Abstract
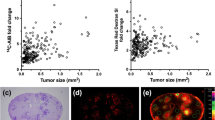
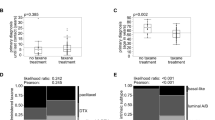
The limited entry of anticancer drugs into the central nervous system represents a special therapeutic challenge for patients with brain metastases and is primarily due to the blood brain barrier (BBB). Albumin-bound Evans blue (EB) dye is too large to cross the BBB but can grossly stain tissue blue when the BBB is disrupted. The course of tumor development and the integrity of the BBB were studied in three preclinical breast cancer brain metastasis (BCBM) models. A luciferase-transduced braintropic clone of MDA-231 cell line was used. Nude mice were subjected to stereotactic intracerebral inoculation, mammary fat pad-derived tumor fragment implantation, or carotid artery injections. EB was injected 30 min prior to euthanasia at various timepoints for each of the BCBM model animals. Serial bioluminescent imaging demonstrated exponential tumor growth in all models. Carotid BCBM appeared as diffuse multifocal cell clusters. EB aided the localization of metastases ex vivo. Tumor implants stained blue at 7 days whereas gross staining was not evident until day 14 in the stereotactic model and day 28 for the carotid model. EB assessment of the integrity of the BBB provides useful information relevant to drug testing in preclinical BCBM models.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aragon-Ching JB, Zujewski JA (2007) CNS metastasis: an old problem in a new guise. Clin Cancer Res 13:1644–1647. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0096
Dawood S, Gonzalez-Angulo AM (2013) Progress in the biological understanding and management of breast cancer-associated central nervous system metastases. Oncologist 18:675–684. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0438
Minisini A, Moroso S, Gerratana L, Giangreco M, Iacono D, Poletto E, Guardascione M, Fontanella C, Fasola G, Puglisi F (2013) Risk factors and survival outcomes in patients with brain metastases from breast cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis. doi:10.1007/s10585-013-9594-5
Lin NU, Claus E, Sohl J, Razzak A, Arnaout A, Winer E (2010) Sites of distant relapse and clinical outcomes in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: high incidence of central nervous system metastases. Cancer 113:2638–2645. doi:10.1002/cncr.23930.Sites
Gril B, Evans L, Palmieri D, Steeg PS (2010) Translational research in brain metastasis is identifying molecular pathways that may lead to the development of new therapeutic strategies. Eur J Cancer 46:1204–1210. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2010.02.033
Olson EM, Abdel-Rasoul M, Maly J, Wu CS, Lin NU, Shapiro CL (2013) Incidence and risk of central nervous system metastases as site of first recurrence in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer treated with adjuvant trastuzumab. Ann Oncol 24:1526–1533. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdt036
Hicks DG, Short SM, Prescott NL, Tarr SM, Coleman KA, Yoder BJ, Crowe JP, Choueiri TK, Dawson AE, Budd T, Tubbs RR, Casey G, Weil RJ (2006) Breast cancers with brain metastases are more likely to be estrogen receptor negative, express the basal cytokeratin CK5/6, and overexpress HER2 or EGFR. Am J Surg Pathol 30:1097–1104
Slimane K, Andre F, Delaloge S, Dunant A, Perez A, Grenier J, Massard C, Spielmann M (2004) Risk factors for brain relapse in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol 15:1640–1644. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdh432
Miller KD (2003) Occult central nervous system involvement in patients with metastatic breast cancer: prevalence, predictive factors and impact on overall survival. Ann Oncol 14:1072–1077. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdg300
Clark GM, Sledge GW, Osborne CK, McGuire WL (1987) Survival from first recurrence: relative importance of prognostic factors in 1,015 breast cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 5:55–61
Hwang TL, Close TP, Grego JM, Brannon WL, Gonzales F (1996) Predilection of brain metastasis in gray and white matter junction and vascular border zones. Cancer 77:1551–1555. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19960415)77:8<1551:AID-CNCR19>3.0.CO;2-Z
Lin NU, Bellon JR, Winer EP (2004) CNS metastases in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 22:3608–3617. doi:10.1200/JCO.2004.01.175
Scott BJ, Kesari S (2013) Leptomeningeal metastases in breast cancer. Am J Cancer Res 3:117–126
Karam I, Lesperance MF, Berrang T, Speers C, Tyldesley S, Truong PT (2013) pN0(i+) breast cancer: treatment patterns, locoregional recurrence, and survival outcomes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 87:731–737. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.07.028
