Abstract
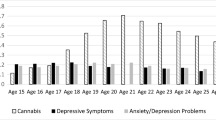
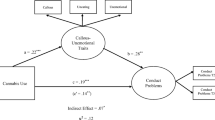
A prospective investigation was conducted to evaluate the accuracy of internalizing and externalizing traits measured at ages 10–12 for predicting a DSM-IV diagnosis of cannabis use disorder manifest by age 22. The sample consisted of 189 boys rated on the Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL) by their biological mothers. The results indicated that externalizing but not internalizing disturbance was a significant predictor of cannabis use disorder. Moreover, a construct capturing their common variance did not predict cannabis use disorder better than externalizing behavior alone.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, T., & Edelbrock, C. (1983). Manual for the revised child behavior checklist and revised child behavior profile. Burlington, VT: T.M. Achenbach.
Buckner, J., Schmidt, N., Bobadilla, L., & Taylor, J. (2006). Social anxiety and problematic cannabis use: evaluating the moderating role of stress reactivity and perceived coping. Behavioral Research and Theory, 44, 1007–1015.
Buckner, J., Schmidt, N., Lang, A., Small, J., Schlauch, R., & Lewinsohn, P. (2008). Specificity of social anxiety disorder as a risk factor for alcohol and cannabis dependence. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 42(3), 230–239.
Caspi, A., Moffit, T. E., Newman, D. L., & Silva, P. A. (1996). Behavioral observations at age 3 years predicts adult psychiatric disorders. Archives of General Psychiatry, 53, 1033–1039.
Cloninger, C. R. (1987). Neurogenetic adaptive mechanisms of alcoholism. Science, 236, 410–416.
Colder, C. R., & Chassin, L. (1997). Affectivity and impulsivity: temperament risk for adolescent alcohol involvement. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 11, 83–97.
Cooper, M. L. (1994). Motivations for alcohol use among adolescents. Development and validation of a four-factor model. Psychological Assessment, 6, 117–128.
Crum, R. M., & Pratt, L. A. (2001). Risk of heavy drinking and alcohol use disorders in social phobia: a prospective analysis. American Journal of Psychiatry, 158, 1693–1700.
Disney, E., Elkins, J., McGue, M., & Iacono, W. (1999). Effects of ADHD, conduct disorder and gender on substance use and abuse in adolescence. American Journal of Psychiatry, 56, 1515–1521.
Feske, U., Tarter, R. E., Kirisci, L., Gao, Z., Reynolds, M., & Vanyukov, M. (in press). Peer environment mediates parental history and individual risk in the etiology of cannabis use disorder in boys: A 10-year prospective study. The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse.
Feske, U., Tarter, R. E., Kirisci, L., & Pilkonis, P. A. (2006). Borderline personality and substance use in women. American Journal on Addictions, 15, 131–37.
Grove, W., Eckert, E., Heston, L., Bouchard, T., Segal, N., & Lykken, D. (1990). Heritability of substance abuse and antisocial behavior: a study of monozygotic twins reared apart. Biological Psychiatry, 27, 1293–1304.
Hicks, B. M., Krueger, R. F., Iacono, W. G., McGue, M., & Patrick, C. J. (2004). Family transmission and heritability of externalizing disorders: a win-family study. Archives of General Psychiatry, 61, 922–928.
Hollingshead, A. (1975). Four factor index of social status. New Haven, CT: Yale Station.
Kaestner, E., Rosen, L., & Appel, P. (1977). Patterns of drug abuse. Relationship with ethnicity, sensation seeking, and anxiety. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 45, 462–468.
Krueger, R., & Markon, D. (2006). Understanding psychopathology. Melding behavior genetics, personality and quantitation psychology to develop an empirically based model. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 15, 113–117.
Kushner, M. G., Sher, K. J., & Erickson, D. J. (1999). Prospective analysis of the relation between DSM-III anxiety disorders and alcohol use disorders. American Journal of Psychiatry, 156, 723–732.
