Abstract
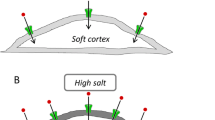
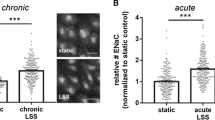
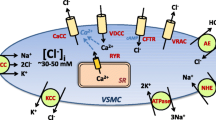
Once upon a time, the expression of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) was mainly assigned to the kidneys, colon and sweat glands where it was considered to be the main determinant of sodium homeostasis. Recent, though indirect, evidence for the possible existence of ENaC in a non-epithelial tissue was derived from the observation that the vascular endothelium is a target for aldosterone. Inhibitory actions of the intracellular aldosterone receptors by spironolactone and, more directly, by ENaC blockers such as amiloride supported this view. Shortly after, direct data on the expression of ENaC in vascular endothelium could be demonstrated. There, endothelial ENaC (EnNaC) could be defined as a major regulator of cellular mechanics which is a critical parameter in differentiating between vascular function and dysfunction. Foremost, the mechanical stiffness of the endothelial cell cortex, a layer 50–200 nm beneath the plasma membrane, has been shown to play a crucial role as it controls the production of the endothelium-derived vasodilator nitric oxide (NO) which directly affects the tone of the vascular smooth muscle cells. In contrast to soft endothelial cells, stiff endothelial cells release reduced amounts of NO, the hallmark of endothelial dysfunction. Thus, the combination of endothelial stiffness and myogenic tone might increase the peripheral vascular resistance. An elevation of arterial blood pressure is supposed to be the consequence of such functional changes. In this review, EnNaC is discussed as an aldosterone-regulated plasma membrane protein of the vascular endothelium that could significantly contribute to maintaining of an appropriate arterial blood pressure but, if overexpressed, could participate in the pathogenesis of arterial hypertension.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abriel H, Horisberger J-D (1999) Feedback inhibition of rat amiloride-sensitive epithelial sodium channels expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Physiol Lond 516:31–43
Alvarez de la Rosa D, Canessa CM, Fyfe GK, Zhang P (2000) Structure and regulation of amiloride-sensitive sodium channels. Annu Rev Physiol 62:573–594
Alvarez de la Rosa D, Li H, Canessa CM (2002) Effects of aldosterone on biosynthesis, traffic, and functional expression of the epithelial sodium channel in A6 cells. J Gen Physiol 119:427–442
Ambrosius WT, Bloem LJ, Zhou L, Rebhun JF, Snyder PM, Wagner MA, Guo C, Pratt JH (1999) Genetic variants in the epithelial sodium channel in relation to aldosterone and potassium excretion and risk for hypertension. Hypertension 34:631–637
Beesley AH, Hornby D, White SJ (1998) Regulation of distal nephron K + channels (ROMK) mRNA expression by aldosterone in rat kidney. J Physiol 509(Pt 3):629–634
Berger S, Bleich M, Schmid W, Greger R, Schutz G (2000) Mineralocorticoid receptor knockout mice: lessons on Na + metabolism. Kidney Int 57:1295–1298
Butterworth MB, Edinger RS, Johnson JP, Frizzell RA (2005) Acute ENaC Stimulation by cAMP in a kidney cell line is mediated by exocytic insertion from a recycling channel pool. J Gen Physiol 125:81–101
Caldwell RA, Boucher RC, Stutts MJ (2004) Serine protease activation of near-silent epithelial Na+ channels. Am J Physiol Cell Physio 286:190–194
Callies C, Fels J, Liashkovich I, Kliche K, Jeggle P, Kusche-Vihrog K, Oberleithner H (2011) Membrane potential depolarization decreases the stiffness of vascular endothelial cells. J Cell Sci 124:1936–1942
