Abstract
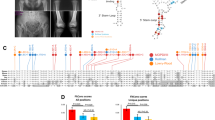
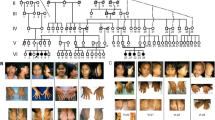
Proteoglycan (PG) synthesis begins with the sequential addition of a “linker chain”, made up of four sugar residues, to a specific region of a core protein. Defects in the enzymes catalyzing steps two to four of the linker chain synthesis have been shown to cause autosomal recessive human phenotypes while no mutation has yet been reported in humans for the xylosyltransferases 1 and 2 (XT1 and XT2), the initiating enzymes in the linker chain formation. Here, we present a consanguineous Turkish family with two affected individuals presenting with short stature, distinct facial features, alterations of fat distribution, and moderate intellectual disability. X-rays showed only mild skeletal changes in the form of a short femoral neck, stocky and plump long bones and thickened ribs. Using a combination of whole-exome sequencing (WES), determination of homozygous stretches by WES variants, and classical linkage analysis, we identified the homozygous missense mutation c.C1441T in XYLT1, encoding XT1, within a large homozygous stretch on chromosome 16p13.12-p12.1. The mutation co-segregated with the phenotype in the family, is not found in over 13,000 alleles in the exome variant server and is predicted to change a highly conserved arginine at position 481 (p.R481W) located in the putative catalytical domain. Immunostaining of primary patient fibroblasts showed a loss of predominance of Golgi localization in mutant cells. Moreover, western blot analysis of decorin in cell culture supernatant demonstrated glycosylation differences between patient and control cells. Our data provide evidence that functional alterations of XT1 cause an autosomal recessive short stature syndrome associated with intellectual disability.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR (2001) GRR: graphical representation of relationship errors. Bioinformatics 17:742–743
Baasanjav S, Al-Gazali L, Hashiguchi T, Mizumoto S, Fischer B, Horn D, Seelow D, Ali BR, Aziz SA, Langer R, Saleh AA, Becker C, Nurnberg G, Cantagrel V, Gleeson JG, Gomez D, Michel JB, Stricker S, Lindner TH, Nurnberg P, Sugahara K, Mundlos S, Hoffmann K (2011) Faulty initiation of proteoglycan synthesis causes cardiac and joint defects. Am J Hum Genet 89:15–27
Baasanjav S, Al-Gazali L, Hashiguchi T, Mizumoto S, Fischer B, Horn D, Seelow D, Ali BR, Aziz SA, Langer R, Saleh AA, Becker C, Nurnberg G, Cantagrel V, Gleeson JG, Gomez D, Michel JB, Stricker S, Lindner TH, Nurnberg P, Sugahara K, Mundlos S, Hoffmann K (2012) Faulty initiation of proteoglycan synthesis causes cardiac and joint defects. Am J Hum Genet 89:15–27
Bui C, Talhaoui I, Chabel M, Mulliert G, Coughtrie MW, Ouzzine M, Fournel-Gigleux S (2010) Molecular characterization of beta1,4-galactosyltransferase 7 genetic mutations linked to the progeroid form of Ehlers–Danlos syndrome (EDS). FEBS Lett 584:3962–3968
Bulow HE, Hobert O (2006) The molecular diversity of glycosaminoglycans shapes animal development. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 22:375–407
Carrino DA, Sorrell JM, Caplan AI (2000) Age-related changes in the proteoglycans of human skin. Arch Biochem Biophys 373:91–101
Condac E, Silasi-Mansat R, Kosanke S, Schoeb T, Towner R, Lupu F, Cummings RD, Hinsdale ME (2007) Polycystic disease caused by deficiency in xylosyltransferase 2, an initiating enzyme of glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:9416–9421
Condac E, Dale GL, Bender-Neal D, Ferencz B, Towner R, Hinsdale ME (2009) Xylosyltransferase II is a significant contributor of circulating xylosyltransferase levels and platelets constitute an important source of xylosyltransferase in serum. Glycobiology 19:829–833
