarbital in the rat mesopontine tegmentum on sensory influx through the spinothalamic tract,” J. Neurophysiol., 102, No. 2, 700–713 (2009).
A. Papadimitriou and K. N. Priftis, “Regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis,” Neuroimmunomodulation, 16, No. 5, 265–271 (2009).
J. J. Rady,W. Lin, and J. M. Fujimoto, “Pentobarbital antagonism of morphine analgesia mediated by spinal cholecystokinin,” J. Pharm. Exp. Ther., 284, No. 3, 878–885 (1998).
A. Ratka,W. Sutanto, and E. R. De Kloet, “Long-lasting glucocorticoid suppression of opioid-induced antinociception,” J. Pharm. Exp. Ther., 284, No. 3, 878–885 (1998).
A. Ratka,W. Sutanto, and E. R. De Kloet, “Long-lasting glucocorticoid suppression of opioid-induced antinociception,” Neuroendocrinology, 48, No. 4, 439–444 (1988).
L. A. Pavcovich and R. J. Valentino, “Regulation of a putative neurotransmitter effect of corticotropin-releasing factor: effects of adrenalectomy,” J. Neurosci., 17, No. 1, 401–408 (1997).
L. R. Poree, A. H. Dickinson, and W. T. Wei, “Corticotropin-releasing factor inhibits the response of trigeminal neurons to noxious heat,” Brain Res., 502, No. 2, 349–355 (1989).
C. L. Rivier, D. E. Grigoriadis, and J. E. Rivier, “Role of corticotropin-releasing factor receptors type 1 and 2 in modulating the rat adrenocorticotropin response to stressors,” Endocrinology, 144, No. 6, 2396–2403 (2003).
D. Roosterman, T. George, S. W. Schneider, et al., “Neuronal control of skin function: the skin as a neuroimmunoendocrine organs,” Physiol. Rev., 86, No. 4, 1309–1379 (2006).
S. Samuelsson, J. S. Lange, R. T. Hinkle, et al., “Corticotropin-releasing factor 2 receptor localization in skeletal muscle,” J. Histochem. Cytochem., 52, No. 7, 967–977 (2004).
M. Schafer, S. A. Mousa, and C. Stein, “Corticotropin-releasing factor in antinociception and inflammation,” Eur. J. Pharmacol., 323, No. 1, 1–10 (1997).
M. Schafer, S. A. Mousa, Q. Zhang, et al., “Expression of corticotropin-releasing factor in inflamed tissue is required for intrinsic peripheral opioid analgesia,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 93, No. 12, 6096–6100 (1996).
C. Stahn and F. Buttgereit, “Genomic and nongenomic effects of glucocorticoids,” Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol., 4, No. 10, 525–533 (2008).
J. P. Steffens F. A. Santos, and G. L. Pilatti, “Postoperative periodontal pain prevention using two dexamethasone medication protocols: a double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial,” Am. J. Dent., 24, No. 6, 354–356 (2011).
I. Sukhotinsky, D. A. Hopkins, J. Lu, et al., “Movement suppression during anesthesia: neural projections from the mesopontine tegmentum to areas involved in motor control,” J. Comp. Neurol., 489, No. 4, 425–448 (2005).
J. G. Tasker, S. Di, and R. Malcher-Lopes, “Minireview: rapid glucocorticoid signaling via membrane-associated receptors,” Endocrinology, 147, No. 12, 5549–5556 (2006).
L. F. Tseng and R. R. Tang, “Pentobarbital attenuates nociception induced by i.c.v. morphine but not beta-endorphin in the mouse,” Eur. J. Pharmacol., 214, No. 2–3, 175–180 (1992).
J. P. Vit, D. J. Clauw, T. Moallem, et al., “Analgesia and hyperalgesia from CRF receptor modulation in the central nervous system of Fischer and Lewis rats,” Pain, 121, No. 3, 241–260 (2006).
S. N. Washburn, B. C. Patton, A. R. Ferguson, et al., “Exposure to intermittent nociceptive stimulation under pentobarbital anesthesia disrupts spinal cord function in rats,” Psychopharmacology (Berlin), 192, No. 2, 243–252 (2007).
K. Wingenfeld, C. Heim, I. Schmidt, et al., “HPA axis reactivity and lymphocyte glucocorticoid sensitivity in fibromyalgia syndrome and chronic pelvic pain,” Psychosomatic. Med., 70, No. 1, 65–72 (2008).
N. I. Yarushkina, T. R. Bagaeva, and L. P. Filaretova, “Central corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) may attenuate somatic pain sensitivity through involvement of glucocorticoids,” J. Physiol. Pharm., 62, No. 5, 541–548 (2011).
N. I. Yarushkina, A. I. Bogdanova, and L. P. Filaretova, “Somatic pain sensitivity during formation and healing of acetic acid-induced gastric ulcers in conscious rats,” Auton. Neurosci. Basic Clin., 126–127, No. 1–2, 100–15 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I. M. Sechenova, Vol. 99, No. 7, pp. 805–819, July, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yarushkina, N.I., Bagaeva, T.R. & Filaretova, L.P. Mechanisms of the Analgesic Action of Corticotrophin-Releasing Factor on Somatic Pain Sensitivity in Rats. Neurosci Behav Physi 45, 449–457 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-015-0095-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-015-0095-7