Abstract
Purpose
The role of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in cardiovascular disease is now recognized. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) is known to have cardiovascular protective effects by decreasing ER stress. This study aimed to assess the ability of TUDCA to decrease ER stress, inhibit dedifferentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), and reduce in-stent restenosis.
Methods
The effect of TUDCA on dedifferentiation of VSMCs and ER stress was investigated in vitro using wound-healing assays, MTT assays, and western blotting. For in vivo studies, 18 rabbits were fed an atherogenic diet to induce atheroma formation. Bare metal stents (BMS), BMS+TUDCA or Firebird stents were implanted in the left common carotid artery. Rabbits were euthanized after 28 days and processed for scanning electron microscope (SEM), histological examination (HE), and immunohistochemistry.
Results
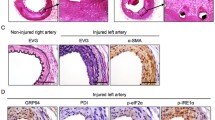
In vitro TUDCA (10–1000 μmol/L) treatment significantly inhibited platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-BB-induced proliferation and migration in VSMCs in a concentration-dependent manner and decreased ER stress markers (IRE1, XBP1, KLF4, and GRP78). In vivo, we confirmed no significant difference in neointimal coverage on three stents surfaces; neointimal was significantly lower with BMS+TUDCA (1.6 ± 0.2 mm2) compared with Firebird (1.90 ± 0.1 mm2) and BMS (2.3 ± 0.1 mm2). Percent stenosis was lowest for BMS+TUDCA, then Firebird, and was significantly higher with BMS (28 ± 4%, 35 ± 7%, 40 ± 1%; respectively; P < 0.001). TUDCA treatment decreased ER stress in the BMS+TUDCA group compared with BMS.
Conclusions
TUDCA inhibited dedifferentiation of VSMCs by decreasing ER stress and reduced in-stent restenosis, possibly through downregulation of the IRE1/XBP1 signaling pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morice MC, Serruys PW, Sousa JE, Fajadet J, Ban Hayashi E, Perin M, et al. A randomized comparison of a sirolimus-eluting stent with a standard stent for coronary revascularization. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1773–80.
Palmerini T, Benedetto U, Biondi-Zoccai G, Della Riva D, Bacchi-Reggiani L, Smits PC, et al. Long-term safety of drug-eluting and bare-metal stents: evidence from a comprehensive network meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:2496–507.
Inoue T, Node K. Molecular basis of restenosis and novel issues of drug-eluting stents. Circ J. 2009;73:615–21.
Kaul U, Bangalore S, Seth A, Arambam P, Abhaichand RK, Patel TM, et al. Paclitaxel-eluting versus everolimus-eluting coronary stents in diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:1709–19.
de la Torre Hernandez JM, Alfonso F, Martin Yuste V, Sanchez Recalde A, Jimenez Navarro MF, Perez de Prado A, et al. Comparison of paclitaxel and everolimus-eluting stents in st-segment elevation myocardial infarction and influence of thrombectomy on outcomes. Estrofa-im study. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2014;67:999–1006.
Pan M, Burzotta F, Trani C, Medina A, Suarez de Lezo J, Niccoli G, et al. Three-year follow-up of patients with bifurcation lesions treated with sirolimus- or everolimus-eluting stents: seaside and corpal cooperative study. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2014;67:797–803.
Joner M, Nakazawa G, Finn AV, Quee SC, Coleman L, Acampado E, et al. Endothelial cell recovery between comparator polymer-based drug-eluting stents. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52:333–42.
Zhang DP, Ge YG, Ni ZH. Very late angiographic stent thrombosis after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation at 54 months. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2008;36:176–7.
Takahashi S, Kaneda H, Tanaka S, Miyashita Y, Shiono T, Taketani Y, et al. Late angiographic stent thrombosis after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation. Circ J. 2007;71:226–8.
Kuriyama N, Kobayashi Y, Nakama T, Mine D, Nishihira K, Shimomura M, et al. Late restenosis following sirolimus-eluting stent implantation. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2011;4:123–8.
