Abstract
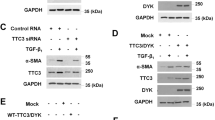
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway-dependent linker phosphorylation of Smad2/3 and subsequent formation of Smad2/3/4 complex and its nuclear translocation are crucial for dysregulated transforming growth factor beta (TGF)-β/Smad signaling in liver fibrosis. Abrogation of this critical step of TGF-β/Smad signaling leading to liver fibrosis could provide new insights for future therapy, but the mechanisms remain incompletely understood. In pursuit, we investigated the subcellular expression and nuclear trafficking of the rate limiting Smad2/3/4 complex in exogenous TGF-β1-stimulated myofibroblasts (MFBs) using three MAPK-specific inhibitors. Our results showed that exogenous TGF-β1 stimulation of MFBs produced both increased protein expression and nuclear translocation of phosphorylated (p)-Smad2C/L, oncogenic pSmad3L, Smad4, importin7/8 (Imp7/8), and plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI)-1 (Protein and mRNA), while decreased Smad7 protein expression. However, the MAPK-specific inhibitors differentially reversed these observations; for instance, ERK-specific inhibitor blocked the expression and nuclear translocation of pSmad2C/L, while both JNK and p38-specific inhibitors blocked the expression and nuclear translocation of pSmad2C/L and oncogenic pSmad3L. The MAPK-specific inhibitors had no significant effect on the total protein expression of Smad4, but rather significantly blocked its nuclear translocation. All the MAPK-specific inhibitors restored Smad7 expression and also decreased Imp7/8 and PAI-1 (Protein and mRNA) expression. Evidently, the MAPK-specific inhibitors blocked Smad2/3/4 complex formation via restoration of inhibitory Smad7 expression and blockade of Smad3L phosphorylation, while they blocked nuclear translocation of Smad2/3/4 complex through inhibition of Imp7/8 leading to decreased PAI-1 (Protein and mRNA) expression.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friedman SL (2010) Evolving challenges in hepatic fibrosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 7:425–436. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2010.97
Elpek GO (2014) Cellular and molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis: an update. World J Gastroenterol 20:7260–7276. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7260
Sun Y, Lu Y, Xie L, Deng Y, Li S, Qin X (2015) Interferon gamma polymorphisms and hepatitis B virus-related liver cirrhosis risk in a Chinese population. Cancer Cell Int 15:35. doi:10.1186/s12935-015-0184-2
Matsuzaki K, Murata M, Yoshida K, Sekimoto G, Uemura Y, Sakaida N, Kaibori M, Kamiyama Y, Nishizawa M, Fujisawa J, Okazaki K, Seki T (2007) Chronic inflammation associated with hepatitis C virus infection perturbs hepatic transforming growth factor beta signaling, promoting cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 46:48–57. doi:10.1002/hep.21672
Cojocariu CE, Trifan AV, Gîrleanu I, Stanciu C (2014) Alcoholic liver disease–epidemiology and risk factors. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi 118:910–917
Yoon HJ, Cha BS (2014) Pathogenesis and therapeutic approaches for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Hepatol 6:800–811. doi:10.4254/wjh.v6.i11.800
Stickel F (2015) Alcoholic cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Adv Exp Med Biol 815:113–130. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-09614-8_7
Furukawa F, Matsuzaki K, Mori S, Tahashi Y, Yoshida K, Sugano Y, Yamagata H, Matsushita M, Seki T, Inagaki Y, Nishizawa M, Fujisawa J, Inoue K (2003) p38 MAPK mediates fibrogenic signal through Smad3 phosphorylation in rat myofibroblasts. Hepatology 38:879–889. doi:10.1053/jhep.2003.50384
Yoshida K, Matsuzaki K, Mori S, Tahashi Y, Yamagata H, Furukawa F, Seki T, Nishizawa M, Fujisawa J, Okazaki K (2005) Transforming growth factor-beta and platelet-derived growth factor signal via c-Jun N-terminal kinase-dependent Smad2/3 phosphorylation in rat hepatic stellate cells after acute liver injury. Am J Pathol 166:1029–1039
Boye A, Kan H, Wu C, Jiang Y, Yang X, He S, Yang Y (2015) MAPK inhibitors differently modulate TGF-beta/Smad signaling in HepG2 cells. Tumour Biol. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-3002-x
Yang Y, Yang S, Chen M, Zhang X, Zou Y, Zhang X (2008) Compound Astragalus and Salvia miltiorrhiza Extract exerts anti-fibrosis by mediating TGF-beta/Smad signaling in myofibroblasts. J Ethnopharmacol 118:264–270. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2008.04.012
He S, Yang Y, Liu X, Huang W, Zhang X, Yang S, Zhang X (2012) Compound Astragalus and Salvia miltiorrhiza extract inhibits cell proliferation, invasion and collagen synthesis in keloid fibroblasts by mediating transforming growth factor-β/Smad pathway. Br J Dermatol 166:564–574. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10674.x
Liu X, Yang Y, Zhang X, Xu S, He S, Huang W, Roberts MS (2010) Compound Astragalus and Salvia miltiorrhiza extract inhibits cell invasion by modulating transforming growth factor-beta/Smad in HepG2 cell. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 25:420–426. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.05981.x
