Abstract
Background
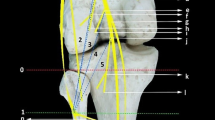
This study was performed to evaluate the clinical effect of translocating the soleus muscular branch of the tibial nerve to repair the deep peroneal nerve.
Methods
Eight patients were treated for high common peroneal nerve injury. The deep peroneal nerve was separated out from the common peroneal nerve if no injury occurred upon opening the epineurium of the common peroneal nerve. The soleus muscular branch of the tibial nerve was then translocated to the deep peroneal nerve.
Results
The average follow-up duration was 21.75 months. Electromyography revealed newly appearing electric potentials in the tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, and extensor toe longus muscle at 8 to 10 months postoperatively. Four patients showed good functional recovery after surgery; functional recovery was poor in other patients.
Conclusions
Translocation of the soleus muscle branch is a feasible method to treat high common peroneal nerve injuries. A full understanding of the indications for this operation is required.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertelli JA (2015) Transfer of the radial nerve branch to the extensor carpi radialis brevis to the anterior interosseous nerve to reconstruct thumb and finger flexion. J Hand Surg [Am] 40:323–328
Bodily KD, Spinner RJ, Bishop AT (2010) Restoration of motor function of the deep fibular (peroneal) nerve by direct nerve transfer of branches from the tibial nerve: an anatomical study. Clin Anat 17:201–205
Cai Y, Hou C (2015) A feasibility study on transposition of proximal motor branch from tibial nerve to reconstruct deep fibular nerve. Chin Reparat Reconstruct Surg 29:58–62 [Article in Chinese]
Chen HH, Zong HY, Meng DP, Cai YW, Hou CL, Lin HD (2018) Experimental study on repairmen of high deep peroneal nerve injury by nerve transposition methods using different proximal tibial nerve muscular branches. Chin J Microsurg 41:57–61 [Article in Chinese]
Cho BK, Park KJ, Choi SM, Im SH, SooHoo NF (2017) Functional outcomes following anterior transfer of the tibialis posterior tendon for foot drop secondary to nerve palsy. Foot Ankle Int 38:627–633
Chotigavanich C (1990) Tendon transfer for radial nerve palsy. Bull Hosp Jt Dis Orthop Inst 50:1–10
Cornwall R, Radomisli TE (2000) Nerve injury in traumatic dislocation of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res 377:84–91
de Bruijn IL, Geertzen JH, Dijkstra PU (2007) Functional outcome after peroneal nerve injury. Int J Rehabil Res 30:333–337
Flores LP (2009) Proximal motor branches from the tibial nerve as direct donors to restore function of the deep fibular nerve for treatment of high sciatic nerve injuries: a cadaveric feasibility study. Neurosurgery 65:218–224
Flores LP, Martins RS, Siqueira MG (2013) Clinical results of transferring a motor branch of the tibial nerve to the deep peroneal nerve for treatment of foot drop. Neurosurgery 73:615–616
Forli A, Bouyer M, Aribert M, Curvale C, Delord M, Corcella D, Moutet F (2017) Upper limb nerve transfers: a review. Hand Surg Rehabil 36:151–172
George SC, Boyce DE (2014) An evidence-based structured review to assess the results of common peroneal nerve repair. Plast Reconstr Surg 134:302e–311e
Giuffre JL, Bishop AT, Spinner RJ, Levy BA, Shin AY (2012) Partial tibial nerve transfer to the tibialis anterior motor branch to treat peroneal nerve injury after knee trauma. Clin Orthop Relat Res 470:779–790
Gousheh J, Babaei A (2002) A new surgical technique for the treatment of high common peroneal nerve palsy. Plast Reconstr Surg 109:994–998
Hamdan FB, Jaffar AA, Ossi RG (2008) The propensity of common peroneal nerve in thigh-level injuries. Trauma 64:300–303
Hohmann E, Wansbrough G, Senewiratne S, Tetsworth K (2016) Medial gastrocnemius flap for reconstruction of the extensor mechanism of the knee following high-energy trauma. Minimum 5 year follow-up. Injury 47:1750–1755
Houschyar KS, Momeni A, Pyles MN, Cha JY, Maan ZN, Duscher D, Jew OS, Siemers F, van Schoonhoven J (2016) The role of current techniques and concepts in peripheral nerve repair. Plast Surg Int 2016:4175293
Kim DH, Murovic JA, Tiel R, Kline DG (2004) Management and outcomes in 353 surgically treated sciatic nerve lesions. J Neurosurg 101:8–17