Kimura T, Morimoto T, Nakagawa Y, Kawai K, Miyazaki S, Muramatsu T, et al. Very late stent thrombosis and late target lesion revascularization after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation: five-year outcome of the j-cypher registry. Circulation. 2012;125:584–91.
Park SJ, Kang SJ, Virmani R, Nakano M, Ueda Y. In-stent neoatherosclerosis: a final common pathway of late stent failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;59:2051–7.
Shah R, Ramos-Bondy B, Mizeracki A. Risk of stent thrombosis with bioresorbable vascular scaffolds. Lancet. 2016;387:1903.
Poupon RE, Poupon R, Balkau B. Ursodiol for the long-term treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis. The udca-pbc study group. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:1342–7.
Rudolph G, Endele R, Senn M, Stiehl A. Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on the kinetics of cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology. 1993;17:1028–32.
Luketic VA, Sanyal AJ. The current status of ursodeoxycholate in the treatment of chronic cholestatic liver disease. Gastroenterologist. 1994;2:74–9.
Lee CS, Kwon YW, Yang HM, Kim SH, Kim TY, Hur J, et al. New mechanism of rosiglitazone to reduce neointimal hyperplasia: activation of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta followed by inhibition of mmp-9. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009;29:472–9.
Makino I, Tanaka H. From a choleretic to an immunomodulator: historical review of ursodeoxycholic acid as a medicament. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998;13:659–64.
Vang S, Longley K, Steer CJ, Low WC. The unexpected uses of urso- and tauroursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of non-liver diseases. Glob Adv Health Med. 2014;3:58–69.
Cho JG, Lee JH, Hong SH, Lee HN, Kim CM, Kim SY, et al. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid, a bile acid, promotes blood vessel repair by recruiting vasculogenic progenitor cells. Stem Cells. 2015;33:792–805.
Ma J, Nakajima T, Iida H, Iwasawa K, Terasawa K, Oonuma H, et al. Inhibitory effects of ursodeoxycholic acid on the induction of nitric oxide synthase in vascular smooth muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003;464:79–86.
Lee WY, Han SH, Cho TS, Yoo YH, Lee SM. Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on ischemia/reperfusion injury in isolated rat heart. Arch Pharm Res. 1999;22:479–84.
Kim SY, Kwon YW, Jung IL, Sung JH, Park SG. Tauroursodeoxycholate (tudca) inhibits neointimal hyperplasia by suppression of erk via pkcalpha-mediated mkp-1 induction. Cardiovasc Res. 2011;92:307–16.
Fan L, Chen LL, Lin CG, Peng YF, Zheng XC, Luo YK, et al. Firebird and cypher sirolimus-eluting stents and bare metal stents in treatment of very long coronary lesions. Chin Med J. 2008;121:1518–23.
Gao Z, Yang YJ, Chen JL, Qiao SB, Xu B, Qin XW, et al. Effects of sirolimus-eluting stent and the paclitaxel-eluting stent: a three-year follow-up study. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008;88:1811–4.
Gao H, Yan HB, Zhu XL, Li N, Ai H, Wang J, et al. Firebird sirolimus eluting stent versus bare mental stent in patients with st-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Chin Med J. 2007;120:863–7.
Iaconetti C, De Rosa S, Polimeni A, Sorrentino S, Gareri C, Carino A, et al. Down-regulation of mir-23b induces phenotypic switching of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro and in vivo. Cardiovasc Res. 2015;107:522–33.
Fitzgerald TN, Shepherd BR, Asada H, Teso D, Muto A, Fancher T, et al. Laminar shear stress stimulates vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis via the akt pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2008;216:389–95.
Palumbo R, Gaetano C, Melillo G, Toschi E, Remuzzi A, Capogrossi MC. Shear stress downregulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta and matrix metalloprotease-2 is associated with inhibition of smooth muscle cell invasion and migration. Circulation. 2000;102:225–30.
