Abstract
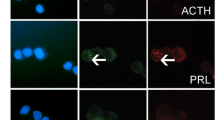
Retinoic acid (RA) plays a critical role in normal development and tissue maintenance and is also a regulatory factor of anterior pituitary cells. We previously demonstrated that a retinoic acid-synthesizing enzyme, retinaldehyde dehydrogenase 1 (RALDH1), is expressed in prolactin cells of adult rats and that estrogen suppressed RALDH1 expression. It is suggested that RA plays a role as a paracrine and/or autocrine signaling molecule in the anterior pituitary gland. However, the presence of RALDH1 in pituitary tumors has not been demonstrated. In this study, we examined the expression of RALDH1 in diethylstilbestrol-induced prolactinoma of LEXF RI rats. Quantitative analysis of mRNA levels by real-time PCR demonstrated drastic reduction of RALDH1 expression in the prolactinoma. We have also detected both mRNA expression and production by in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry. Both mRNA-expressing cells and immunopositive cells remarkably decreased after 4 weeks of treatment with diethylstilbestrol. Fluorescence double immunohistochemistry of RALDH1 and prolactin revealed that prolactin-immunopositive cells do not colocalize with RALDH1 in the prolactinoma. These results suggest that the reduction of local RA generation relates to cell proliferation and tumorigenesis of lactotrophs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen LE, Zanger K, Brue T, Wondisford FE, Radovick S (1999) Defective retinoic acid regulation of the Pit-1 gene enhancer: a novel mechanism of combined pituitary hormone deficiency. Mol Endocrinol 13:476–484
Bedo G, Santisteban P, Aranda A (1989) Retinoic acid regulates growth hormone gene expression. Nature (Lond) 339:231–234
Mogi C, Goda H, Mogi K, Takaki A, Yokoyama K, Tomida M, Inoue K (2005) Multistep differentiation of GH-producing cells from their immature cells. J Endocrinol 184:41–50
Duester G (2000) Families of retinoid dehydrogenases regulating vitamin A function: production of visual pigment and retinoic acid. Eur J Biochem 267:4315–4432
Fujiwara K, Maekawa F, Kikuchi M, Takigami S, Yada T, Yashiro T (2007) Expression of retinaldehyde dehydrogenase (RALDH)2 and RALDH3 but not RALDH1 in the developing anterior pituitary glands of rats. Cell Tissue Res 328:129–135
Fujiwara K, Kikuchi M, Takigami S, Kouki T, Yashiro T (2007) Expression of retinaldehyde dehydrogenase 1 in the anterior pituitary glands of adult rats. Cell Tissue Res 329:321–327
Sarkar DK (2006) Genesis of prolactinomas: studies using estrogen-treated animals. Front Horm Res 35:32–49
De Nicola AF, von Lawzewitsch I, Kaplan SE, Libertun C (1978) Biochemical and ultrastructural studies on estrogen-induced pituitary tumors in F344 rats. J Natl Cancer Inst 61:753–763
Holtzman S, Stone JP, Shellabarger CJ (1979) Influence of diethylstilbestrol treatment on prolactin cells of female ACI and Sprague-Dawley rats. Cancer Res 39:779–784
Fujiwara K, Davaadash B, Kikuchi M, Takigami S, Yashiro T (2008) Estrogen suppresses retinaldehyde dehydrogenase 1 expression in the anterior pituitary glands of female rats. Endocr J 55:91–96
Tachibana M, Lu L, Hiai H, Tamura A, Matsushima Y, Shisa H (2006) Quantitative trait loci determining weight reduction of testes and pituitary by diethylstilbesterol in LEXF and FXLE recombinant inbred strain rats. Exp Anim 55:91–95
Momose K, Nunomiya S, Nakata M, Yada T, Kikuchi M, Yashiro T (2006) Immunohistochemical and electron-microscopic observation of beta-cells in pancreatic islets of spontaneously diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. Med Mol Morphol 39:146–153
Kikuchi M, Yatabe M, Fujiwara K, Takigami S, Sakamoto A, Soji T, Yashiro T (2006) Distinctive localization of N-and E-cadherins in rat anterior pituitary gland. Anat Rec A Disc Mol Cell Evol Biol 288A:1183–1189
Shisa H, Lu L, Katoh H, Kawarai A, Tanuma J, Matsushima Y, Hiai H (1997) The LEXF: a new set of rat recombinant inbred strains between LE/Stm and F344. Mamm Genome 8:324–327
Nogami H, Matsubara M, Harigaya T, Katayama M, Kawamura K (2000) Retinoic acids and thyroid hormone act synergistically with dexamethasone to increase growth hormone-releasing hormone receptor messenger ribonucleic acid expression. Endocrinology 141:4396–4401
Breen JJ, Matsuura T, Ross AC, Gurr JA (1995) Regulation of thyroid-stimulating hormone beta-subunit and growth hormone messenger ribonucleic acid levels in the rat: effect of vitamin A status. Endocrinology 136:543–549
Breen JJ, Hickok NJ, Gurr JA (1997) The rat TSH-beta gene contains distinct response elements for regulation by retinoids and thyroid hormone. Mol Cell Endocrinol 131:137–146
Angioni AR, Lania A, Cattaneo A, Beck-Peccoz P, Spada A (2005) Effects of chronic retinoid administration on pituitary function. J Endocrinol Invest 28:961–964
Samad TA, Krezel W, Chambon P, Borrelli E (1997) Regulation of dopaminergic pathways by retinoids: activation of the D2 receptor promoter by members of the retinoic acid receptorretinoid X receptor family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:14349–14354
Jaber M, Robinson SW, Missale C, Caron MG (1996) Dopamine receptors and brain function. Neuropharmacology 35:1503–1519
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujiwara, K., Davaadash, B., Yatabe, M. et al. Reduction of retinaldehyde dehydrogenase 1 expression and production in estrogen-induced prolactinoma of rat. Med Mol Morphol 41, 126–131 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-008-0411-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-008-0411-1