Abstract
Background
The role of insulin resistance (IR) in stroke prognosis remains largely unknown. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between IR and the risk of early neurological deterioration (END) in non-diabetic patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Methods
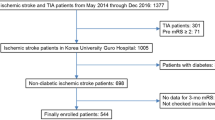
This is a retrospective analysis of non-diabetic patients with acute ischemic stroke enrolled in the prospective multicenter ACROSS-China study. The homeostasis model assessment 2 (HOMA2-IR) was evaluated and the patients were divided into HOMA2-IR quartiles (Q1 0–1.24, Q2 1.25–1.95, Q3 1.96–2.96, Q4 ≥ 2.97). END was defined as an increment in total National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) of ≥ 2 points or ≥ 4 points on day 14 ± 3 after stroke onset. Logistic regression was performed to explore the relationship between HOMA2-IR and END.
Results
Finally, 556 patients were included (63.7 ± 12.9 years, 64.6% male); thirty-three patients developed END. The median HOMA2-IR of all patients was 1.95 (inter-quartile = 1.24–2.96). There were 148, 135, 130, and 143 patients in Q1, Q2, Q3, and Q4, respectively. Compared with Q1, END (NIHSS ≥ 2) risk was increased in Q4: adjusted odds ratio (OR) = 6.051, 95% CI = 1.638–22.354, P = 0.0069. In additon, END (NIHSS ≥ 2) risk was increased in Q4 compared with the Q1–Q3 combined group: adjusted OR = 2.853, 95% CI = 1.308–6.224, P = 0.0084. END (NIHSS ≥ 4) risk was also increased in Q4: adjusted OR = 7.507, 95% CI = 2.357–23.906, P = 0.0006) compared with the Q1–Q3 combined group.
Conclusion
This study strongly suggests that IR is probably an independent risk factor for END in non-diabetic patients with acute ischemic stroke.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnston SC, Mendis S, Mathers CD (2009) Global variation in stroke burden and mortality: estimates from monitoring, surveillance, and modelling. Lancet Neurol 8(4):345–354
Liu LP, Wong LK, Wang DZ, Miao ZR (2014) Current status of endovascular procedures in management of ischemic stroke in China. CNS Neurosci Ther 20(6):483–484
Liu L, Wang D, Wong KS, Wang Y (2011) Stroke and stroke care in China: huge burden, significant workload, and a national priority. Stroke 42(12):3651–3654
Li H, Qiu W, Hu B, Kang Z, Wu AM, Dai Y, Lin Y, Lu Z (2013) Ischemic volumes and early neurologic deterioration in acute brainstem infarctions with hemoglobin A1c. Eur Neurol 70(3–4):225–232
Kwon HM, Lim JS, Park HK, Lee YS (2011) Hypertriglyceridemia as a possible predictor of early neurological deterioration in acute lacunar stroke. J Neurol Sci 309(1–2):128–130
Simonsen CZ, Schmitz ML, Madsen MH, Mikkelsen IK, Chandra RV, Leslie-Mazwi T, Andersen G (2016) Early neurological deterioration after thrombolysis: clinical and imaging predictors. Int J Stroke 11(7):776–782
Bhatia K, Mohanty S, Tripathi BK, Gupta B, Mittal MK (2015) Predictors of early neurological deterioration in patients with acute ischaemic stroke with special reference to blood urea nitrogen (BUN)/creatinine ratio & urine specific gravity. Indian J Med Res 141(3):299–307
Bas DF, Ozdemir AO, Colak E, Kebapci N (2016) Higher insulin resistance level is associated with worse clinical response in acute ischemic stroke patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis. Transl Stroke Res 7(3):167–171
Mi D, Zhang L, Wang C, Liu L, Pu Y, Zhao X, Wang Y, Wang Y (2012) Impact of metabolic syndrome on the prognosis of ischemic stroke secondary to symptomatic intracranial atherosclerosis in Chinese patients. PLoS One 7(12):e51421
Jia Q, Zheng H, Zhao X, Wang C, Liu G, Wang Y, Liu L, Li H, Zhong L, Wang Y, Investigators for the Survey on Abnormal Glucose Regulation in Patients With Acute Stroke Across China (ACROSS-China) (2012) Abnormal glucose regulation in patients with acute stroke across China: prevalence and baseline patient characteristics. Stroke 43(3):650–657
Jia Q, Liu G, Zheng H, Zhao X, Wang C, Wang Y, Liu L, Wang Y, Investigators for the Survey on Abnormal Glucose Regulation in Patients With Acute Stroke Across China (2014) Impaired glucose regulation predicted 1-year mortality of Chinese patients with ischemic stroke: data from abnormal glucose regulation in patients with acute stroke across China. Stroke 45(5):1498–1500
Stroke--1989. Recommendations on stroke prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. Report of the WHO Task Force on Stroke and other Cerebrovascular Disorders. Stroke, 1989. 20(10): p. 1407–31
Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ (1998) Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med 15(7):539–553
American Diabetes A (2006) Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 29(Suppl 1):S43–S48
Wallace TM, Levy JC, Matthews DR (2004) Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care 27(6):1487–1495
Jeong HG, Kim BJ, Yang MH, Han MK, Bae HJ (2015) Neuroimaging markers for early neurologic deterioration in single small subcortical infarction. Stroke 46(3):687–691
