Abstract
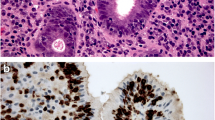
Toll-like receptor 5 (TLR5) is an immune receptor, which recognizes bacterial flagellin. Increased expression has been reported in various premalignant and malignant lesions indicating a role in carcinogenesis. We assessed the expression of TLR5 in normal esophageal squamous epithelium, Barrett’s esophagus with and without dysplasia, and in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Specimens with normal esophagus (n = 93), gastric (n = 75) or intestinal metaplasia (n = 53) without dysplasia, and low-grade (n = 56) or high-grade dysplasia (n = 33) and esophageal adenocarcinoma (n = 94) were studied. TLR5 immunohistochemical stainings were analyzed for the proportion of positive cells and the intensity of expression. In normal squamous epithelium, only the basal third showed TLR5 expression. In esophageal gastric or intestinal metaplasia, expression was present in majority of the cells but significantly weaker (p < 0.001) than in dysplastic epithelium. In dysplasia, expression extended to the apical cytoplasm, contrasting basolateral expression in non-dysplastic columnar epithelium. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis showed that moderate to high expression intensity of TLR5 indicates low-grade dysplasia with 86 % sensitivity and 83 % specificity. Carcinomas showed increased expression in comparison with non-dysplastic columnar epithelium, but there was no association with prognosis. Our results indicate that the esophageal columnar dysplasia is associated with clear increase of TLR5 expression and dissolution of regular polarized expression. TLR5 staining provides a possible biomarker for the recognition of low-grade dysplasia. In addition, the findings suggest a role for abnormal expression of TLR5 in the pathogenesis of esophageal adenocarcinoma and suggest importance of altered microbiome in the pathogenesis of complications of Barrett’s esophagus.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takeda K, Akira S (2007) Toll-like receptors. Curr Protoc Immunol. doi:10.1002/0471142735.im1412s77
Kumar H, Kawai T, Akira S (2011) Pathogen recognition by the innate immune system. Int Rev Immunol 30:16–34
Akira S, Takeda K (2004) Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 4:499–511
Moresco EM, LaVine D, Beutler B (2011) Toll-like receptors. Curr Biol 21:R488–R493
Liew FY, Xu D, Brint EK, O’Neill LA (2005) Negative regulation of Toll-like receptor-mediated immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol 5:446–458
Huang B, Zhao J, Li H, He KL, Chen Y, Chen SH, Mayer L, Unkeless JC, Xiong H (2005) Toll-like receptors on tumor cells facilitate evasion of immune surveillance. Cancer Res 65:5009–5014
Pimentel-Nunes P, Afonso L, Lopes P, Roncon-Albuquerque R Jr, Goncalves N, Henrique R, Moreira-Dias L, Leite-Moreira AF, Dinis-Ribeiro M (2011) Increased expression of Toll-like receptors (TLR) 2, 4 and 5 in gastric dysplasia. Pathol Oncol Res 17:677–683
Kauppila JH, Takala H, Selander KS, Lehenkari PP, Saarnio J, Karttunen TJ (2011) Increased Toll-like receptor 9 expression indicates adverse prognosis in oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Histopathology 59:643–649
Hayashi F, Smith KD, Ozinsky A, Hawn TR, Yi EC, Goodlett DR, Eng JK, Akira S, Underhill DM, Aderem A (2001) The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. Nature 410:1099–1103
Schmausser B, Andrulis M, Endrich S, Lee SK, Josenhans C, Muller-Hermelink HK, Eck M (2004) Expression and subcellular distribution of Toll-like receptors TLR4, TLR5 and TLR9 on the gastric epithelium in Helicobacter pylori infection. Clin Exp Immunol 136:521–526
Park JH, Yoon HE, Kim DJ, Kim SA, Ahn SG, Yoon JH (2011) Toll-like receptor 5 activation promotes migration and invasion of salivary gland adenocarcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med 40:187–193
Kauppila JH, Mattila AE, Karttunen TJ, Salo T (2013) Toll-like receptor 5 (TLR5) expression is a novel predictive marker for recurrence and survival in squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. Br J Cancer 108(3):638–43
Jones RM, Sloane VM, Wu H, Luo L, Kumar A, Kumar MV, Gewirtz AT, Neish AS (2011) Flagellin administration protects gut mucosal tissue from irradiation-induced apoptosis via MKP-7 activity. Gut 60:648–657
Kim WY, Lee JW, Choi JJ, Choi CH, Kim TJ, Kim BG, Song SY, Bae DS (2008) Increased expression of Toll-like receptor 5 during progression of cervical neoplasia. Int J Gynecol Cancer 18:300–305
Pohl H, Welch HG (2005) The role of overdiagnosis and reclassification in the marked increase of esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:142–146
Pei Z, Bini EJ, Yang L, Zhou M, Francois F, Blaser MJ (2004) Bacterial biota in the human distal esophagus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:4250–4255
Yang L, Lu X, Nossa CW, Francois F, Peek RM, Pei Z (2009) Inflammation and intestinal metaplasia of the distal esophagus are associated with alterations in the microbiome. Gastroenterology 137:588–597
Pei Z, Yang L, Peek RM Jr, Levine SM, Pride DT, Blaser MJ (2005) Bacterial biota in reflux esophagitis and Barrett’s esophagus. World J Gastroenterol 11:7277–7283