Fidler IJ (2011) The role of the organ microenvironment in brain metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol 21:107–112. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2010.12.009
Abbott NJ, Patabendige AA, Dolman DE, Yusof SR, Begley DJ (2010) Structure and function of the blood–brain barrier. Neurobiol Dis 37:13–25. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2009.07.030
Palmieri D, Chambers AF, Felding-Habermann B, Huang S, Steeg PS (2007) The biology of metastasis to a sanctuary site. Clin Cancer Res 13:1656–1662. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2659
Lorger M, Felding-Habermann B (2010) Capturing changes in the brain microenvironment during initial steps of breast cancer brain metastasis. Am J Pathol 176:2958–2971. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2010.090838
Schackert G, Fidler IJ (1988) Development of in vivo models for studies of brain metastasis. Int J Cancer 41:589–594
Balathasan L, Beech JS, Muschel RJ (2013) Ultrasonography-guided intracardiac injection: an improvement for quantitative brain colonization assays. Am J Pathol 183:26–34. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.03.003
Chua JY, Pendharkar AV, Wang N, Choi R, Andres RH, Gaeta X, Zhang J, Moseley ME, Guzman R (2011) Intra-arterial injection of neural stem cells using a microneedle technique does not cause microembolic strokes. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31:1263–1271. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2010.213
Rapoport SI, Fredericks WR, Ohno K, Pettigrew KD (1980) Quantitative aspects of reversible osmotic opening of the blood–brain barrier. Am J Physiol 238:R421–R431
Liu R, Martuza RL, Rabkin SD (2005) Intracarotid delivery of oncolytic HSV vector G47 D to metastatic breast cancer in the brain. Gene Ther 12:647–654. doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3302445
Mehmet K, Ahishali B (2011) Assessment of permeability in barrier type of endothelium in brain using tracers: Evans blue, sodium fluorescein, and horseradish peroxidase. In: Turksen K (ed) Methods Mol Biol. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 369–382
Lockman PR, Mittapalli RK, Taskar KS, Rudraraju V, Gril B, Bohn KA, Adkins CE, Roberts A, Thorsheim HR, Gaasch JA, Huang S, Palmieri D, Steeg PS, Smith QR (2010) Heterogeneous blood-tumor barrier permeability determines drug efficacy in experimental brain metastases of breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16:5664–5678. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1564
Inoue Y, Kiryu S, Watanabe M, Tojo A, Ohtomo K (2010) Timing of imaging after d-luciferin injection affects the longitudinal assessment of tumor growth using in vivo bioluminescence imaging. Int J Biomed Imaging 2010:7–12. doi:10.1155/2010/471408
Nieuwenhuys R, Voogd J, Van Huijzen C (2007) The human central nervous system: a synopsis and atlas. Springer, Berlin
Daphu I, Sundstrøm T, Horn S, Huszthy PC, Niclou SP, Sakariassen PO, Immervoll H, Miletic H, Bjerkvig R, Thorsen F (2013) In vivo animal models for studying brain metastasis: value and limitations. Clin Exp Metastasis 30:695–710. doi:10.1007/s10585-013-9566-9
Berghoff A, Bago-Horvath Z, Ilhan-Mutlu A, Magerle M, Dieckmann K, Marosi C, Birner P, Widhalm G, Steger G, Zielinski C, Bartsch R, Preusser M (2012) Brain-only metastatic breast cancer is a distinct clinical entity characterised by favourable median overall survival time and a high rate of long-term survivors. Br J Cancer 107:1454–1458. doi:10.1038/bjc.2012.440
Deeken JF, Löscher W (2007) The blood–brain barrier and cancer: transporters, treatment, and Trojan horses. Clin Cancer Res 13:1663–1674. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2854
Prabhu SS, Broaddus WC, Oveissi C, Berr SS, Gillies GT (2000) Determination of intracranial tumor volumes in a rodent brain using magnetic resonance imaging, Evans blue, and histology: a comparative study. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 47:259–265
Zhou H, Chen M, Zhao D (2013) Longitudinal MRI evaluation of intracranial development and vascular characteristics of breast cancer brain metastases in a mouse model. PLoS One 8:1–11
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Sanjiv Sam Gambhir for his technical support. This study was supported in part by the Komen for the Cure grant (KG090545), Small Animal Imaging Resource NIH-NCI ICMIC P50-CA114747-02 (Gambhir, PI), and Stanford University Cancer Center NIH NCI CCSG P30-CA124435-02 (Mitchell, PI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
John Do and Deshka Foster have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Do, J., Foster, D., Renier, C. et al. Ex vivo Evans blue assessment of the blood brain barrier in three breast cancer brain metastasis models. Breast Cancer Res Treat 144, 93–101 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-014-2854-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-014-2854-5