Hu X, Rui W, Wu C, He S, Jiang J, Zhang X, Yang Y (2014) Compound Astragalus and Salvia miltiorrhiza extracts suppress hepatocarcinogenesis by modulating transforming growth factor-β/Smad signaling. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 29:1284–1291. doi:10.1111/jgh.12490
Tahashi Y, Matsuzaki K, Date M, Yoshida K, Furukawa F, Sugano Y, Matsushita M, Himeno Y, Inagaki Y, Inoue K (2002) Differential regulation of TGF-beta signal in hepatic stellate cells between acute and chronic rat liver injury. Hepatology 35:49–61. doi:10.1053/jhep.2002.30083
He S, Liu X, Yang Y, Huang W, Xu S, Yang S, Zhang X, Roberts MS (2010) Mechanisms of transforming growth factor beta(1)/Smad signalling mediated by mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in keloid fibroblasts. Br J Dermatol 162:538–546. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2009.09511.x
Bae E, Kim SJ, Hong S, Liu F, Ooshima A (2012) Smad3 linker phosphorylation attenuates Smad3 transcriptional activity and TGF-β1/Smad3-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 427:593–599. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.09.103
Meng XM, Huang XR, Xiao J, Chung AC, Qin W, Chen HY, Lan HY (2012) Disruption of Smad4 impairs TGF-β/Smad3 and Smad7 transcriptional regulation during renal inflammation and fibrosis in vivo and in vitro. Kidney Int 81:266–279. doi:10.1038/ki.2011.327
Choi MJ, Song KM, Park JM, Kwon MH, Kwon KD, Park SH, Ryu DS, Ryu JK, Suh JK (2014) Effect of SMAD7 gene overexpression on TGF-β1-induced profibrotic responses in fibroblasts derived from Peyronie’s plaque. Asian J Androl. doi:10.4103/1008-682X.142130
Wells RG, Kruglov E, Dranoff JA (2004) Autocrine release of TGF-beta by portal fibroblasts regulates cell growth. FEBS Lett 559:107–110. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(04)00037-7
Hidaka H, Nakazawa T, Shibuya A, Minamino T, Takada J, Tanaka Y, Okuwaki Y, Watanabe M, Koizumi W (2011) Effects of 1-year administration of olmesartan on portal pressure and TGF-beta1 in selected patients with cirrhosis: a randomized controlled trial. J Gastroenterol 46:1316–1323. doi:10.1007/s00535-011-0449-z
Liu ZM, Tseng HY, Tsai HW, Su FC, Huang HS (2015) Transforming growth factor β-interacting factor-induced malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma cells depends on superoxide production from Nox4. Free Radic Biol Med. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.03.028
Zhang H, Ozaki I, Mizuta T, Yoshimura T, Matsuhashi S, Eguchi Y, Yasutake T, Hisatomi A, Sakai T, Yamamoto K (2004) Transforming growth factor-beta 1-induced apoptosis is blocked by beta 1-integrin-mediated mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in human hepatoma cells. Cancer Sci 95:878–886
Matsuzaki K, Seki T, Okazaki K (2014) TGF-β signal shifting between tumor suppression and fibro-carcinogenesis in human chronic liver diseases. J Gastroenterol 49:971–981. doi:10.1007/s00535-013-0910-2
Murata M, Yoshida K, Yamaguchi T, Matsuzaki K (2014) Linker phosphorylation of Smad3 promotes fibro-carcinogenesis in chronic viral hepatitis of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 20:15018–15027. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15018
Dong XM, Yin RH, Yang Y, Feng ZW, Ning HM, Dong L, Zheng WW, Tang LJ, Wang J, Jia YX, Jiang YN, Liu ED, Chen H, Zhan YQ, Yu M, Ge CH, Li CY, Yang XM (2014) GATA-2 inhibits transforming growth factor-β signaling pathway through interaction with Smad4. Cell Signal 26:1089–1097. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.01.028
Dooley S, Hamzavi J, Breitkopf K, Wiercinska E, Said HM, Lorenzen J, Ten Dijke P, Gressner AM (2003) Smad7 prevents activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis in rats. Gastroenterology 125:178–191
Yao X, Chen X, Cottonham C, Xu L (2008) Preferential utilization of Imp7/8 in nuclear import of Smads. J Biol Chem 283:22867–22874. doi:10.1074/jbc.M801320200
Chen X, Xu L (2011) Mechanism and regulation of nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of smad. Cell Biosci 1:40. doi:10.1186/2045-3701-1-40
Xu L, Yao X, Chen X, Lu P, Zhang B, Ip YT (2007) Msk is required for nuclear import of TGF-{beta}/BMP-activated Smads. J Cell Biol 178:981–994
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. K Matsuzaki (Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Kansai Medical University, Osaka, Japan) for providing us with the following Abs: Anti-pSmad2L and Anti-pSmad3L. Also, this work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81073098, No. 81374012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yufeng Jiang and Chao Wu have been contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Wu, C., Boye, A. et al. MAPK inhibitors modulate Smad2/3/4 complex cyto-nuclear translocation in myofibroblasts via Imp7/8 mediation. Mol Cell Biochem 406, 255–262 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2443-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2443-x