Odze RD (2009) Barrett esophagus: histology and pathology for the clinician. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 6:478–490
Reid BJ, Haggitt RC, Rubin CE, Roth G, Surawicz CM, Van Belle G, Lewin K, Weinstein WM, Antonioli DA, Goldman H (1988) Observer variation in the diagnosis of dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus. Hum Pathol 19:166–178
Baker BS, Ovigne JM, Powles AV, Corcoran S, Fry L (2003) Normal keratinocytes express Toll-like receptors (TLRs) 1, 2 and 5: modulation of TLR expression in chronic plaque psoriasis. Br J Dermatol 148:670–679
Takala H, Kauppila JH, Soini Y, Selander KS, Vuopala KS, Lehenkari PP, Saarnio J, Karttunen TJ (2011) Toll-like receptor 9 is a novel biomarker for esophageal squamous cell dysplasia and squamous cell carcinoma progression. J Innate Immun 3:631–638
Yang L, Francois F, Pei Z (2012) Molecular pathways: pathogenesis and clinical implications of microbiome alteration in esophagitis and Barrett esophagus. Clin Cancer Res 18:2138–2144
Mullin JM, Valenzano MC, Trembeth S, Allegretti PD, Verrecchio JJ, Schmidt JD, Jain V, Meddings JB, Mercogliano G, Thornton JJ (2006) Transepithelial leak in Barrett’s esophagus. Dig Dis Sci 51:2326–2336
Ormsby AH, Petras RE, Henricks WH, Rice TW, Rybicki LA, Richter JE, Goldblum JR (2002) Observer variation in the diagnosis of superficial oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Gut 51:671–676
Kerkhof M, van Dekken H, Steyerberg EW, Meijer GA, Mulder AH, de Bruine A, Driessen A, ten Kate FJ, Kusters JG, Kuipers EJ, Siersema PD, CYBAR study group (2007) Grading of dysplasia in Barrett’s oesophagus: substantial interobserver variation between general and gastrointestinal pathologists. Histopathology 50:920–927
Curvers WL, ten Kate FJ, Krishnadath KK, Visser M, Elzer B, Baak LC, Bohmer C, Mallant-Hent RC, van Oijen A, Naber AH, Scholten P, Busch OR, Blaauwgeers HG, Meijer GA, Bergman JJ (2010) Low-grade dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus: overdiagnosed and underestimated. Am J Gastroenterol 105:1523–1530
Skacel M, Petras RE, Gramlich TL, Sigel JE, Richter JE, Goldblum JR (2000) The diagnosis of low-grade dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus and its implications for disease progression. Am J Gastroenterol 95:3383–3387
Srivastava A, Hornick JL, Li X, Blount PL, Sanchez CA, Cowan DS, Ayub K, Maley CC, Reid BJ, Odze RD (2007) Extent of low-grade dysplasia is a risk factor for the development of esophageal adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol 102:483–493, quiz 694
Bennett C, Vakil N, Bergman J, Harrison R, Odze R, Vieth M, Sanders S, Gay L, Pech O, Longcroft-Wheaton G, Romero Y, Inadomi J, Tack J, Corley DA, Manner H, Green S, Al Dulaimi D, Ali H, Allum B, Anderson M, Curtis H, Falk G, Fennerty MB, Fullarton G, Krishnadath K, Meltzer SJ, Armstrong D, Ganz R, Cengia G, Going JJ, Goldblum J, Gordon C, Grabsch H, Haigh C, Hongo M, Johnston D, Forbes-Young R, Kay E, Kaye P, Lerut T, Lovat LB, Lundell L, Mairs P, Shimoda T, Spechler S, Sontag S, Malfertheiner P, Murray I, Nanji M, Poller D, Ragunath K, Regula J, Cestari R, Shepherd N, Singh R, Stein HJ, Talley NJ, Galmiche JP, Tham TC, Watson P, Yerian L, Rugge M, Rice TW, Hart J, Gittens S, Hewin D, Hochberger J, Kahrilas P, Preston S, Sampliner R, Sharma P, Stuart R, Wang K, Waxman I, Abley C, Loft D, Penman I, Shaheen NJ, Chak A, Davies G, Dunn L, Falck-Ytter Y, Decaestecker J, Bhandari P, Ell C, Griffin SM, Attwood S, Barr H, Allen J, Ferguson MK, Moayyedi P, Jankowski JA (2012) Consensus statements for management of Barrett’s dysplasia and early-stage esophageal adenocarcinoma, based on a Delphi process. Gastroenterology 143:336–346
Cai Z, Sanchez A, Shi Z, Zhang T, Liu M, Zhang D (2011) Activation of Toll-like receptor 5 on breast cancer cells by flagellin suppresses cell proliferation and tumor growth. Cancer Res 71:2466–2475
Rhee SH, Im E, Pothoulakis C (2008) Toll-like receptor 5 engagement modulates tumor development and growth in a mouse xenograft model of human colon cancer. Gastroenterology 135:518–528
Song EJ, Kang MJ, Kim YS, Kim SM, Lee SE, Kim CH, Kim DJ, Park JH (2011) Flagellin promotes the proliferation of gastric cancer cells via the Toll-like receptor 5. Int J Mol Med 28:115–119
Yu L, Wang L, Chen S (2012) Exogenous or endogenous Toll-like receptor ligands: which is the MVP in tumorigenesis? Cell Mol Life Sci 69:935–949
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Emil Aaltonen Foundation (J.H.K.), Cancer Foundation of Northern Ostrobotnia (J.H.K.), Oulu University Research Foundation (J.H.K.), Georg C. and Mary Ehrnroot Foundation (J.H.K.), and the Finnish Medical Foundation (J.H.K. and H.H.). T.J.K. received travel grant from Amgen and a single lecture payment from Novartis.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Joonas H. Kauppila and Tuomo J. Karttunen contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Helminen, O., Huhta, H., Takala, H. et al. Increased Toll-like receptor 5 expression indicates esophageal columnar dysplasia. Virchows Arch 464, 11–18 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-013-1505-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-013-1505-2