Abstract.
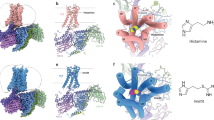
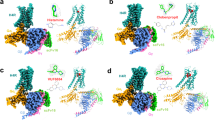
It is well established that histamine exerts its effects by activating histamine receptors that belongs to the family of seven transmembrane G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). Many ligands with important therapeutic actions that had been assumed to be antagonists at histamine H2 receptor have been shown to be inverse agonists. The mechanism whereby these drugs achieve their effects seems to be not unique. Theoretical models predict at least three ways in which inverse agonists can exert their action that are supported by experimental observations. These different mechanisms have crucial consequences on basic pharmacology and clinical treatments. The pharmacological models, the feasible mechanisms of action of H2 inverse agonists, findings about molecular basis of tiotidine inverse agonism in particular, and their impact on clinical protocols will be discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monczor, F. Mechanisms of inverse agonism at histamine H2 receptors – potential benefits and concerns. Inflammopharmacol 14, 89–96 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-006-1516-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-006-1516-6