Abstract
Purpose
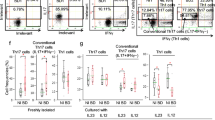
Th17 cells and their cytokines play a critical role in the pathogenesis of various autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Recently, we have demonstrated that intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) suppresses differentiation, amplification, and functions of human Th17 cells. In this report we investigated whether IVIG inhibits IL-17 production by Th17 cells cultured in the presence of IL-23 and whether the inhibitory effect of IVIG on IL-17 production implicates anti-IL-17 antibodies.
Methods
Naive CD4+ T cells were stimulated in the presence of TGF-β, IL-21, and IL-23 for the differentiation of Th17 cells. Memory CD4+ T cells were stimulated with IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-23 for the amplification of Th17 cells. IVIG (0.15 mM) was added to the cells 12 h after initiation of cultures. IL-17A cytokine and anti-IL-17 antibodies were measured by ELISA.
Results
IL-23 did not deter the inhibitory effect of IVIG on IL-17 production from the differentiating and expanding Th17 cells. Further, suppression of IL-17 by IVIG did not implicate anti-IL-17 antibodies in the immunoglobulin preparations.
Conclusion
The effect of IVIG on the inhibition of IL-17 production by Th17 cells is a consequence of modulation of Th17 cells and their intracellular signaling pathways and not due to passive neutralization of IL-17 by anti-IL-17 antibodies in the immunoglobulin preparations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Korn T, Bettelli E, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK. IL-17 and Th17 Cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:485–517.
Maddur MS, Miossec P, Kaveri SV, Bayry J. Th17 cells: biology, pathogenesis of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, and therapeutic strategies. Am J Pathol. 2012;181:8–18.
Kazatchkine MD, Kaveri SV. Immunomodulation of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases with intravenous immune globulin. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:747–55.
Bayry J, Negi VS, Kaveri SV. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7:349–59.
Ballow M. The IgG molecule as a biological immune response modifier: mechanisms of action of intravenous immune serum globulin in autoimmune and inflammatory disorders. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127:315–25.
Anthony RM, Ravetch JV. A novel role for the IgG Fc glycan: the anti-inflammatory activity of sialylated IgG Fcs. J Clin Immunol. 2010;30 Suppl 1:S9–S14.
Baerenwaldt A, Biburger M, Nimmerjahn F. Mechanisms of action of intravenous immunoglobulins. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2010;6:425–34.
Lazarus AH. Adoptive-transfer effects of intravenous immunoglobulin in autoimmunity. J Clin Immunol. 2010;30 Suppl 1:S20–3.
Seite JF, Shoenfeld Y, Youinou P, Hillion S. What is the contents of the magic draft IVIg? Autoimmun Rev. 2008;7:435–9.
Maddur MS, Vani J, Hegde P, Lacroix-Desmazes S, Kaveri SV, Bayry J. Inhibition of differentiation, amplification, and function of human TH17 cells by intravenous immunoglobulin. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127:823–30.
Maddur MS, Kaveri SV, Bayry J. Comparison of different IVIg preparations on IL-17 production by human Th17 cells. Autoimmun Rev. 2011;10:809–10.
Puel A, Doffinger R, Natividad A, Barcenas-Morales G, Picard C, Cobat A, et al. Autoantibodies against IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-22 in patients with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis and autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I. J Exp Med. 2010;207:291–7.
Maddur MS, Vani J, Lacroix-Desmazes S, Kaveri S, Bayry J. Autoimmunity as a predisposition for infectious diseases. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6(11):e1001077.
Aimanianda V, Haensler J, Lacroix-Desmazes S, Kaveri SV, Bayry J. Novel cellular and molecular mechanisms of induction of immune responses by aluminum adjuvants. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009;30:287–95.
Bayry J, Lacroix-Desmazes S, Carbonneil C, Misra N, Donkova V, Pashov A, et al. Inhibition of maturation and function of dendritic cells by intravenous immunoglobulin. Blood. 2003;101:758–65.
Aubin E, Lemieux R, Bazin R. Indirect inhibition of in vivo and in vitro T-cell responses by intravenous immunoglobulins due to impaired antigen presentation. Blood. 2010;115:1727–34.
Kessel A, Ammuri H, Peri R, Pavlotzky ER, Blank M, Shoenfeld Y, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy affects T regulatory cells by increasing their suppressive function. J Immunol. 2007;179:5571–5.
Ephrem A, Chamat S, Miquel C, Fisson S, Mouthon L, Caligiuri G, et al. Expansion of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells by intravenous immunoglobulin: a critical factor in controlling experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Blood. 2008;111:715–22.
De Groot AS, Moise L, McMurry JA, Wambre E, Van Overtvelt L, Moingeon P, et al. Activation of natural regulatory T cells by IgG Fc-derived peptide “Tregitopes”. Blood. 2008;112:3303–11.
Maddur MS, Othy S, Hegde P, Vani J, Lacroix-Desmazes S, Bayry J, et al. Immunomodulation by intravenous immunoglobulin: role of regulatory T cells. J Clin Immunol. 2010;30 Suppl 1:S4–8.
Bayry J, Mouthon L, Kaveri SV. Intravenous immunoglobulin expands regulatory T cells in autoimmune rheumatic disease. J Rheumatol. 2012;39:450–1.
Massoud AH, Guay J, Shalaby KH, Bjur E, Ablona A, Chan D, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin attenuates airway inflammation through induction of forkhead box protein 3-positive regulatory T cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129:1656–1665 e3.
Acknowledgments
Supported by grants from Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale (INSERM), Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Université Paris Descartes and European Community’s Seventh Framework Programme [FP7-2007-2013] under Grant Agreement N° HEALTH-F2-2010-260338-ALLFUN.
Conflict of interest
The research activities on IVIG are partly supported by research grants from Octapharma AG, CSL Behring, Laboratoires Français de Fractionnement et des Biotechnologies, and Talecris Biotherapeutics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maddur, M.S., Sharma, M., Hegde, P. et al. Inhibitory Effect of IVIG on IL-17 Production by Th17 Cells is Independent of Anti-IL-17 Antibodies in the Immunoglobulin Preparations. J Clin Immunol 33 (Suppl 1), 62–66 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-012-9752-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-012-9752-6