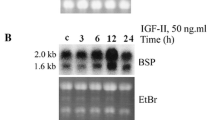
Abstract
The insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system is an important regulator of bone formation. The IGFs (IGF-I and IGF-II) are the most abundant growth factors produced by bone, and are regulated by their six high affinity binding proteins (IGFBPs). The IGFBPs are produced by osteoblasts and are responsible for transporting the IGFs and extending their half-lives. In general, IGFBP-1, -2, -4, and -6 inhibit and IGFBP-3 and –5 stimulate osteoblast function. IGFBP-4 and -5 are the most abundant IGFBPs produced by osteoblasts, and therefore they are the primary focus of this review. IGFBP-5 is an important stimulator of bone formation and may also function independently of IGFs. IGFBP-4 inhibits osteoblast function by sequestering IGF and preventing it from binding to its receptor. This review focuses on the specific IGF-dependent and IGF-independent roles of the IGFBPs in bone formation, as well as their potential mechanisms of action. In addition, discussion of the regulation of the IGFBPs by post-translational modification (i.e., proteolysis) has been included. Studies on the regulation of production and actions of IGFBPs suggest that the IGFBP system in bone is pleiotropic and capable of serving multiple effector inputs from systemic and local sources.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mohan S, Richman C, Guo R, Amaar Y, Donahue LR, Wergedal J, Baylink DJ (2003) Insulin-like growth factor regulates peak bone mineral density in mice by both growth hormone-dependent and –independent mechanisms. Endocrinology 144:929–936
Woods KA, Camacho-Hübner C, Savage MO, Clark A (1996) Intrauterine growth retardation and postnatal growth failure associated with deletion of the insulin-like growth factor I gene. N Engl J Med 335:1363–1367
Pereira Arias A, Walenkamp M-J, Hilhorst-Hofstee Y, Karperien M, Van Duyvenvoorde H, Bax J, Doorn J van, Romijn JA, Wit J-M (2003) Clinical and biochemical expression of a homozygous missense mutation in the IGF-1 gene (abstract). Abstracts of the 85th Annual Endocrine Society Meeting, Philadelphia
Walenkamp M-J, Pereira Arias A, Sluimers C, Hilhorst-Hofstee Y, Thiel S van, Karperien M, Duyvenvoorde H van, Laat J de, Doorn J van, Romijn J, Wit J-M (2003) Heterozygosity for a missense mutation (V44 M) in the IGF-I gene leads to a lower height and head circumference and a higher plasma IGF-I than observed in non-carriers (abstract). Abstracts of the 85th Annual Endocrine Society Meeting, Philadelphia
Mohan S, Baylink DJ (1999) Role of growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor axis. In: Rosen CJ, Glowacki J, Bilezikian J (eds) The aging skeleton. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 195–204
Liu JP, Baker J, Perkins AS, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A (1993) Mice carrying null mutations of the genes encoding insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and type 1 IGF receptor (IGFr). Cell 75:59–72
Baker J, Liu JP, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A (1993) Role of insulin-like growth factors in embryonic and postnatal growth. Cell 75:73–82
Yakar, S, Liu J, Stannard B, Butler A, Accili D, Sauer B, LeRoith D (1999) Normal growth and development in the absence of hepatic insulin-like growth factor I. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:7324–7329
Yakar S, Rosen CJ, Beamer WG, Ackert-Bicknell CL, Wu Y, Liu J, Ooi GT, Setser J, Frystyk J, Boisclair YR, LeRoith D (2002) Circulating levels of IGF-I directly regulate bone growth and density. J Clin Invest 110:771–781
Mohan S, Baylink DJ (1996) Insulin-like growth factor system components and the coupling of bone formation to resorption. Horm Res 45 [Suppl 1]:59–66
Rosen CJ, Donahue LR (1998) Insulin-like growth factors and bone: the osteoporosis connection revisited. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 219:1–7
Mohan S, Baylink DJ (1997) Serum insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-4 and IGFBP-5 levels in aging and age-associated diseases. Endocrine 7:87–91
Boonen S, Mohan S, Dequeker J, Aerssens J, Vanderschueren D, Verbeke G, Broos P, Bouillon R, Baylink DJ (1999) Down-regulation of the serum stimulatory components of the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system (IGF-I, IGF-II, IGF binding protein [BP]-3, and IGFBP-5) in age-related (type II) femoral neck osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 14:2150–2158
Amaar YG, Thompson GR, Linkhart TA, Chen ST, Baylink DJ, Mohan S (2002) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 (IGFBP-5) interacts with a four and a half LIM protein 2 (FHL2). J Biol Chem 277:12053–12060
Firth SM, Baxter RC (2002) Cellular actions of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr Rev 23:824–854
