Abstract
Introduction
Chronic pancreatitis is a painful inflammatory disease that leads to progressive and irreversible destruction of pancreatic parenchyma [1]. A lateral pancreaticojejunostomy, also known as the Puestow procedure, is performed for symptomatic chronic pancreatitis associated with a dilated pancreatic duct secondary to calcifications or strictures [4]. An open approach is used traditionally due to the complexity of the case, and there have only been a handful of laparoscopic case reports [2]. This video depicts a laparoscopic lateral pancreaticojejunostomy for chronic pancreatitis.
Methods
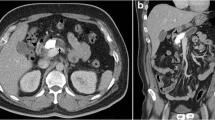
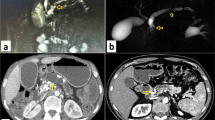
A 45-year-old gentleman with a 20-year history of chronic alcohol abuse presented with diffuse abdominal pain. His pain was worse postprandially and associated with loose stools. A computed tomography scan revealed multiple calcified deposits within the body and tail of the pancreas, and a dilated pancreatic duct measuring 1.4 cm with a proximal obstructing calcified stone. A 5-port foregut technique was used, and a 15-cm pancreatic ductotomy was performed with an ultrasonic scalpel. Calcified stones were cleared from the duct, and a roux-en-y pancreaticojejunostomy was performed using a hand-sewn technique.
Results
The patient had a relatively uncomplicated hospital course with return of bowel function on postoperative day 4. His patient-controlled analgesic device was discontinued on post operative day 3. He was ambulating, tolerating a regular diet and discharged home on postoperative day 5. At 12- and 26-month follow-up, he remains off narcotics, but still requires 1–2 tabs of pancreatic enzyme replacement per meal. Most importantly, he has not had any alcohol for over 2 years.
Conclusion
The two primary goals in treating chronic pancreatitis include long-term pain relief and improvements in quality of life [3]. For patients with chronic pancreatitis and a dilated pancreatic duct, a laparoscopic lateral pancreaticojejunostomy may be an effective approach to decrease pain and improve quality of life.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cahen DL, Gouma DJ, Nio Y, Rauws EA, Boermeester MA, Busch OR, Stoker J, Lameris JS, Dijkgraaf MG, Huibregtse K, Bruno MJ (2007) Endoscopic versus surgical drainage of the pancreatic duct in chronic pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 357:676–684
D’Haese JG, Ceyhan GO, Demir IE, Tieftrunk E, Friess H (2014) Treatment options in painful chronic pancreatitis: a systematic review. HBP (Oxford) 16(6):512–521
Sukharamwala PB, Patel KD, Teta AF, Parikh S, Ross SB, Carrie E, Rosemurgy AS (2015) Long-term outcomes favor duodenum-preserving pancreatic head resection over pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy for chronic pancreatitis: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Am Surg 81(9):909–914
Peustow CB, Gillesby WJ (1958) Retrograde surgical drainage of pancreas for chronic relapsing pancreatitis. AMA Arch Surg 76(6):898–907
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MP4 479821 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biteman, B.R., Harr, J.N. & Brody, F. Laparoscopic Puestow: lateral pancreaticojejunostomy. Surg Endosc 30, 5624 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-4920-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-4920-z