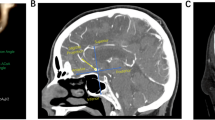
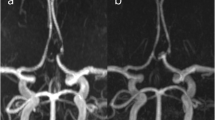
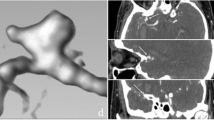
Abstract
The aim of this study is to characterize demographic and morphologic characteristics of aneurysms located in the anterior communicating artery (ACoA) and to investigate possible associations between these characteristics and aneurysm rupture. We investigated 112 consecutive patients (72 ruptured and 40 unruptured) with ACoA aneurysms from a single-center database. The effects of demographic and morphologic characteristics on the risk of rupture in ACoA aneurysms were tested using univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses, respectively. We found that larger size, greater size ratio, larger flow angle, irregular shape, and smoking of the patient were associated with the rupture of ACoA aneurysms based on univariate analysis. Size ratio (OR = 3.890, P = 0.003), irregular shape (OR = 1.068, P = 0.001), flow angle (OR = 1.054, P = 0.001), and current smoking (OR = 4.435, P = 0.009) were the strongest factors related to ruptured ACoA aneurysms based on multivariate logistic regression analysis. The areas under the curves for the flow angle and size ratio were 0.742 (95% CI 0.646–0.838; P = 0.001) and 0.736 (95% CI 0.621–0.796; P = 0.001), respectively. The strongest risk factors for rupture include size ratio, irregular shape, flow angle, and current smoking. These features should be taken into consideration to aid in the prediction of the rupture risk of ACoA aneurysms.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Andaluz N, van Loveren HR, Keller JT, Zuccarello M (2003) Anatomic and clinical study of the orbitopterional approach to anterior communicating artery aneurysms. Neurosurgery 52:1140–1149. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000057834.83222.9f
Baharoglu MI, Schirmer CM, Hoit DA, Gao BL, Malek AM (2010) Aneurysm inflow-angle as a discriminant for rupture in sidewall cerebral aneurysms: morphometric and computational fluid dynamic analysis. Stroke 41:1423–1430. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.570770
Beck J, Rohde S, Berkefeld J, Seifert V, Raabe A (2006) Size and location of ruptured and unruptured intracranial aneurysms measured by 3-dimensional rotational angiography. Surg Neurol 65:18–25; discussion 25-17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2005.05.019
Bjorkman J, Frosen J, Tahtinen O, Backes D, Huttunen T, Harju J, Huttunen J, Kurki MI, von Und Zu Fraunberg M, Koivisto T, Manninen H, Jaaskelainen JE, Lindgren AE (2017) Irregular shape identifies ruptured intracranial aneurysm in subarachnoid hemorrhage patients with multiple aneurysms. Stroke 48:1986–1989. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.017147
Chalouhi N, Ali MS, Starke RM, Jabbour PM, Tjoumakaris SI, Gonzalez LF, Rosenwasser RH, Koch WJ, Dumont AS (2012) Cigarette smoke and inflammation: role in cerebral aneurysm formation and rupture. Mediat Inflamm 2012:271582–271512. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/271582
Fang S, Brinjikji W, Murad MH, Kallmes DF, Cloft HJ, Lanzino G (2014) Endovascular treatment of anterior communicating artery aneurysms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35:943–947. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A3802
Frosen J (2014) Smooth muscle cells and the formation, degeneration, and rupture of saccular intracranial aneurysm wall--a review of current pathophysiological knowledge. Transl Stroke Res 5:347–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-014-0340-3
Futami K, Nambu I, Kitabayashi T, Sano H, Misaki K, Uchiyama N, Nakada M (2017) Inflow hemodynamics evaluated by using four-dimensional flow magnetic resonance imaging and the size ratio of unruptured cerebral aneurysms. Neuroradiology 59:411–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-017-1801-7
Investigators UJ, Morita A, Kirino T, Hashi K, Aoki N, Fukuhara S, Hashimoto N, Nakayama T, Sakai M, Teramoto A, Tominari S, Yoshimoto T (2012) The natural course of unruptured cerebral aneurysms in a Japanese cohort. N Engl J Med 366:2474–2482. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1113260
Kataoka K, Taneda M, Asai T, Kinoshita A, Ito M, Kuroda R (1999) Structural fragility and inflammatory response of ruptured cerebral aneurysms : a comparative study between ruptured and unruptured cerebral aneurysms. Stroke 30:1396–1401. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.30.7.1396
Korja M, Lehto H, Juvela S, Kaprio J (2016) Incidence of subarachnoid hemorrhage is decreasing together with decreasing smoking rates. Neurology 87:1118–1123. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000003091
Lin N, Ho A, Gross BA, Pieper S, Frerichs KU, Day AL, Du R (2012) Differences in simple morphological variables in ruptured and unruptured middle cerebral artery aneurysms. J Neurosurg 117:913–919. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.7.JNS111766
Lin N, Ho A, Charoenvimolphan N, Frerichs KU, Day AL, Du R (2013) Analysis of morphological parameters to differentiate rupture status in anterior communicating artery aneurysms. PLoS One 8:e79635. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0079635