Canessa CM, Horisberger J-D, Schild L, Rossier BC (1995) Expression cloning of the epithelial sodium channel. Kidney Intern 48:950–955
Canessa CM, Schild L, Buell G, Thorens B, Gautschi I, Horisberger J-D, Rossier BC (1994) Amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel is made of three homologous subunits. Nature 367:463–467
Caprio M, Newfell BG, la Sala A, Baur W, Fabbri A, Rosano G, Mendelsohn ME, Jaffe IZ (2008) Functional mineralocorticoid receptors in human vascular endothelial cells regulate intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression and promote leukocyte adhesion. Circ Res 102:1359–1367
Carattino MD, Hughey RP, Kleyman TR (2008) Proteolytic processing of the epithelial sodium channel gamma subunit has a dominant role in channel activation. J Biol Chem 283:25290–25295
Chen W, Valamanesh F, Mirshahi T, Soria J, Tang R, Agarwal MK, Mirshahi M (2004) Aldosterone signaling modifies capillary formation by human bone marrow endothelial cells. Vascul Pharmacol 40(6):269–277
Chen LM, Wang C, Chen M, Marcello MR, Chao J, Chao L, Chai KX (2006) Prostasin attenuates inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in lipopolysaccharide-induced urinary bladder inflammation. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 291:F567–F577
Debonneville C, Flores SY, Kamynina E, Plant PJ, Tauxe C, Thomas MA, Muenster C, Chraibi A, Pratt HJ, Horisberger J-D, Pearce D, Loffing J, Staub O (2001) Phosphorylation of Nedd4-2 by Sgk1 regulates epithelial Na+ channel surface expression. EMBO J 20:7052–7059
Diakov A, Bera K, Mokrushina M, Krueger B, Korbmacher C (2008) Cleavage in the γ-subunit of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) plays an important role in the proteolytic activation of near-silent channels. J Physiol 283:25290–25295
Druppel V, Kusche-Vihrog K, Grossmann C, Gekle M, Kasprzak B, Brand E, Pavenstadt H, Oberleithner H, Kliche K (2013) Long-term application of the aldosterone antagonist spironolactone prevents stiff endothelial cell syndrome. FASEB J 27:3652–3659
Endemann DH, Schiffrin EL (2004) Endothelial dysfunction. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:1983–1992
Falkenstein E, Christ M, Feuring M, Wehling M (2000) Specific nongenomic actions of aldosterone. Kidney Intern 57:1390–1394
Feletou M, Vanhoutte PM (2006) Endothelial dysfunction: a multifaceted disorder (The Wiggers Award Lecture). Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291:H985–H1002
Fels J, Callies C, Kusche-Vihrog K, Oberleithner H (2010) Nitric oxide release follows endothelial nanomechanics and not vice versa. Pflugers Arch 460:915–923
Firsov D, Gautschi I, Merillat A-M, Rossier BC, Schild L (1998) The heterotetrameric architecture of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC). EMBO J 17:344–352
Funder JW (2005) Mineralocorticoid receptors: distribution and activation. Heart Fail Rev 10:15–22
Funder JW, Reincke M (2010) Aldosterone: a cardiovascular risk factor? Biochimica Biophysica Acta 1802:1188–1192
Furchgott RF, Zawadzki JV (1980) The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature 288:373–376
Fyfe GK, Canessa CM (1998) Subunit composition determines the single chancel kinetics of the epithelial sodium channel. J Gen Physiol 112:423–432
Garty H, Palmer LG (1997) Epithelial sodium channels: function, structure, and regulation. Physiol Rev 77:359–396
Gimbrone MA Jr (1995) Vascular endothelium: an integrator of pathophysiologic stimuli in atherosclerosis. Am J Cardiol 75:67B–70B
Golestaneh N, Klein C, Valamanesh F, Suarez G, Agarwal MK, Mirshahi M (2001) Mineralocorticoid receptor-mediated signaling regulates the ion gated sodium channel in vascular endothelial cells and requires an intact cytoskeleton. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 280:1300–1306
