Abstract
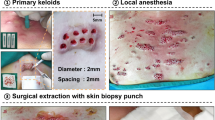
Laser-assisted drug delivery has generated intense interest. The objectives of this study are to evaluate the clinical benefit of laser-assisted corticosteroid delivery and to compare this technique to corticosteroid intralesional injection, a standard treatment for keloids. Patients with keloids on the left shoulder after BCG vaccination were enrolled in this study. The entire lesion was first treated with an ablative fractional erbium-YAG laser. After this treatment, the lesion was divided into two halves. The first half received an intralesional injection of corticosteroid, whereas the second half received topical application of corticosteroids that were occluded for 3 hours. Four treatment sessions were conducted, with treatments occurring once every 6 weeks. Treatment outcomes were evaluated using the Vancouver Scar Scale (VSS). Pain was self-assessed by the patient during the procedure. The mean keloid VSS score before treatment was 8.59 ± 1.23 for the corticosteroid injection site and 8.31 ± 2.09 for the topical site. After treatment, the mean keloid VSS score was decreased on both sides (4.56 ± 1.09 vs 5.02 ± 0.87, respectively, P > 0.05). Patients rated their satisfaction level as “moderate” on both sides. However, the mean pain score was 1.1 out of 10 on the topical side versus 6.1 on the corticosteroid injection site. The combination of ablative fractional laser treatment and topical corticosteroid application is a promising modality for the treatment of keloids. Moreover, this procedure was not associated with any serious adverse reactions or unbearable pain.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stucker FJ, Shaw GY (1992) An approach to management of keloids. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 118:63–67
Chen MA, Davidson TM (2005) Scar management: prevention and treatment strategies. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 13:242–247
Al-Attar A, Mess S, Thomassen JM, Kauffman CL, Davison SP (2006) Keloid pathogenesis and treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:286–300
Kim S, Choi TH, Liu W, Ogawa R, Suh JS, Mustoe TA (2013) Update on scar management: guidelines for treating Asian patients. Plast Reconstr Surg 132:1580–1589
Gold MH, McGuire M, Mustoe TA, Pusic A, Sachdev M, Waibel J, Murcia C (2014) International Advisory Panel on Scar Management. Updated international clinical recommendations on scar management: part 2—algorithms for scar prevention and treatment. Dermatol Surg 40:825–831
Muneuchi G, Suzuki S, Onodera M, Ito O, Hata Y, Igawa HH (2006) Long-term outcome of intralesional injection of triamcinolone acetonide for the treatment of keloid scars in Asian patients. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 40:111–116
Mishra S (2010) Safe and less painful injection of triamcinolone acetonide into a keloid—a technique. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 63:e205
Chuang GS, Rogers GS, Zeltser R (2008) Poiseuille’s law and large-bore needles: insights into the delivery of corticosteroid injections in the treatment of keloids. J Am Acad Dermatol 59:167–168
Waibel JS, Wulkan AJ, Shumaker PR (2013) Treatment of hypertrophic scars using laser and laser assisted corticosteroid delivery. Lasers Surg Med 45:135–140
Cavalié M, Sillard L, Montaudié H, Bahadoran P, Lacour JP, Passeron T (2015) Treatment of keloids with laser-assisted topical steroid delivery: a retrospective study of 23 cases. Dermatol Ther 28:74–78
Issa MC, Kassuga LE, Chevrand NS, Pires MT (2013) Topical delivery of triamcinolone via skin pretreated with ablative radiofrequency: a new method in hypertrophic scar treatment. Int J Dermatol 52:367–370
Bloom BS, Brauer JA, Geronemus RG (2013) Ablative fractional resurfacing in topical drug delivery: an update and outlook. Dermatol Surg 39:839–848
Fearmonti R, Bond J, Erdmann D, Levinson H (2010) A review of scar scales and scar measuring devices. Eplasty 21(10):e43
