Abstract
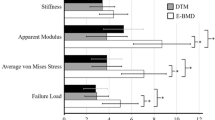
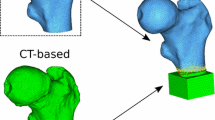
Osteoporotic (Colles’ type) fractures of the distal radius occur relatively early in lifetime and could estimate risk of fracture of other, more endangered anatomical sites. High-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT) based micro finite element (μFE) analysis was shown to better predict fracture load of the distal radius than densitometry or histomorphometric measures. As an alternative to μFE, homogenization-based FE (hFE) approach may provide at least equivalent predictive power with reduced computational needs. The aim of this study was to validate the hFE approach with compression tests of 25 distal radius sections extracted at the location which is relevant in Colles’ fractures. HR-pQCT-based input parameters of the hFE models were calibrated with respect to μCT. HR-pQCT-based hFE models were then built and their ability to predict experimental stiffness and ultimate load was compared to those of the density-based parameters, histomorphometric indices and μFE models assessed from the same input images. Bone mineral content was the best non-FE-based predictor (R 2 = 0.86) of ultimate force. Both FE methods were not only the strongest predictors, but provided quantitatively correct fracture loads. The calibrated hFE approach provided closely as strong prediction (R 2 = 0.94) as μFE (R 2 = 0.95), but the former was computationally cheaper. The results of this validation study suggest that FE simulation could be used as an efficient and precise tool to predict Colles’ fracture load.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbenz P, van Lenthe GH, Mennel U, Müller R, Sala M et al (2008) A scalable multi-level preconditioner for matrix-free μ-finite element analysis of human bone structures. Int J Numer Methods Eng 73(7): 927–947. doi:10.1002/nme.2101
Boutroy S, Rietbergen BV, Sornay-Rendu E, Munoz F, Bouxsein ML, Delmas PD et al (2008) Finite element analysis based on in vivo HR-pQCT images of the distal radius is associated with wrist fracture in postmenopausal women. J Bone Min Res 23(3): 392–399. doi:10.1359/jbmr.071108
Buie HR, Campbell GM, Klinck RJ, MacNeil JA, Boyd SK (2007) Automatic segmentation of cortical and trabecular compartments based on a dual threshold technique for in vivo micro-CT bone analysis. Bone 41(4): 505–515. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2007.07.007
Burghardt A, Kazakia G, Link T, Majumdar S (2009) Automated simulation of areal bone mineral density assessment in the distal radius from high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography. Osteoporos Int 20(12): 2017–2024. doi:10.1007/s00198-009-0907-0
Chevalier Y, Charlebois M, Pahr D, Varga P, Heini P, Schneider E, Zysset P et al (2008) A patient-specific finite element methodology to predict damage accumulation in vertebral bodies under axial compression, sagittal flexion and combined loads. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng 11(5): 477–487. doi:10.1080/10255840802078022
Cuddihy MT, Gabriel SE, Crowson CS, Atkinson EJ, Tabini C, O’Fallon WM, Melton LJ (2002) Osteoporosis intervention following distal forearm fractures: a missed opportunity. Arch Intern Med 162(4): 421–426
Dall’Ara E, Schmidt R, Pahr D, Varga P, Chevalier Y, Patsch J, Kainberger F, Zysset P (2010) A nonlinear finite element model validation study based on a novel experimental technique for inducing anterior wedge-shape fractures in human vertebral bodies in vitro. J Biomech. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2010.04.023
Eastell R, Wahner HW, O’Fallon WM, Amadio PC, Melton LJ, Riggs BL (1989) Unequal decrease in bone density of lumbar spine and ultradistal radius in colles’ and vertebral fracture syndromes. J Clin Invest 83(1): 168–174. doi:10.1172/JCI113854
Ebbesen EN, Thomsen JS, Beck-Nielsen H, Nepper-Rasmussen HJ, Mosekilde L (1999) Lumbar vertebral body compressive strength evaluated by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, quantitative computed tomography, and ashing. Bone 25(6): 713–724
Eckstein F, Kuhn V, Lochmüller EM (2004) Strength prediction of the distal radius by bone densitometry–evaluation using biomechanical tests. Ann Biomed Eng 32(3): 487–503
Garcia D, Zysset PK, Charlebois M, Curnier A (2009) A three-dimensional elastic plastic damage constitutive law for bone tissue. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 8(2): 149–165. doi:10.1007/s10237-008-0125-2
Goldfarb CA, Yin Y, Gilula LA, Fisher AJ, Boyer MI (2001) Wrist fractures: what the clinician wants to know. Radiology 219(1): 11–28
Hoffler CE, Moore KE, Kozloff K, Zysset PK, Brown MB, Goldstein SA (2000) Heterogeneity of bone lamellar-level elastic moduli. Bone 26(6): 603–609
Keaveny TM, Wachtel EF, Ford CM, Hayes WC (1994) Differences between the tensile and compressive strengths of bovine tibial trabecular bone depend on modulus. J Biomech 27(9): 1137–1146
Koh S, Andersen CR, Buford WL, Patterson RM, Viegas SF (2006) Anatomy of the distal brachioradialis and its potential relationship to distal radius fracture. J Hand Surg Am 31(1): 2–8. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2005.08.012
Laib A, Häuselmann HJ, Rüegsegger P (1998) In vivo high resolution 3D-QCT of the human forearm. Technol Health Care 6(5–6): 329–337
MacNeil JA, Boyd SK (2007) Accuracy of high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography for measurement of bone quality. Med Eng Phys 29(10): 1096–1105. doi:10.1016/j.medengphy.2006.11.002