Grossmann C, Gekle M (2009) New aspects of rapid aldosterone signaling. Mol Cell Endocrinol 308:53–62
Guyton AC (1991) Blood pressure control—special role of the kidneys and body fluids. Science 252:1813–1816
Harvey KF, Dinudom A, Komwatana P, Jolliffe CN, Day ML, Parasivam G, Cook DI, Kumar S (1999) All three WW domains of murine Nedd4 are involved in the regulation of epithelial sodium channels by intracellular Na+. J Biol Chem 274:12525–12530
He FJ, Burnier M, MacGregor GA (2011) Nutrition in cardiovascular disease: salt in hypertension and heart failure. Eur Heart J 32:3073–3080
Hillebrand U, Schillers H, Riethmüller C, Stock C, Wilhelmi M, Oberleithner H, Hausberg M (2007) Dose-dependent endothelial cell growth and stiffening by aldosterone: endothelial protection by eplerenone. J Hypertens 25:639–647
Horisberger J-D, Chraibi A (2004) Epithelial sodium channel: a ligand-gated channel? Nephron Physiol 96(2):37–41
Hughey RP, Mueller GM, Bruns JB, Kinlough CL, Poland PA, Harkleroad KL, Carattino MD, Kleyman TR (2003) Maturation of the epithelial Na+ channel involves proteolytic processing of the a- and g-subunits. J Biol Chem 278:37073–37082
Jeggle P, Callies C, Tarjus A, Fassot C, Fels J, Oberleithner H, Jaisser F, Kusche-Vihrog K (2013) Epithelial sodium channel stiffens the vascular endothelium in vitro and in Liddle mice. Hypertension 61:1053–1059
Jernigan NL, Drummond HA (2005) Vascular ENaC proteins are required for renal myogenic constriction. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 289:F891–F901
Kasas S, Wang X, Hirling H, Marsault R, Huni B, Yersin A, Regazzi R, Grenningloh G, Riederer B, Forro L, Dietler G, Catsicas S (2005) Superficial and deep changes of cellular mechanical properties following cytoskeleton disassembly. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 62:124–132
Kliche K, Jeggle P, Pavenstadt H, Oberleithner H (2011) Role of cellular mechanics in the function and life span of vascular endothelium. Pflugers Arch 462:209–217
Knight KK, Wentzlaff DM, Snyder PM (2008) Intracellular sodium regulates proteolytic activation of the epithelial sodium channel. J Biol Chem 283:27477–27482
Kolla V, Litwack G (2000) Transcriptional regulation of the human Na/K ATPase via the human mineralocorticoid receptor. Mol Cell Biochem 204:35–40
Komarova Y, Malik AB (2010) Regulation of endothelial permeability via paracellular and transcellular transport pathways. Annu Rev Physiol 72:463–493
Korte S, Wiesinger A, Straeter AS, Peters W, Oberleithner H, Kusche-Vihrog K (2011) Firewall function of the endothelial glycocalyx in the regulation of sodium homeostasis. Pflugers Arch 463:269–278
Kosari F, Sheng S, Li J, Mak D-OD, Foskett JK, Kleyman TR (1998) Subunit stoichiometry of the epithelial sodium channel. J Biol Chem 273:13469–13474
Krueger B, Schlotzer-Schrehardt U, Haerteis S, Zenkel M, Chankiewitz VE, Amann KU, Kruse FE, Korbmacher C (2012) Four subunits (alphabetagammadelta) of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) are expressed in the human eye in various locations. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53:596–604
Kusche-Vihrog K, Callies C, Fels J, Oberleithner H (2009) The epithelial sodium channel (ENaC): mediator of the aldosterone response in the vascular endothelium? Steroids 75:544–549
Kusche-Vihrog K, Sobczak K, Bangel N, Wilhelmi M, Nechyporuk-Zloy V, Schwab A, Schillers H, Oberleithner H (2008) Aldosterone and amiloride alter ENaC abundance in vascular endothelium. Pflugers Arch 455:849–857
Lang F (2011) Stiff endothelial cell syndrome in vascular inflammation and mineralocorticoid excess. Hypertension 57:146–147