Lindbohm JV, Kaprio J, Jousilahti P, Salomaa V, Korja M (2016) Sex, smoking, and risk for subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 47:1975–1981. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.012957
Lindgren AE, Koivisto T, Bjorkman J, von Und Zu Fraunberg M, Helin K, Jaaskelainen JE, Frosen J (2016) Irregular shape of intracranial aneurysm indicates rupture risk irrespective of size in a population-based cohort. Stroke 47:1219–1226. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.012404
Ma D, Tremmel M, Paluch RA, Levy EI, Meng H, Mocco J (2010) Size ratio for clinical assessment of intracranial aneurysm rupture risk. Neurol Res 32:482–486. https://doi.org/10.1179/016164109X12581096796558
Moon K, Nakaji P, Albuquerque FC, McDougall CG, Spetzler RF (2015) Modern paradigms for the treatment of ruptured anterior communicating artery aneurysms. Neurosurgery 62(Suppl 1):177–179. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000000809
Nossek E, Setton A, Karimi R, Dehdashti AR, Langer DJ, Chalif DJ (2016) Analysis of superiorly projecting anterior communicating artery aneurysms: anatomy, techniques, and outcome. A proposed classification system. Neurosurg Rev 39:225–235; discussion 235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-015-0677-4
Ohashi Y, Horikoshi T, Sugita M, Yagishita T, Nukui H (2004) Size of cerebral aneurysms and related factors in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Surg Neurol 61:239–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0090-3019(03)00427-0
O'Neill AH, Chandra RV, Lai LT (2017) Safety and effectiveness of microsurgical clipping, endovascular coiling, and stent assisted coiling for unruptured anterior communicating artery aneurysms: a systematic analysis of observational studies. J Neurointerv Surg 9:761–765. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2016-012629
Petitti D, Wingerd J (1978) Use of Oral contraceptives, cigarette smoking, and risk of subarachnoid hæmorrhage. Lancet 312:234–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91745-2
Raghavan ML, Ma B, Harbaugh RE (2005) Quantified aneurysm shape and rupture risk. J Neurosurg 102:355–362. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2005.102.2.0355
Rahman M, Smietana J, Hauck E, Hoh B, Hopkins N, Siddiqui A, Levy EI, Meng H, Mocco J (2010) Size ratio correlates with intracranial aneurysm rupture status: a prospective study. Stroke 41:916–920. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.574244
Ruigrok YM, Buskens E, Rinkel GJE (2001) Attributable risk of common and rare determinants of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 32:1173–1175. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.32.5.1173
Tada Y, Wada K, Shimada K, Makino H, Liang EI, Murakami S, Kudo M, Kitazato KT, Nagahiro S, Hashimoto T (2014) Roles of hypertension in the rupture of intracranial aneurysms. Stroke 45:579–586. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.003072
Tarulli E, Fox AJ (2010) Potent risk factor for aneurysm formation: termination aneurysms of the anterior communicating artery and detection of A1 vessel asymmetry by flow dilution. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:1186–1191. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A2065
Tulamo R, Niemela M (2014) Smoking and cerebral aneurysms—potential pathobiologic mechanisms. World Neurosurg 82:e79–e80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2014.03.025
Vlak MH, Rinkel GJ, Greebe P, Algra A (2013) Independent risk factors for intracranial aneurysms and their joint effect: a case-control study. Stroke 44:984–987. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.000329
Wang GX, Gong MF, Wen L, Liu LL, Yin JB, Duan CM, Zhang D (2018) Computed tomography angiography evaluation of risk factors for unstable intracranial aneurysms. World Neurosurg 115:e27–e32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.03.083
Wiebers DO (2003) Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment. Lancet 362:103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(03)13860-3
Woo D, Khoury J, Haverbusch MM, Sekar P, Flaherty ML, Kleindorfer DO, Kissela BM, Moomaw CJ, Deka R, Broderick JP (2009) Smoking and family history and risk of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurology 72:69–72. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000338567.90260.46
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Approval for the retrospective study was obtained from the research ethics committee of Chaoyang Hospital affiliated with the Capital Medical University.
Informed consent
All individual participants included in the study provided informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, X., Yang, Y., Liu, D. et al. Demographic and morphological characteristics associated with rupture status of anterior communicating artery aneurysms. Neurosurg Rev 43, 589–595 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-019-01080-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-019-01080-w