Abstract
Objective
Carotid artery stenting (CAS) is a well-accepted treatment for atherosclerotic stenosis of carotid arteries. Since the occurrence of distal embolization with CAS is still a major concern embolus protection devices (EPD) are usually employed during the procedure. We examined two types of embolus protection filters (Angioguard XP (AG); Filterwire EZ (FW)) and evaluated the function. Thus, the filter was examined postoperatively and the cause of intraoperative flow impairment was evaluated.
Materials and methods
CAS was performed for 54 patients with carotid artery stenosis (55 lesions: 25 AG; 27 FW; 3 others). After completing CAS the filter membrane was stained with hematoxylin-eosin (HE) solution and removed from the filter strut. Once mounted on a glass slide the filter was evaluated under a microscope. The area occupied with debris was measured and the relationship to intraoperative flow impairment was evaluated. Furthermore, the relationship between perioperative ischemic complications and intraoperative flow impairment was statistically analyzed.
Results
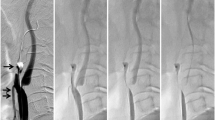
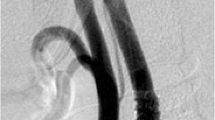
Microscopic observation of the slide revealed the pore density of the FW was 1.5 times higher than that of the AG and the filter area of the FW was 2.5 times wider than than the AG. HE staining facilitated characterization of the debris composition. The area occupied with debris was significantly more in the AG (0.241 ±0.13 cm2) than in the FW (0.129 ±0.093 cm2). Thus, fibrin was significantly more precipitated in the AG. Flow impairment occurred in 6 AG cases (24.0 %) and 4 FW cases (14.8 %). It was induced by filter obstruction in the AG and by vasospasms in the FW. Three cases treated with AG (12.0 %) were complicated with cerebral infarction and all of them were related to flow impairment. One FW case (3.7 %) was complicated with cerebral infarction in presence of preserved flow throughout the intervention.
Conclusion
Filter function is different according to each design. The cause of flow impairment was attributable to filter obstruction in the AG group and to vasospasms in the FW group. Filter obstruction tends to result in cerebral infarction.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelini A, Reimers B, Della Barbera M, Saccà S, Pasquetto G, Cernetti C, Valente M, Pascotto P, Thiene G (2002) Cerebral protection during carotid artery stenting: collection and histopathologic analysis of embolized debris. Stroke 33:456–461
Casserly IP, Abou-Chebl A, Fathi RB, Lee DS, Saw J, Exaire JE, Kapadia SR, Bajzer CT, Yadav JS (2005) Slow-flow phenomenon during carotid artery intervention with embolic protection devices: predictors and clinical outcome. J Am Coll Cardiol 46:1466–1472
Hayashi K, Kitagawa N, Morikawa M (2005) Observing the carotid debris aspirated during carotid stenting: technical note. Neurol Res 27:22–26
Hayashi K, Kitagawa N, Morikawa M, Hiu T, Morofuji Y, Suyama K, Nagata I (2009) Observation of the embolus protection filter for carotid artery stenting. Surg Neurol 72:532–537
Honda M, Kitagawa N, Tsutsumi K, Nagata I, Morikawa M, Hayashi T (2006) High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging for detection of carotid plaques. Neurosurgery 58:338–346
Horie N, Morikawa M, Ishizaka S, Takeshita T, So G, Hayashi K, Suyama K, Nagata I (2012) Assessment of carotid plaque stability based on the dynamic enhancement pattern in plaque components with multidetector CT angiography. Stroke 43:393–398
Iyer V, de Donato G, Deloose K, Peeters P, Castriota F, Cremonesi A, Setacci C, Bosiers M (2007) The type of embolic protection does not influence the outcome in carotid artery stenting. J Vasc Surg 46:251–256