Li XY, Cai XL, Bian PD, Hu LR (2012) High salt intake and stroke: meta-analysis of the epidemiologic evidence. CNS Neurosci Ther 18:691–701
Loffing J, Korbmacher C (2009) Regulated sodium transport in the renal connecting tubule (CNT) via the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC). Pflugers Arch 458:111–135
Mazzochi C, Benos DJ, Smith PR (2006) Interaction of epithelial ion channels with the actin-based cytoskeleton. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 291:F1113–F1122
Mazzochi C, Bubien JK, Smith PR, Benos DJ (2006) The carboxyl terminus of the alpha-subunit of the amiloride-sensitive epithelial sodium channel binds to F-actin. J Biol Chem 281:6528–6538
Meneton P, Jeunemaitre X, de Wardener HE, MacGregor GA (2005) Links between dietary salt intake, renal salt handling, blood pressure, and cardiovascular diseases. Physiol Rev 85:679–715
Mirshahi M, Nicolas C, Mirshahi S, Golestaneh N, d' Hermies F, Agarwal MK (1999) Immunochemical analysis of the sodium channel in rodent and human eye. Exp Eye Res 69:21–32
Mullins LJ, Bailey MA, Mullins JJ (2006) Hypertension, kidney, and transgenics: a fresh perspective. Physiol Rev 86:709–746
Murdaca J, Treins C, Monthouel-Kartmann MN, Pontier-Bres R, Kumar S, Van OE, Giorgetti-Peraldi S (2004) Grb10 prevents Nedd4-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 degradation. J Biol Chem 279:26754–26761
Nagase M, Matsui H, Shibata S, Gotoda T, Fujita T (2007) Salt-induced nephropathy in obese spontaneously hypertensive rats via paradoxical activation of the mineralocorticoid receptor: role of oxidative stress. Hypertension 50:877–883
Nguyen Dinh CA, Griol-Charhbili V, Loufrani L, Labat C, Benjamin L, Farman N, Lacolley P, Henrion D, Jaisser F (2010) The endothelial mineralocorticoid receptor regulates vasoconstrictor tone and blood pressure. FASEB J 24:2454–2463
Nguyen Dinh CA, Jaisser F (2012) Extrarenal effects of aldosterone. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 21:147–156
Oberleithner H (2012) Two barriers for sodium in vascular endothelium? Ann Med 44(Suppl 1):S143–S148
Oberleithner H (2013) Vascular endothelium leaves fingerprints on the surface of erythrocytes. Pflugers Arch. doi:10.1007/s00424-013-1288-y
Oberleithner H, Callies C, Kusche-Vihrog K, Schillers H, Shahin V, Riethmuller C, MacGregor GA, de Wardener HE (2009) Potassium softens vascular endothelium and increases nitric oxide release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:2829–2834
Oberleithner H, Kusche-Vihrog K, Schillers H (2010) Endothelial cells as vascular salt sensors. Kidney Int 77:490–494
Oberleithner H, Peters W, Kusche-Vihrog K, Korte S, Schillers H, Kliche K, Oberleithner K (2011) Salt overload damages the glycocalyx sodium barrier of vascular endothelium. Pflugers Arch 462:519–528
Oberleithner H, Riethmuller C, Ludwig T, Hausberg M, Schillers H (2006) Aldosterone remodels human endothelium. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 187:305–312
Oberleithner H, Riethmüller C, Ludwig T, Shahin V, Stock C, Schwab A, Hausberg M, Kusche K, Schillers H (2006) Differential action of steroid hormones on human endothelium. J Cell Sci 119:1926–1932
Oberleithner H, Riethmuller C, Schillers H, MacGregor GA, de Wardener HE, Hausberg M (2007) Plasma sodium stiffens vascular endothelium and reduces nitric oxide release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:16281–16286
Oberleithner H, Schneider SW, Albermann L, Hillebrand U, Ludwig T, Riethmüller C, Shahin V, Schäfer C, Schillers H (2003) Endothelial cell swelling by aldosterone. J Membr Biol 196:163–172