Manuskiatti W, Fitzpatrick RE (2002) Treatment response of keloidal and hypertrophic sternotomy scars: comparison among intralesional corticosteroid, 5-fluorouracil, and 585-nm flashlamp-pumped pulsed-dye laser treatments. Arch Dermatol 138:1149–1155
Mustoe TA, Cooter RD, Gold MH, Hobbs FD, Ramelet AA, Shakespeare PG, Stella M, Teot L, Wood FM, Ziegler UE (2002) International clinical recommendations on scar management. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:560–571
Trisliana Perdanasari A, Lazzeri D, Su W, Xi W, Zheng Z, Ke L, Min P, Feng S, Zhang YX, Persichetti P (2014) Recent developments in the use of intralesional injections keloid treatment. Arch Plast Surg 41(6):620–629
Ledon JA, Savas J, Franca K, Chacon A, Nouri K (2013) Intralesional treatment for keloids and hypertrophic scars: a review. Dermatol Surg 39:1745–1757
Koike S, Akaishi S, Nagashima Y, Dohi T, Hyakusoku H, Ogawa R (2015) Nd:YAG laser treatment for keloids and hypertrophic scars: an analysis of 102 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 8(2):e272
Alster TS, Williams CM (1995) Treatment of keloid sternotomy scars with 585 nm flash lamp-pumped pulsed-dye laser. Lancet 345:1198–1200
Paquet P, Hermanns JF, Pierard GE (2001) Effect of the 585 nm flash lamp-pumped pulsed dye laser for the treatment of keloids. Dermatol Surg 27:171–174
Nino M, Calabro G, Santoianni P (2010) Topical delivery of active principles: the field of dermatological research. Dermatol Online J 16(1):4
Sandberg C, Halldin CB, Ericson MB, Larko O, Krogstad AL, Wennberg AM (2008) Bioavailability of aminolaevulinic acid and methylaminolaevulinate in basal cell carcinomas: a perfusion study using microdialysis in vivo. Br J Dermatol 159:1170–1176
Sommer AP, Haddad MK, Fecht HJ (2015) Light effect on water viscosity: implication for ATP biosynthesis. Sci Rep 8(5):12029
Sommer AP, Mester AR, Trelles MA (2015) Tuning the mitochondrial rotary motor with light. Ann Transl Med 3(2):346
Sommer AP (2015) A mechanism for ultrasound/light-induced biostimulation. Ann Transl Med 3(19):291
Sommer AP, Zhu D, Scharnweber T (2010) Laser modulated transmembrane convection. Implement Cancer Chemother 148(2):131–134
Oni G, Brown SA, Kenkel JM (2012) Can fractional lasers enhance transdermal absorption of topical lidocaine in an in vivo animal model? Lasers Surg Med 44:168–174
Yu J, Bachhav YG, Summer S, Heinrich A, Bragagna T, Bohler C, Kalia YN (2010) Using controlled laser-microporation to increase transdermal delivery of prednisone. J Control Release 148:e71–e73
Koh JL, Harrison D, Swanson V, Norvell DC, Coomber DC (2007) A comparison of laser-assisted drug delivery at two output energies for enhancing the delivery of topically applied LMX-4 cream prior to venipuncture. Anesth Analg 104:847–849
Boyadjiev C, Popchristova E, Mazgalova J (1995) Histomorphologic changes in keloids treated with Kenacort. J Trauma 38:299–302
Gupta S, Sharma VK (2011) Standard guidelines of care: keloids and hypertrophic scars. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 77:94–100
Ogawa R, Okai K, Tokumura F, Mori K, Ohmori Y, Huang C, Hyakusoku H, Akaishi S (2012) The relationship between skin stretching/contraction and pathologic scarring: the important role of mechanical forces in keloid generation. Wound Repair Regen 20:149–157
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the ethics committee of our institution (2013-06071).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Role of funding source
There is no funding source.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional review board and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J.H., Chun, J.Y. & Lee, J.H. Laser-assisted topical corticosteroid delivery for the treatment of keloids. Lasers Med Sci 32, 601–608 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-017-2154-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-017-2154-5