Abstract
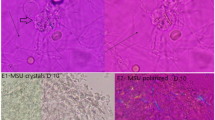
The aim of this study was to evaluate dried SF cytospin preparations as a suitable medium for long-time storage and delayed crystal analysis. For this purpose, we analyzed ten MSU-positive, ten CPPD-positive and 20 crystal-negative SF at baseline (wet preparation), after 24 h, 1 week, 4 weeks, 6 months and 12 months for the occurrence of crystals. After cytocentrifugation for 10 min at 700 rpm in a Shandon Cytospin 4 cytocentrifuge (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, USA), the sediments were dried on the slides and examined in blinded fashion at any time point by an experienced analyst using polarized microscopy. The crystal content of the initially MSU- and CPPD-positive samples was positively confirmed at any time point of the study, whereas the controls remained crystal-negative during the whole study period. Thus, compared to the examined wet preparations at baseline, there were no false positive or false negative results observed. In conclusion, dried cytospin preparations were confirmed as a suitable material for long-time storage and delayed crystal identification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kerolus G, Clayburne G, Schumacher HR Jr (1989) Is it mandatory to examine synovial fluids promptly after arthrocentesis? Arthritis Rheum 34(1):118–20
Robier C, Neubauer M, Stettin M, Rainer F (2011) Microscopic examination of stained cytospin preparations is a reliable method for the detection of calcium pyrophosphate crystals in synovial fluid. Scand J Rheumatol 40(5):406–7, Epub 2011 Aug. 8
Galvez J, Saiz E, Linares LF, Climent A, Marras C, Pina MF et al (2002) Delayed examination of synovial fluid by ordinary and polarised microscopy to detect and identify crystals. Ann Rheum Dis 61:444–7
Salinas M, Rosas J, Iborra J, Manero H, Pascual E (1997) Comparison of manual and automated cell counts in EDTA preserved synovial fluids. Storage has little influence on the results. Ann Rheum Dis 56:622–6
McGill NW, Swan A, Dieppe PA (1991) Survival of calcium pyrophosphate crystals in stored synovial fluids. Ann Rheum Dis 50:939–41
Selvi E, Manganelli S, Catenaccio M, De Stefano R, Frati E, Cucini S et al (2001) Diff Quik staining method for detection and identification of monosodium urate and calcium pyrophosphate crystals in synovial fluids. Ann Rheum Dis 60:194–8
Petrocelli A, Wong AL, Swezey RL (1998) Identification of pathologic synovial fluid crystals on gram stains. J Clin Rheumatol 4(2):103–4
Gordon C, Swan A, Dieppe P (1989) Detection of crystals in synovial fluids by light microscopy: sensitivity and reliability. Ann Rheum Dis 48:737–42
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the haematology team of the Central Laboratory of the Hospital Barmherzige Brueder Graz-Eggenberg for the excellent technical support.
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robier, C., Neubauer, M., Stettin, M. et al. Dried cytospin preparations of synovial fluid are a stable material for long-time storage and delayed crystal analysis. Clin Rheumatol 31, 1115–1116 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-012-1967-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-012-1967-7