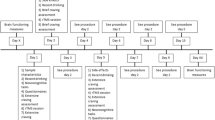
Abstract
Alcohol craving has been shown to be an important factor for relapses in alcohol-dependent patients. Furthermore, brain activity in reward-related areas in response to alcohol-related cues is positively related to the amount of post-relapse alcohol consumption. On the other hand, it has been shown that cue-exposure based extinction training (CET) leads to larger decrease of striatal and left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dLPFC) cue-induced activation compared to standard clinical day-care treatment, but the effect sizes are relatively small. The question of this study was, whether it is possible to change cue-reactivity and subjective craving by applying bilateral prefrontal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS). We stimulated 30 detoxified alcohol-dependent patients (50 % with a sham and 50 % with left cathodal/right anodal stimulation) and presented emotional as well as alcohol-related pictures. We measured the emotional startle modulation and found significantly increased startle amplitudes in the verum stimulation condition for alcohol-related cues, indicating a more negative processing of this cues in alcohol-dependent patients after verum tDCS stimulation. Additionally we found tendencies for stronger reduction in subjective craving in verum-stimulated patients. Therefore our study underscores the positive value of DCS in reducing craving and might help to improve the understanding and therapy of alcohol dependence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asthana M et al (2013) Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation on consolidation of fear memory. Front Psychiatry 4:107
Bellaiche L, Asthana M, Ehlis AC, Polak T, Herrmann MJ (2013) The modulation of error processing in the medial frontal cortex by transcranial direct current stimulation. Neurosc J 2013:187692
Blumenthal TD et al (2005) Committee report: guidelines for human startle eyeblink electromyographic studies. Psychophysiology 42:1–15
Bradley MM, Lang PJ (1994) Measuring emotion: the self-assessment manikin and the semantic differential. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry 25:49–59
Chick J, Howlett H, Morgan MY, Ritson B (2000) United Kingdom Multicentre Acamprosate Study (UKMAS): a 6-month prospective study of acamprosate versus placebo in preventing relapse after withdrawal from alcohol. Alcohol Alcohol 35:176–187
Conson M et al (2015) Transcranial electrical stimulation over dorsolateral prefrontal cortex modulates processing of social cognitive and affective information. PLoS One 10:e0126448
Feeser M, Prehn K, Kazzer P, Mungee A, Bajbouj M (2014) Transcranial direct current stimulation enhances cognitive control during emotion regulation. Brain Stimul 7:105–112
George MS et al (2001) Activation of prefrontal cortex and anterior thalamus in alcoholic subjects on exposure to alcohol-specific cues. Arch Gen Psychiatry 58:345–352
Grusser SM, Heinz A, Flor H (2000) Standardized stimuli to assess drug craving and drug memory in addicts. J Neural Transm 107:715–720
Hayashi T, Ko JH, Strafella AP, Dagher A (2013) Dorsolateral prefrontal and orbitofrontal cortex interactions during self-control of cigarette craving. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:4422–4427
Jansen JM et al (2013) Effects of non-invasive neurostimulation on craving: a meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37:2472–2480
Jasinska AJ, Stein EA, Kaiser J, Naumer MJ, Yalachkov Y (2014) Factors modulating neural reactivity to drug cues in addiction: a survey of human neuroimaging studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 38:1–16
John U, Hapke U, Rumpf HJ (2001) SESA: Skala zur Erfassung der Schwere der Alkoholabhängigkeit. Hogrefe, Göttingen
Kessing LV (2015) Course and cognitive outcome in major affective disorder. Dan Med J 62(11):B5160
Klauss J et al (2014) A randomized controlled trial of targeted prefrontal cortex modulation with tDCS in patients with alcohol dependence. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 17:1793–1803
Lang PJ, Bradley MM, Cuthbert BN (2008) International affective picture system (IAPS): affective ratings of pictures and instruction manual. Technical Report A-8. University of Florida, Gainesville
Laux L, GP, Schaffner P, Spielberger CD (1981) State-Trait-Angst Inventar STAI. Beltz, Weinheim
McBride D, Barrett SP, Kelly JT, Aw A, Dagher A (2006) Effects of expectancy and abstinence on the neural response to smoking cues in cigarette smokers: an fMRI study. Neuropsychopharmacol Off Publ Am Coll Neuropsychopharmacol 31:2728–2738
Mucha RF, Geier A, Stuhlinger M, Mundle G (2000) Appetitive effects of drug cues modelled by pictures of the intake ritual: generality of cue-modulated startle examined with inpatient alcoholics. Psychopharmacology 151:428–432
Radloff L (1977) The CES-D Scale: a self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl Psychol Meas 3:385–401
Rubio G et al (2013) Variables involved in the cue modulation of the startle reflex in alcohol-dependent patients. Addict Biol 18:170–180
Vierheilig N, Mühlberger A, Polak T, Herrmann MJ (2016) Transcranial direct current stimulation of the prefrontal cortex increases attention to visual target stimuli. J Neural Transm. doi:10.1007/s00702-016-1542-5
Watson D, Clark LA, Tellegen A (1988) Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. J Pers Soc Psychol 54:1063–1070
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wietschorke, K., Lippold, J., Jacob, C. et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation of the prefrontal cortex reduces cue-reactivity in alcohol-dependent patients. J Neural Transm 123, 1173–1178 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-016-1541-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-016-1541-6