Qin X, Strong DD, Baylink DJ, Mohan S (1998) Structure-function analysis of the human insulin-like growth factor binding protein-4. J Biol Chem 273:23509–23516
Rajaram S, Baylink DJ, Mohan S (1997) Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins in serum and other biological fluids: regulation and functions. Endocr Rev 18:801–831
Conover CA (1996) Regulation and physiological role of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr J 43 [Suppl]:S43–S48
Jones JI, Clemmons DR (1995) Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocr Rev. 16:3–34
Mohan S, Baylink DJ (2002) IGF binding proteins are multifunctional and act via IGF-dependent and IGF-independent mechanisms. J Endocrinol 175:19–31
Rechler MM (1993) Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Vitam Horm 47:1–114
Miyakoshi N, Richman C, Qin X, Baylink DJ, Mohan S (1999) Effects of recombinant insulin-like growth factor binding protein-4 on bone formation parameters in mice. Endocrinology 140:5719–5728
Mohan S, Nakao Y, Honda Y, Landale E, Leser U, Dony C, Lang K, Baylink DJ (1995) Studies on the mechanisms by which insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP-4) and IGFBP-5 modulate IGF actions in bone cells. J Biol Chem 270:20424–20431
Jones JI, Gockerman A, Busby WH Jr, Wright G, Clemmons DR (1993) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 stimulates cell migration and binds to the alpha 5 beta 1 integrin by means of its Arg-Gly-Asp sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10553–10557
Gleeson LM, Chakraborty C, McKinnon T, Lala PK (2001) Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 1 stimulates human trophoblast migration by signaling through alpha 5 beta 1 integrin via mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:2484–2493
Richman C, Baylink DJ, Lang K, Dony C, Mohan S (1999) Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 (rhIGFBP-5) stimulates bone formation parameters in vitro and in vivo. Endocrinology 140:4699–4705
Miyakoshi N, Richman C, Kasukawa Y, Linkhart TA, Baylink DJB, Mohan S (2001) Evidence that IGF-binding protein-5 functions as a growth factor. J Clin Invest 107:73–81
Silha JV, Mishra S, Rosen CJ, Beamer WG, Turner RT, Powell DR, Murphy LJ (2003) Perturbations in bone formation and resorption in insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 transgenic mice. J Bone Miner Res 18:1834–1841
Kanatani M, Sugimoto T, Mishiyama K, Chihara K (2000) Stimulatory effect of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 on mouse osteoblast formation and osteoclastic bone-resorbing activity. J Bone Miner Res 15:902–910
Jehle P, Schulten K, Jehle DR, Stracke S, Manfras B, Boehm B, Baylink DJ, Mohan S (2003) Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF binding protein (IGFBP) 1 through 6 and relationship to bone metabolism in osteoporosis patients. Eur J Intern Med 14:32–38
Bautista CM, Baylink DJ, Mohan S (1991) Isolation of a novel insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein from human bone: a potential candidate for fixing IGF-II in human bone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 176:756–763
Nicolas V, Mohan S, Honda Y, Prewett A, Finkelman RD, Baylink DJ, Farley JR (1995) An age-related decrease in the concentration of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 in human cortical bone. Calcif Tissue Int 57:206–212
Andress DL (1998) Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-5 (IGFBP-5) stimulates phosphorylation of the IGFBP-5 receptor. Am J Physiol 274:E744–E750
Delvin RD, Du Z, Buccilli V, Jogetti V, Canalis E (2002) Transgenic mice overexpressing insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 display transiently decreased osteoblastic function and osteopenia. Endocrinology 143:3955–3962
Andress DL (2001) IGF-binding protein-5 stimulates osteoblast activity and bone accretion in ovariectomized mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 218:E283–E288
Bauss F, Lang K, Dony C, Kling L (2001) The complex of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-I (rhIGF-I) and its binding protein-5 (IGFBP-5) induces local bone formation in murine calvariae and in rat cortical bone after local or systemic administration. Growth Horm IGF Res 11:1–9
Lotinun S, Sibonga JD, Turner T (2002) Differential effects of intermittent and continuous administration of parathyroid hormone on bone histomorphometry and gene expression. Endocrine 17:29–36
Schedlich LJ, Young TF, Firth SM, Baxter RC (1998) Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP)-3 and IGFBP-5 share a common nuclear transport pathway in T47D human breast carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 273:18347–18352
Schedlich LJ, Le Page SL, Firth SM, Briggs JL, Jans DA, Baxter RC (2000) Nuclear import of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 and −5 is mediated by the importin beta subunit. J Biol Chem 275:23462–23470