Zhang X et al (2016) Metabolic syndrome augments the risk of early neurological deterioration in acute ischemic stroke patients independent of inflammatory mediators: a hospital-based prospective study. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2016:8346301
Seners P, Turc G, Tisserand M, Legrand L, Labeyrie MA, Calvet D, Meder JF, Mas JL, Oppenheim C, Baron JC (2014) Unexplained early neurological deterioration after intravenous thrombolysis: incidence, predictors, and associated factors. Stroke 45(7):2004–2009
Calleja, A.I., et al., Blood biomarkers of insulin resistance in acute stroke patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis: temporal profile and prognostic value.J Diab Res Clin Metab, 2013
Kernan WN, Ovbiagele B, Black HR, Bravata DM, Chimowitz MI, Ezekowitz MD, Fang MC, Fisher M, Furie KL, Heck DV, Johnston SC, Kasner SE, Kittner SJ, Mitchell PH, Rich MW, Richardson D, Schwamm LH, Wilson JA, American Heart Association Stroke Council, Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing, Council on Clinical Cardiology, and Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease (2014) Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 45(7):2160–2236
Kaur J (2014) A comprehensive review on metabolic syndrome. Cardiol Res Pract 2014:943162
Janszky I, Hallqvist J, Ljung R, Ahlbom A, Hammar N (2009) Prognostic role of the glucometabolic status assessed in a metabolically stable phase after a first acute myocardial infarction: the SHEEP study. J Intern Med 265(4):465–475
Kernan WN, Viscoli CM, Furie KL, Young LH, Inzucchi SE, Gorman M, Guarino PD, Lovejoy AM, Peduzzi PN, Conwit R, Brass LM, Schwartz GG, Adams HP Jr, Berger L, Carolei A, Clark W, Coull B, Ford GA, Kleindorfer D, O’Leary JR, Parsons MW, Ringleb P, Sen S, Spence JD, Tanne D, Wang D, Winder TR, IRIS Trial Investigators (2016) Pioglitazone after ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack. N Engl J Med 374(14):1321–1331
Davalos A et al (1999) Neurological deterioration in acute ischemic stroke: potential predictors and associated factors in the European cooperative acute stroke study (ECASS) I. Stroke 30(12):2631–2636
Kwan J, Hand P (2006) Early neurological deterioration in acute stroke: clinical characteristics and impact on outcome. QJM 99(9):625–633
DeGraba TJ et al (1999) Progression in acute stroke: value of the initial NIH stroke scale score on patient stratification in future trials. Stroke 30(6):1208–1212
Ois A, Martinez-Rodriguez JE, Munteis E, Gomis M, Rodríguez-Campello A, Jimenez-Conde J, Cuadrado-Godia E, Roquer J (2008) Steno-occlusive arterial disease and early neurological deterioration in acute ischemic stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis 25(1–2):151–156
Vila N, Castillo J, Dávalos A, Chamorro A (2000) Proinflammatory cytokines and early neurological worsening in ischemic stroke. Stroke 31(10):2325–2329
Seo WK, Seok HY, Kim JH, Park MH, Yu SW, Oh K, Koh SB, Park KW (2012) C-reactive protein is a predictor of early neurologic deterioration in acute ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 21(3):181–186
Calleja AI, García-Bermejo P, Cortijo E, Bustamante R, Rojo Martínez E, González Sarmiento E, Fernández-Herranz R, Arenillas JF (2011) Insulin resistance is associated with a poor response to intravenous thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke. Diabetes Care 34(11):2413–2417
Wang Q, Chen C, Chen XY, Han JH, Soo Y, Leung TW, Mok V, Wong KS (2012) Low-molecular-weight heparin and early neurologic deterioration in acute stroke caused by large artery occlusive disease. Arch Neurol 69(11):1454–1460
Awadh M, MacDougall N, Santosh C, Teasdale E, Baird T, Muir KW (2010) Early recurrent ischemic stroke complicating intravenous thrombolysis for stroke: incidence and association with atrial fibrillation. Stroke 41(9):1990–1995
Seners P et al (2015) Incidence, causes and predictors of neurological deterioration occurring within 24 h following acute ischaemic stroke: a systematic review with pathophysiological implications. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 86(1):87–94
Duan Z, Fu C, Chen B, Xu G, Tao L, Tang T, Hou H, Fu X, Yang M, Liu Z, Zhang X (2015) Lesion patterns of single small subcortical infarct and its association with early neurological deterioration. Neurol Sci 36(10):1851–1857
Siegler JE, Martin-Schild S (2011) Early neurological deterioration (END) after stroke: the END depends on the definition. Int J Stroke 6(3):211–212
Availability of data and materials
The data sets during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81601015) and Beijing Talents Fund (2015000021469G220).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mi, D., Wang, Y., Wang, Y. et al. Insulin resistance is an independent risk factor for early neurological deterioration in non-diabetic patients with acute ischemic stroke. Neurol Sci 41, 1467–1473 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-019-04221-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-019-04221-7