Kawahara I, Morikawa M, Nakamoto M, Kitagawa N, Tsutsumi K, Nagata I (2007) Evaluation of carotid artery plaque volume using high-resolution MRI. Jpn J Stroke 29:29–37
Kwon BJ, Han MH, Kang HS, Jung C (2006) Protection filter-related events in extracranial carotid artery stenting: a single-center experience. J Endovasc Ther 13:711–722
Kwon OK, Kim SH, Jacobsen EA, Marks MP (2012) Clinical implications of internal carotid artery flow impairment caused by filter occlusion during carotid artery stenting. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:494–499
Loghmanpour NA, Siewiorek GM, Wanamaker KM, Muluk SC, Chaer R, Wholey MH, Finol EA (2013) Assessing the impact of distal protection filter design characteristics on 30-day outcomes of carotid artery stenting procedures. J Vasc Surg 57:309–317
Maleux G, Demaerel P, Verbeken E, Daenens K, Heye S, Van Sonhoven F, Nevelsteen A, Wilms G (2006) Cerebral ischemia after filter-protected carotid artery stenting is common and cannot be predicted by the presence of substantial amount of debris captured by the filter device. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1830–1833
Mas JL, Chatellier G, Beyssen B, Branchereau A, Moulin T, Becquemin JP, Larrue V, Lièvre M, Leys D, Bonneville JF, Watelet J, Pruvo JP, Albucher JF, Viguier A, Piquet P, Garnier P, Viader F, Touzé E, Giroud M, Hosseini H, Pillet JC, Favrole P, Neau JP, Ducrocq X, EVA-3S Investigators (2006) Endarterectomy versus stenting in patients with symptomatic severe carotid stenosis. N Engl J Med 355:1660–1671
Powell RJ, Alessi C, Nolan B, Rzucidlo E, Fillinger M, Walsh D, Wyers M, Zwolak R, Cronenwett JL (2006) Comparison of embolization protection device-specific technical difficulties during carotid artery stenting. J Vasc Surg 44:56–61
Roffi M, Greutmann M, Schwarz U, Luscher TF, Eberli FR, Amann-Vesti B (2008) Flow impairment during protected carotid artery stenting: impact of filter device design. J Endovasc Ther 15:103–109
Roffi M, Yadav JS (2006) Carotid stenting. Circulation 114:e1–e4
Sakamoto M, Taoka T, Nakagawa H, Takayama K, Wada T, Myouchin K, Akashi T, Miyasaka T, Fukusumi A, Iwasaki S, Kichikawa K (2010) Magnetic resonance plaque imaging to predict the occurrence of the slow-flow phenomenon in carotid artery stenting procedures. Neuroradiology 52:275–283
Schönholz CJ, Uflacker R, Mendaro E, Parodi JC, Guimaraes M, Hannegan C, Selby B (2005) Techniques for carotid artery stenting under cerebral protection. J Cardiovasc Surg 46:201–217
Ringleb PA, Allenberg J, Brückmann H, Eckstein HH, Fraedrich G, Hartmann M, Hennerici M, Jansen O, Klein G, Kunze A, Marx P, Niederkorn K, Schmiedt W, Solymosi L, Stingele R, Zeumer H, Hacke W, SPACE Collaborative Group (2006) 30 day results from the SPACE trial of stent-protected angioplasty versus carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients: a randomised non-inferiority trial. Lancet 368:1239–1247
Yadav JS, Wholey MH, Kuntz RE, Fayad P, Katzen BT, Mishkel GJ, Bajwa TK, Whitlow P, Strickman NE, Jaff MR, Popma JJ, Snead DB, Cutlip DE, Firth BG, Ouriel K (2004) Protected carotid-artery stenting versus endarterectomy in high-risk patients. N Engl J Med 351:1493–1501
Disclosure
None.
Source of funding
No
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayashi, K., Horie, N., Morikawa, M. et al. Pathophysiology of flow impairment during carotid artery stenting with an embolus protection filter. Acta Neurochir 156, 1721–1728 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-014-2180-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-014-2180-z