Levy, F., Hay, D., McStephen, M., Wood, C., & Waldman, I. (1997). Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. A category of a continuum? Genetic analysis of a large-scale twin study. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 36, 737–744.
Loehlin, J. (2004). Latent variable models (4th ed.). Marwah, New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Maziade, M., Caron, C., Cote, R., Boutin, P., & Thiverge, J. (1990a). Extreme temperament and diagnosis. Study in a consecutive child psychiatric sample. Archives of General Psychiatry, 47, 477–484.
Maziade, M., Caron, C., Cote, R., Merrette, C., Bernier, H., Laplante, B., et al. (1990b). Psychiatric status of adolescents who had extreme temperaments at age 7. American Journal of Psychiatry, 147, 1531–1537.
Monshouwer, K., Van Dorsselaer, S., Verdurmen, J., Bogt, T., Graaf, R., & Vollebergh, W. (2006). Cannabis use and mental health in secondary school children. British Journal of Psychiatry, 188, 148–153.
Muthen, B., & Muthen, L. (2001). Mplus user’s guide. Los Angeles, CA: Muthen and Muthen Associates.
Newcomb, M. D., Chou, C. P., Bentler, P. M., & Huba, G. J. (1988). Cognitive motivations for drug use among adolescents: longitudinal tests of gender differences and predictors of change in drug use. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 35, 426–438.
Spitzer, R., Williams, B., Gibbons, M., & First, M. (1990). Users guide for structured clinical interview for DSM-III-R. New York, NY: New York State Psychiatric Institute.
Steele, R., Forehand, R., Amistaad, L., & Brody, G. (1995). Predicting alcohol and drug use in early adulthood: the role of internalizing and externalizing behavior problems in early adolescence. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 65, 380–388.
Tarter, R., Kabene, M., Escallier, E., Laird, S., & Jacob, T. (1990). Temperament deviations and risk for alcoholism. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 14, 380–382.
Tarter, R., & Kirisci, L. (2001). Validity of the Drug Use Screening Inventory for predicting DSM-III-R substance use disorder. Journal of Child and Adolescent Substance Abuse, 10, 45–53.
Tarter, R., Kirisci, L., Mezzich, A., Cornelius, J., Pajer, K., Vanyukov, M., et al. (2003). Neurobehavior disinhibition in childhood predicts early age onset substance disorder. American Journal of Psychiatry, 160, 1078–1085.
Tarter, R., Vanyukov, M., Giancola, P., Dawes, M., Blackson, T., Mezzich, A., et al. (1999). Etiology of early age onset substance abuse: a maturational perspective. Development and Psychopathology, 11, 657–683.
Trull, T. J., Sher, K. J., Minks-Brown, C., Durbin, J., & Burr, R. (2000). Borderline personality disorder and substance use disorders: a review and integration. Clinical Psychology Review, 20, 235–253.
Wittchen, H.-U., Frohlich, C., Behrendt, S., Gunther, A., Rehm, J., Zimmerman, P., et al. (1997). Cannabis use and cannabis use disorders and their relationship to mental disorders: A 10-year prospective longitudinal community study in adolescents. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 885, 560–570.
Zimmermann, P., Wittchen, H. U., Hofler, M., Pfister, R., Kessler, R., & Lieb, R. (2003). Primary anxiety disorders and the development of subsequent alcohol use disorders. A 4-year community study of adolescents and young adults. Psychological Medicine, 33, 1211–1222.
Acknowledgement
Supported by grants from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (P50-DA05605, K02, K02-01957, and K02-017822).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tarter, R.E., Kirisci, L., Ridenour, T. et al. Prediction of Cannabis Use Disorder Between Childhood and Young Adulthood Using the Child Behavior Checklist. J Psychopathol Behav Assess 30, 272–278 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-008-9083-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-008-9083-3