MacNeil JA, Boyd SK (2008) Bone strength at the distal radius can be estimated from high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography and the finite element method. Bone 42(6): 1203–1213. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2008.01.017
Marshall D, Johnell O, Wedel H (1996) Meta-analysis of how well measurses of bone mineral density predict occurrence of osteoporotic fractures. BMJ 312(7041): 1254–1259
Mazza G, Franzoso G, Pretterklieber M, Zysset P (2008) Anisotropic elastic properties of vertebral compact bone measured by microindentation. J Biomech 41(Supp 1):S75–S75. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/B6T82-4T0F85V-2N/2/b08081e7be14917642236e076754004e
Melton LJ, Eddy DM, Johnston CC (1990) Screening for osteoporosis. Ann Intern Med 112(7): 516–528
Melton LJ, Thamer M, Ray NF, Chan JK, Chesnut CH, Einhorn TA, Johnston CC, Raisz LG, Silverman SL, Siris ES (1997) Fractures attributable to osteoporosis: report from the national osteoporosis foundation. J Bone Miner Res 12(1): 16–23
Melton LJ, Riggs BL, van Lenthe GH, Achenbach SJ, Müller R, Bouxsein ML, Amin S, Atkinson EJ, Khosla S et al (2007) Contribution of in vivo structural measurements and load/strength ratios to the determination of forearm fracture risk in postmenopausal women. J Bone Miner Res 22(9): 1442–1448. doi:10.1359/jbmr.070514
Mueller TL, Wirth AJ, Müller R, van Lenthe GH (2008) Computational bone mechanics to determine bone strength of the human radius. In: Transactions of the ORS annual meeting, vol 33. San Francisco, CA. http://www.pre-ors.org/abstracts/preors2008/03_Mueller_TL.pdf
Pahr DH, Zysset PK (2008) Influence of boundary conditions on computed apparent elastic properties of cancellous bone. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 7(6): 463–476. doi:10.1007/s10237-007-0109-7
Pahr DH, Zysset PK (2009a) A comparison of enhanced continuum FE with micro FE models of human vertebral bodies. J Biomech 42(4): 455–462. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2008.11.028
Pahr DH, Zysset PK (2009b) From high-resolution CT data to finite element models: development of an integrated modular framework. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng 12(1): 45–57. doi:10.1080/10255840802144105
Pistoia W, van Rietbergen B, Lochmüller EM, Lill CA, Eckstein F, Rüegsegger P (2002) Estimation of distal radius failure load with micro-finite element analysis models based on three-dimensional peripheral quantitative computed tomography images. Bone 30(6): 842–848
Pistoia W, van Rietbergen B, Lochmüller EM, Lill CA, Eckstein F, Rüegsegger P (2004) Image-based micro-finite-element modeling for improved distal radius strength diagnosis: moving from bench to bedside. J Clin Densitom 7(2): 153–160
Ridler TW, Calvard S (1978) Picture thresholding using an iterative selection method. IEEE T Syst Man Cyb 8(8): 630–632. doi:10.1109/TSMC.1978.4310039
Rietbergen BV, Odgaard A, Kabel J, Huiskes R (1998) Relationships between bone morphology and bone elastic properties can be accurately quantified using high-resolution computer reconstructions. J Orthop Res 16(1): 23–28. doi:10.1002/jor.1100160105
Rincón-Kohli L, Zysset PK (2009) Multi-axial mechanical properties of human trabecular bone. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 8(3): 195–208. doi:10.1007/s10237-008-0128-z
Sornay-Rendu E, Munoz F, Garnero P, Duboeuf F, Delmas PD (2005) Identification of osteopenic women at high risk of fracture: the OFELY study. J Bone Miner Res 20(10): 1813–1819. doi:10.1359/JBMR.050609
Spadaro JA, Werner FW, Brenner RA, Fortino MD, Fay LA, Edwards WT (1994) Cortical and trabecular bone contribute strength to the osteopenic distal radius. J Orthop Res 12(2): 211–218. doi:10.1002/jor.1100120210
van Rietbergen B, Weinans H, Huiskes R, Odgaard A (1995) A new method to determine trabecular bone elastic properties and loading using micromechanical finite-element models. J Biomech 28(1): 69–81
Varga P, Zysset PK (2009) Assessment of volume fraction and fabric in the distal radius using HR-pQCT. Bone 45(5): 909–917. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2009.07.001
Varga P, Baumbach S, Pahr D, Zysset PK (2009) Validation of an anatomy specific finite element model of colles’ fracture. J Biomech 42(11): 1726–1731. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2009.04.017
Verhulp E, van Rietbergen B, Huiskes R (2008) Load distribution in the healthy and osteoporotic human proximal femur during a fall to the side. Bone 42(1): 30–35. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2007.08.039
Whitehouse WJ (1974) The quantitative morphology of anisotropic trabecular bone. J Microsci 101(Pt 2): 153–168
Zysset PK (2003) A review of morphology–elasticity relationships in human trabecular bone: theories and experiments. J Biomech 36(10):1469–1485. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/B6T82-48V7WBF-1/2/b92caeb3be3bac66fb0d16a9247601fe
Zysset PK, Curnier A (1995) An alternative model for anisotropic elasticity based on fabric tensors. Mech Mater 21(4):243–250. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/B6TX6-3YCM0GH-B/2/c1c1c251e1628943fa09dc167f87e0ec
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varga, P., Dall’Ara, E., Pahr, D.H. et al. Validation of an HR-pQCT-based homogenized finite element approach using mechanical testing of ultra-distal radius sections. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 10, 431–444 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-010-0245-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-010-0245-3