Eames BF, Yan YL, Swartz ME, Levic DS, Knapik EW, Postlethwait JH, Kimmel CB (2011) Mutations in fam20b and xylt1 reveal that cartilage matrix controls timing of endochondral ossification by inhibiting chondrocyte maturation. PLoS Genet 7:e1002246
Esko JD, Lindahl U (2001) Molecular diversity of heparan sulfate. J Clin Invest 108:169–173
Esko JD, Zhang L (1996) Influence of core protein sequence on glycosaminoglycan assembly. Curr Opin Struct Biol 6:663–670
Furukawa K, Okajima T (2002) Galactosyltransferase I is a gene responsible for progeroid variant of Ehlers–Danlos syndrome: molecular cloning and identification of mutations. Biochim Biophys Acta 1573:377–381
Gotting C, Kuhn J, Brinkmann T, Kleesiek K (1998) Xylosylation of alternatively spliced isoforms of Alzheimer APP by xylosyltransferase. J Protein Chem 17:295–302
Gotting C, Kuhn J, Zahn R, Brinkmann T, Kleesiek K (2000) Molecular cloning and expression of human UDP-d-Xylose:proteoglycan core protein beta-d-xylosyltransferase and its first isoform XT-II. J Mol Biol 304:517–528
Gotting C, Kuhn J, Tinneberg HR, Brinkmann T, Kleesiek K (2002) High xylosyltransferase activities in human follicular fluid and cultured granulosa-lutein cells. Mol Hum Reprod 8:1079–1086
Gotting C, Kuhn J, Kleesiek K (2007) Human xylosyltransferases in health and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:1498–1517
Gudbjartsson DF, Jonasson K, Frigge ML, Kong A (2000) Allegro, a new computer program for multipoint linkage analysis. Nat Genet 25:12–13
Hurtado A, Podinin H, Oudega M, Grimpe B (2008) Deoxyribozyme-mediated knockdown of xylosyltransferase-1 mRNA promotes axon growth in the adult rat spinal cord. Brain 131:2596–2605
Kalkan Ucar S, Ozbaran B, Demiral N, Yuncu Z, Erermis S, Coker M (2010) Clinical overview of children with mucopolysaccharidosis type III A and effect of Risperidone treatment on children and their mothers psychological status. Brain Dev 32(2):156–161
Kleesiek K, Reinards R, Okusi J, Wolf B, Greiling H (1987) UDP-d-xylose: core protein b-d-xylosyltransferase: a new marker of cartilage destruction in chronic joint diseases. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 25:473–481
Komosinska-Vassev KB, Winsz-Szczotka K, Kuznik-Trocha K, Olczyk P, Olczyk K (2008) Age-related changes of plasma glycosaminoglycans. Clin Chem Lab Med 46:219–224
Kuhn J, Prante C, Schon S, Gotting C, Kleesiek K (2006) Measurement of fibrosis marker xylosyltransferase I activity by HPLC electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chem 52:2243–2249
Li H, Durbin R (2010) Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 26:589–595
Malfait F, Kariminejad A, Van Damme T, Gauche C, Syx D, Merhi-Soussi F, Gulberti S, Symoens S, Vanhauwaert S, Willaert A, Bozorgmehr B, Kariminejad MH, Ebrahimiadib N, Hausser I, Huysseune A, Fournel-Gigleux S, De Paepe A (2013) Defective initiation of glycosaminoglycan synthesis due to B3GALT6 mutations causes a pleiotropic Ehlers–Danlos syndrome-like connective tissue disorder. Am J Hum Genet. doi:10.1016/jajhg201304016
Muller B, Prante C, Gastens M, Kuhn J, Kleesiek K, Gotting C (2008) Increased levels of xylosyltransferase I correlate with the mineralization of the extracellular matrix during osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Matrix Biol 27:139–149
Nakajima M, Mizumoto S, Miyake N, Kogawa R, Iida A, Ito H, Kitoh H, Hirayama A, Mitsubuchi H, Miyazaki O, Kosaki R, Horikawa R, Lai A, Mendoza-Londono R, Dupuis L, Chitayat D, Howard A, Leal GF, Cavalcanti D, Tsurusaki Y, Saitsu H, Watanabe S, Lausch E, Unger S, Bonafé L, Ohashi H, Superti-Furga A, Matsumoto N, Sugahara K, Nishimura G, Ikegawa S (2013) Mutations in B3GALT6, which encodes a glycosaminoglycan linker region enzyme, cause a spectrum of skeletal and connective tissue disorders. Am J Hum Genet. doi:10.1016/jajhg201304003
