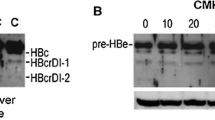
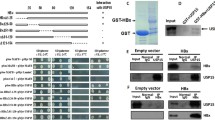
Abstract
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) core protein (HBc) is a major component of viral nucleocapsid and a multifunctional protein involved in viral maturation and release. It is unstable and present in cells at low level because of K96 lysine residue, which is a ubiquitin acceptor site. Np95/ICBP90-like RING finger protein (NIRF) has auto-ubiquitination activity which is the hallmark of a ubiquitin ligase. In the present study, ubiquitin ligase, NIRF, binds to HBc and leads to the proteasome-mediated degradation of HBc in vivo. NIRF down-regulates HBc protein level, resulting in the decrease of the amount of HBV particles in supernatant of HepG2.2.15 cells. However knockdown of NIRF significantly increases endogenous HBc protein level, leading to HBV release. The results reveal that NIRF interacts with HBc and promotes the degradation of HBc in vivo. The pathway of NIRF-mediated ubiquitin–proteasome affects the release of HBV particles by controlling the amounts of HBc. It indicates that NIRF may participate in the maturation of HBV.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbuthnot P, Kew M (2001) Hepatitis B virus and hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Exp Pathol 82(2):77–100
Blot V, Perugi F, Gay B, Prevost MC, Briant L, Tangy F, Abriel H, Staub O, Dokelar MC, Pique C (2004) Nedd4.1-mediated ubiquitination and subsequent recruitment of Tsg101 ensure HTLV-1 Gag trafficking towards the multivesicular body pathway prior to virus budding. J Cell Sci 117(Pt 11):2357–2367
Bronner C, Achour M, Arima Y, Chataigneau T, Saya H, Schini-Kerth VB (2007) The UHRF family: oncogenes that are druggable targets for cancer therapy in the near future? Pharmacol Ther 115(3):419–434
Dawson SP (2008) Hepatocellular carcinoma and the ubiquitin–proteasome system. Biochim Biophys Acta 1782(12):775–784
Duan CZ, Pu SP, Mori T, Kochi H, Qiu ZY (2006)) Studies on the interactions between NIRF and P53. Prog Biochem Biophys 33(2):163–168
Funk A, Mhamdi M, Will H, Sirma H (2007) Avian hepatitis B viruses: molecular and cellular biology, phylogenesis, and host tropism. World J Gastroenterol 13(1):91–103
Gao G, Luo HL (2006) The ubiquitin–proteasome pathway in viral infections. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 84(1):5–14
He XY, Duan CZ, Chen JX, Ouyang X, Zhang Z, Li CL, Peng HM (2009) Let-7a elevates p21WAF1 levels by targeting of NIRF and suppresses the growth of A549 lung cancer cells. FEBS Lett 583:3501–3507
Ingham RJ, Gish G, Pawson T (2004) The Nedd4 family of E3 ubiquitin ligases: functional diversity within a common modular architecture. Oncogene 23(11):1972–1984
Iwata A, Nagashima Y, Matsumoto L, Suzuki T, Yamanaka T, Date H, Deoka K, Nukina N, Tsuji S (2009) Intranuclear degradation of polyglutamine aggregates by the ubiquitin–proteasome system. J Biol Chem 284(15):9796–9803
Jackson PK, Eldridge AG, Freed E, Furstenthal L, Hsu JY, Kaiser BK, Reimann JD (2000) The lore of the RINGs-substrate recognition and catalysis by ubiquitin ligases. Trends Cell Biol 10(10):429–439
Kee Y, Huibregtse JM (2007) Regulation of catalytic activities of HECT ubiquitin ligases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 354(2):329–333
Kim JH, Kang S, Kim J, Ahn BY (2003) Hepatitis B virus core protein stimulates the proteasome-mediated degradation of viral X protein. J Virol 77(13):7166–7173
Lambert C, Doring T, Prange R (2007) Hepatitis B virus maturation is sensitive to functional inhibition of ESCRT-III, Vps4, and 2-adaptin. J Virol 81(17):9050–9060
Li Y, Mori T, Hata H, Homma Y, Kochi H (2004) NIRF induces G1 arrest and associates with Cdk2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 319(2):464–468
Li HC, Huang EY, Su PY, Wu SY, Yang CC, Lin YS, Chang WC, Shih C (2010) Nuclear export and import of human HBV capsid protein and particles. PLoS Pathog 6(10):e1001162
Madden CR, Finegold MJ, Slagle BL (2002) Altered DNA mutation spectrum in aflatoxin B1-treated transgenic mice that express the hepatitis B virus X protein. J Virol 76(22):11770–11774
Mori T, Li Y, Hata H, Ono K, Kochi H (2002) NIRF, a novel RING finger protein, is involved in cell-cycle regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 296(3):530–536
Mori T, Li Y, Hata H, Kochi H (2004) NIRF is a ubiquitin ligase that is capable of ubiquitinating PCNP, a PEST-containing nuclear protein. FEBS Lett 557(1–3):209–214
Pickart CM, Eddins MJ (2004) Ubiquitin: structures, functions, mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta 1695(1–3):55–72
Ponsel D, Bruss V (2003) Mapping of amino acid side chains on the surface of hepatitis B virus capsids required for envelopment and virion formation. J Virol 77(1):416–422
Rost M, Mann S, Lambert C, Doring T, Thome N, Prange R (2006) γ2-Adaptin, a novel ubiquitin-interacting adaptor, and Nedd4 ubiquitin ligase control hepatitis B virus maturation. J Biol Chem 281(39):29297-29308
Seeger C, Mason WS (2000) Hepatitis B virus biology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64(1):51–68
Shearwin-Whyatt L, Dalton HE, Foot N, Kumar S (2006) Regulation of functional diversity within the Nedd4 family by accessory and adaptor proteins. Bioessays 28(6):617–628
Vana ML, Tang Y, Chen AP, Medina G, Carter C, Leis J (2004) Role of Nedd4 and ubiquitination of Rous sarcoma virus Gag in budding of virus-like particles from cells. J Virol 78(24):13943–13953
Xu WS, Zhao KK, Miao XH, Wu N, Cai X, Zhang RQ, Wan J (2010) Effect of oxymatrine on the replication cycle of hepatitis B virus in vitro. World J Gastroenterol 16(16):2028–2037
Yeh CT, Wong SW, Fung YK, Ou JH (1993) Cell cycle regulation of nuclear localization of hepatitis B virus core protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:6459–6463
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 30872248), Chongqing Science Commission (CSTC, 2008BB5400) and Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (KJ080326). We are grateful to Professor OU JH (University of Southern California) for pCMV-core.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, G., Jin, F., Chang, L. et al. NIRF, a novel ubiquitin ligase, interacts with hepatitis B virus core protein and promotes its degradation. Biotechnol Lett 34, 29–36 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-011-0751-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-011-0751-0