Abstract.
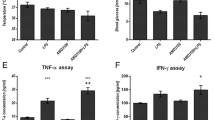
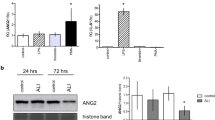
Endotoxemia is associated with a systemic inflammatory response leading to organ-specific leukocyte recruitment and tissue injury. Chemokine expression has been demonstrated in various models of sepsis and may mediate tissue infiltration with inflammatory cells. In this study we examined expression of the C-X-C chemokine interferon-γ-inducible protein-10 (IP-10), a potent T-lymphocyte chemoattractant, in a canine model of endotoxemia and investigated mechanisms of cytokine-mediated IP-10 induction in endothelial cells. Control canine tissues showed negligible expression of IP-10 message, with the exception of the spleen. Endotoxemic dogs demonstrated a robust induction of IP-10 mRNA in the heart, lung, kidney, liver, and spleen. Immunohistochemical studies indicated that IP-10 was predominantly localized in cardiac venular endothelial cells, bronchial epithelial cells, renal mesangial cells, and in the splenic red pulp of endotoxemic dogs. In addition, IP-10 expression was associated with T-lymphocyte infiltration in canine tissues. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) induced a marked upregulation of IP-10 message in canine venular endothelial cells. IP-10 expression in TNF-α-stimulated endothelial cells peaked at 6 h of stimulation and returned to baseline levels after 24 h. In addition, macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) induced a dose-dependent induction of IP-10 mRNA in canine endothelial cells. M-CSF-mediated IP-10 expression peaked after 6 h of incubation and returned to baseline levels after 24 h. Canine endotoxemia is associated with a robust early expression of IP-10 in multiple tissues. IP-10 induction may be important in regulating lymphocyte recruitment and function. TNF-α, IL-1β, and M-CSF are potent inducers of IP-10 in canine endothelial cells and may indirectly mediate lymphocyte chemotaxis and activation in inflammatory processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frangogiannis, N., Mendoza, L., Smith, C. et al. Induction of the synthesis of the C-X-C chemokine interferon-γ-inducible protein-10 in experimental canine endotoxemia. Cell Tissue Res 302, 365–376 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004410000274
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004410000274