O’Connell JR, Weeks DE (1998) PedCheck: a program for identification of genotype incompatibilities in linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet 63:259–266
Okajima T, Fukumoto S, Furukawa K, Urano T (1999) Molecular basis for the progeroid variant of Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. Identification and characterization of two mutations in galactosyltransferase I gene. J Biol Chem 274:28841–28844
Orlando C, Ster J, Gerber U, Fawcett JW, Raineteau O (2012) Perisynaptic chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans restrict structural plasticity in an integrin-dependent manner. J Neurosci 32:18009–18017
Prante C, Bieback K, Funke C, Schon S, Kern S, Kuhn J, Gastens M, Kleesiek K, Gotting C (2006) The formation of extracellular matrix during chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells correlates with increased levels of xylosyltransferase I. Stem Cells 24:2252–2261
Prante C, Kuhn J, Kleesiek K, Gotting C (2009) High xylosyltransferase activity in children and during mineralization of osteoblast-like SAOS-2 cells. Glycoconj J 26:219–227
Quentin E, Gladen A, Roden L, Kresse H (1990) A genetic defect in the biosynthesis of dermatan sulfate proteoglycan: galactosyltransferase I deficiency in fibroblasts from a patient with a progeroid syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:1342–1346
Rahuel-Clermont S, Daligault F, Piet MH, Gulberti S, Netter P, Branlant G, Magdalou J, Lattard V (2010) Biochemical and thermodynamic characterization of mutated beta1,4-galactosyltransferase 7 involved in the progeroid form of the Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. Biochem J 432:303–311
Roch C, Kuhn J, Kleesiek K, Gotting C (2010) Differences in gene expression of human xylosyltransferases and determination of acceptor specificities for various proteoglycans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391:685–691
Ruschendorf F, Nurnberg P (2005) ALOHOMORA: a tool for linkage analysis using 10 K SNP array data. Bioinformatics 21:2123–2125
Sandbrink R, Monning U, Masters CL, Beyreuther K (1997) Expression of the APP gene family in brain cells, brain development and aging. Gerontology 43:119–131
Savasir I, Sezgin N, Erol N (1989) Ankara Gelisim Tarama Envanteri (AGTE) El Kitabi, 2nd edn. Reklamay Lim. Şti, Ankara, pp 1–29 (in Turkish)
Schon S, Prante C, Bahr C, Kuhn J, Kleesiek K, Gotting C (2006) Cloning and recombinant expression of active full-length xylosyltransferase I (XT-I) and characterization of subcellular localization of XT-I and XT-II. J Biol Chem 281:14224–14231
Schwartz N (2000) Biosynthesis and regulation of expression of proteoglycans. Front Biosci 5:D649–D655
Scott PG, McEwan PA, Dodd CM, Bergmann EM, Bishop PN, Bella J (2004) Crystal structure of the dimeric protein core of decorin, the archetypal small leucine-rich repeat proteoglycan. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(44):15633–15638
Stoolmiller AC, Horwitz AL, Dorfman A (1972) Biosynthesis of the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan. Purification and properties of xylosyltransferase. J Biol Chem 247:3525–3532
Weilke C, Brinkmann T, Kleesiek K (1997) Determination of xylosyltransferase activity in serum with recombinant human bikunin as acceptor. Clin Chem 43:45–51
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Prof. Bernd Wollnik for the valuable discussions and constructive suggestions concerning this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schreml, J., Durmaz, B., Cogulu, O. et al. The missing “link”: an autosomal recessive short stature syndrome caused by a hypofunctional XYLT1 mutation. Hum Genet 133, 29–39 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-013-1351-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-013-1351-y