Garanich JS, Pahakis M, Tarbell JM. Shear stress inhibits smooth muscle cell migration via nitric oxide-mediated downregulation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;288:H2244–52.
Wang CF, Yuan JR, Qin D, Gu JF, Zhao BJ, Zhang L, et al. Protection of tauroursodeoxycholic acid on high glucose-induced human retinal microvascular endothelial cells dysfunction and streptozotocin-induced diabetic retinopathy rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;185:162–70.
Chen S, Liu B, Kong D, Li S, Li C, Wang H, et al. Atorvastatin calcium inhibits phenotypic modulation of pdgf-bb-induced vsmcs via down-regulation the akt signaling pathway. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0122577.
Ikegami T, Matsuzaki Y. Ursodeoxycholic acid: mechanism of action and novel clinical applications. Hepatol Res. 2008;38:123–31.
Beuers U. Drug insight: mechanisms and sites of action of ursodeoxycholic acid in cholestasis. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;3:318–28.
Hua Y, Kandadi MR, Zhu M, Ren J, Sreejayan N. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid attenuates lipid accumulation in endoplasmic reticulum-stressed macrophages. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2010;55:49–55.
Ozcan U, Yilmaz E, Ozcan L, Furuhashi M, Vaillancourt E, Smith RO, et al. Chemical chaperones reduce er stress and restore glucose homeostasis in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Science. 2006;313:1137–40.
Chen Y, Liu CP, Xu KF, Mao XD, Lu YB, Fang L, et al. Effect of taurine-conjugated ursodeoxycholic acid on endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis induced by advanced glycation end products in cultured mouse podocytes. Am J Nephrol. 2008;28:1014–22.
Yanagitani K, Imagawa Y, Iwawaki T, Hosoda A, Saito M, Kimata Y, et al. Cotranslational targeting of xbp1 protein to the membrane promotes cytoplasmic splicing of its own mrna. Mol Cell. 2009;34:191–200.
Zeng L, Li Y, Yang J, Wang G, Margariti A, Xiao Q, et al. Xbp 1-deficiency abrogates neointimal lesion of injured vessels via cross talk with the pdgf signaling. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015;35:2134–44.
Ben Mosbah I, Alfany-Fernandez I, Martel C, Zaouali MA, Bintanel-Morcillo M, Rimola A, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibition protects steatotic and non-steatotic livers in partial hepatectomy under ischemia-reperfusion. Cell Death Dis. 2010;1:e52.
Omar HR, Sprenker C, Karlnoski R, Camporesi EM, Mangar D. Late and very late drug-eluting stent thrombosis in the immediate postoperative period after antiplatelet withdrawal: a retrospective study. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2014;8:185–92.
Franck C, Eisenberg MJ, Dourian T, Grandi SM, Filion KB. Very late stent thrombosis in patients with first-generation drug-eluting stents: a systematic review of reported cases. Int J Cardiol. 2014;177:1056–8.
Bechiri MY, Souteyrand G, Lefevre T, Trouillet C, Range G, Cayla G, et al. Characteristics of stent thrombosis in bifurcation lesions analysed by optical coherence tomography [J]. EuroIntervention. 2018;13(18):e2174–e2181.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Faculty of Agriculture, Life and Environment Science at Zhejiang University for their valuable technical assistance. We thank Sarah Bubeck, Ph.D., from Liwen Bianji, Edanz Editing China (www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by Co construction of Provincial Department key project (Grant No. WKJ-ZJ-1729) and Zhejiang Science and Technology Department Animal Experimental Research Project (2017C37141).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, H., Zhou, C., Chi, J. et al. The Role of Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid on Dedifferentiation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells by Modulation of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and as an Oral Drug Inhibiting In-Stent Restenosis. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 33, 25–33 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-018-6844-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-018-6844-4