Mohan S, Thompson GR, Amaar YG, Hathaway G, Tschesche H, Baylink DJ (2002) ADAM-9 is an insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 protease produced and secreted by human osteoblasts. Biochemistry 41:15394–15403
Andress DL, Loop SM, Zapf J, Kiefer MC (1993) Carboxy-truncated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 stimulates mitogenesis in osteoblast-like cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 195:25–30
Zhang, M, Faugere MC, Malluche H, Rosen CJ, Chernausek SD, Clemens TL (2003) Paracrine overexpression of IGFBP-4 in osteoblasts of transgenic mice decreases bone turnover and causes global growth retardation. J Bone Miner Res 18:836–843
Miyakoshi N, Qin X, Richman C, Srivastava AK, Baylink DJ, Mohan S (2001) Studies on the mechanism by which systemically administered insulin-like growth factor binding protein-4 increases bone formation parameters in mice. Endocrinology 142:2641–2648
Qin X, Sexton C, Byun D, Strong D, Baylink D, Mohan S (2002) Differential regulation of pregnancy associated plasma protein (PAPP)-A during pregnancy in human and mouse. Growth Horm IGF Res 12:359–365
Conover CA, Bale LK, Overgaard MT, Johnstone EW, Laursen UH, Fuchtbauer EM, Oxvig C, Van Deursen J (2004) Metalloproteinase pregnancy-associated plasma protein A is a critical growth regulatory factor during fetal development. Development 131:1187–1194
Yan T, Wergedal J, Zhou Y, Mohan S, Baylink DJ, Strong DD (2001) Inhibition of human osteoblast marker gene expression by retinoids is mediated in part by insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6. GH and IGF Res 11:368–377
Zhou Y, Mohan S, Linkhart TA, Baylink DJ, Strong DD (1996) Retinoic acid regulates insulin-like growth factor-binding protein expression in human osteoblast cells. Endocrinology 137:975–983
Strong DD, Chen ST, Linkhart TA, Yan T, Baylink DJ, Mohan S (2002) IGF binding protein-6 (BP-6) markedly inhibits osteoblast differentiation: evidence for a intracrine mechanism involving nuclear localization utilizing a novel nuclear localization signal (NLS) (abstract). Abstracts of the 84th Annual Meeting Endocrine Society, San Francisco
Strong DD, Linkhart TA, Gunn Y, Kim R, Rung-Aroon J, Mohan S, Baylink DJ, Amaar Y (2003) Evidence that the mechanism whereby insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-6 markedly inhibits osteoblast differentiation is through sequestration of an activator of osteoblast differentiation, the LIM mineralization protein-1 (LMP-1) (abstract). Abstracts of the 25th Annual Meeting of American Society for Bone and Mineral Research, Minneapolis
Boden SD, Liu Y, Hair GA, Helms JA, Hu D, Racine M, Nanes MS, Titus L (1998) LMP-1, a LIM-domain protein, mediates BMP-6 effects on bone formation. Endocrinology 139:5125–5134
Ernst M, Rodan GA (1990) Increased activity of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) in osteoblastic cells in the presence of growth hormone (GH): positive correlation with the presence of the GH-induced IGF-binding protein BP-3. Endocrinology 127:807–814
Conover CA, Khosla S (2003) Role of extracellular matrix in insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein-2 regulation of IGF-II action in normal human osteoblasts. GH and IGF Res 13:328–335
Eckstein F, Pavicic T, Nedbal S, Schmidt C, Wehr U, Rambeck W, Wolf E, Hoeflich A (2002) Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 (IGFBP-2) overexpression negatively regulates bone size and mass, but not density, in the absence and presence of growth hormone/IGF-I excess in transgenic mice. Anat Embryol (Berl) 206:139–148
Campbell PG, Novak JF (1991) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein inhibits IGF action in human osteosarcoma cells. J Cell Physiol 149:293–300
Mohan S, Bautista CM, Wergedal J, Baylink DJ (1989) Isolation of an inhibitory insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein from bone cell-conditioned medium: a potential local regulator of IGF action. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:8338–8342
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by funds from the National Institutes of Health (AR31062 and AR48139) and the Department of Veterans Affairs. We would like to thank Sean Belcher for his help in the preparation of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was presented in part at the IPNA Seventh Symposium on Growth and Development in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease: The Molecular Basis of Skeletal Growth, 1–3 April 2004, Heidelberg, Germany
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Govoni, K.E., Baylink, D.J. & Mohan, S. The multi-functional role of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in bone. Pediatr Nephrol 20, 261–268 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-004-1658-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-004-1658-y