Kline DG, Kim D, Midha R, Harsh C, Tiel R (1998) Management and results of sciatic nerve injuries: a 24-year experience. J Neurosurg 89:13–23
Leclère FM, Badur N, Mathys L, Vögelin E (2015) Nerve transfers for persistent traumatic peroneal nerve palsy: the Inselspital Bern experience. Neurosurgery 77:572–580
Mackinnon SE (2016) Donor distal, recipient proximal and other personal perspectives on nerve transfers. Hand Clin 32:141–151
Mackinnon SE, Colbert SH (2008) Nerve transfers in the hand and upper extremity surgery. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg 12:20–33
Millesi H (2007) Surgery on muscles in consequence of peripheral nerve lesions. Acta Neurochir Suppl 100:179–181
Mohanty CB, Bhat D, Devi BI (2015) Role of central plasticity in the outcome of peripheral nerve regeneration. Neurosurgery 77:418–423
Molund M, Engebretsen L, Hvaal K, Hellesnes J, Ellingsen Husebye E (2014) Posterior tibial tendon transfer improves function for foot drop after knee dislocation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472:2637–2643
Movahedi Yeganeh M (2016) Triple tendon transfer for correction of foot deformity in common peroneal nerve palsy. Foot Ankle Int 37:665–669
Nath RK, Somasundaram C (2017) Gait improvements after peroneal or tibial nerve transfer in patients with foot drop: a retrospective study. Eplasty 17:e31
Nath RK, Lyons AB, Paizi M (2008) Successful management of foot drop by nerve transfers to the deep peroneal nerve. J Reconstr Microsurg 24:419–427
Park JW, Lee YS, Oh JK, Park JH, Lee JW, Park JS (2009) Knee extensor mechanism reconstruction with an extended gastrocnemius flap and a saphenous neurocutaneous flap. Orthop Trauma 23:309–12g
Rhomberg M, Schwabegger AH, Ninkovic M, Bauer T, Ninkovic M (2000) Gastrocnemius myotendinous flap for patellar or quadriceps tendon repair, or both. Clin Orthop Relat Res:152–160
Richard BM (1989) Interosseous transfer of tibialis posterior for common peroneal nerve palsy. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 71:834–837
Socolovsky M, Malessy M, Lopez D, Guedes F, Flores L (2017) Current concepts in plasticity and nerve transfers: relationship between surgical techniques and outcomes. Neurosurg Focus 42:E13
Steinau HU, Tofaute A, Huellmann K, Goertz O, Lehnhardt M, Kammler J, Steinstraesser L, Daigeler A (2011) Tendon transfers for drop foot correction: long-term results including quality of life assessment, and dynamometric and pedobarographic measurements. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 131:903–910
Vloka JD, Hadzić A, Lesser JB (1997) A common epineural sheath for the nerves in the popliteal fossa and its possible implications for sciatic nerve block. Anesth Analg 9:387–390
Funding
This study was supported by the Key Project of the Health and family Planning Commission of shanghai (grant number 201440510) and the Project of Research doctor of Changzheng Hospital (grant number 201712).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee (Guilan University of Medical Sciences) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from the patients.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Comments
This article describes a technique using a nerve transfer using a tibial branch to the soleus muscle to restore peroneal nerve function mediating the important function of foot dorsiflexion. This transfer is particularly useful in the setting of proximal peroneal nerve injuries where tribal nerve function is 5/5. Although such a transfer involves activating antagonistic muscles in terms of function, over time the patient learns to selectively activate the muscles so as to produce useful foot dorsiflexion. This technique is another useful addition to the peripheral nerve’s toolkit box.
Michel Kliot
California, USA
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Peripheral Nerves
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Meng, D., Yin, G. et al. Translocation of the soleus muscular branch of the tibial nerve to repair high common peroneal nerve injury. Acta Neurochir 161, 271–277 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-018-03797-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-018-03797-x