Oberleithner H, Wilhelmi M (2013) Determination of erythrocyte sodium sensitivity in man. Pflugers Arch. doi:10.1007/s00424-013-1289-x
Oda T, Makino K, Yamashita I, Namba K, Maeda Y (2001) Distinct structural changes detected by X-ray fiber diffraction in stabilization of F-actin by lowering pH and increasing ionic strength. Biophys J 80:841–851
Patel AB, Frindt G, Palmer LG (2013) Feedback inhibition of ENaC during acute sodium loading in vivo. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 304:F222–F232
Perez FR, Venegas F, Gonzalez M, Andres S, Vallejos C, Riquelme G, Sierralta J, Michea L (2009) Endothelial epithelial sodium channel inhibition activates endothelial nitric oxide synthase via phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt in small-diameter mesenteric arteries. Hypertension 53:1000–1007
Pesen D, Hoh JH (2005) Micromechanical architecture of the endothelial cell cortex. Biophys J 88:670–679
Pesen D, Hoh JH (2005) Modes of remodeling in the cortical cytoskeleton of vascular endothelial cells. FEBS Lett 579:473–476
Peters W, Drueppel V, Kusche-Vihrog K, Schubert C, Oberleithner H (2012) Nanomechanics and sodium permeability of endothelial surface layer modulated by hawthorn extract WS 1442. PLoS One 7:e29972
Ritz E (2010) Salt and hypertension. Nephrology (Carlton ) 15(Suppl 2):49–52
Ronzaud C, Loffing-Cueni D, Hausel P, Debonneville A, Malsure SR, Fowler-Jaeger N, Boase NA, Perrier R, Maillard M, Yang B, Stokes JB, Koesters R, Kumar S, Hummler E, Loffing J, Staub O (2013) Renal tubular NEDD4-2 deficiency causes NCC-mediated salt-dependent hypertension. J Clin Invest 123:657–665
Rotin D, Bar-Sagi D, O'Brodovich H, Merilainen J, Lehto VP, Canessa CM, Rossier BC, Downey GP (1994) An SH3 binding region in the epithelial Na + channel (alpha rENaC) mediates its localization at the apical membrane. EMBO J 13:4440–4450
Rotin D, Staub O (2011) Role of the ubiquitin system in regulating ion transport. Pflugers Arch 461:1–21
Rotin D, Staub O (2012) Nedd4-2 and the regulation of epithelial sodium transport. Front Physiol 3:212
Sanders PW (2009) Vascular consequences of dietary salt intake. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297:F237–F243
Sausbier M, Arntz C, Bucurenciu I, Zhao H, Zhou XB, Sausbier U, Feil S, Kamm S, Essin K, Sailer CA, Abdullah U, Krippeit-Drews P, Feil R, Hofmann F, Knaus HG, Kenyon C, Shipston MJ, Storm JF, Neuhuber W, Korth M, Schubert R, Gollasch M, Ruth P (2005) Elevated blood pressure linked to primary hyperaldosteronism and impaired vasodilation in BK channel-deficient mice. Circulation 112:60–68
Schild L (2010) The epithelial sodium channel and the control of sodium balance. Biochimica Biophysica Acta 1802:1159–1165
Sessa WC (2004) eNOS at a glance. J Cell Sci 117:2427–2429
Sheng S, Maarouf AB, Bruns JB, Hughey RP, Kleyman TR (2007) Functional role of extracellular loop cysteine residues of the epithelial Na + channel in Na + self-inhibition. J Biol Chem 282:20180–20190
Shimkets RA, Warnock DG, Bositis CM, Nelson-Williams C, Hansson JH, Schambelan M, Gill JR Jr, Ulick S, Milora RV, Findling JW (1994) Liddle's syndrome: heritable human hypertension caused by mutations in the beta subunit of the epithelial sodium channel. Cell 79:407–414
Si H, Heyken WT, Wolfle SE, Tysiac M, Schubert R, Grgic I, Vilianovich L, Giebing G, Maier T, Gross V, Bader M, de Wit C, Hoyer J, Kohler R (2006) Impaired endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor-mediated dilations and increased blood pressure in mice deficient of the intermediate-conductance Ca2 + -activated K + channel. Circ Res 99:537–544
Smith PR, Saccomani G, Joe E-H, Angelides KJ, Benos DJ (1991) Amiloride-sensitive sodium channel is linked to the cytoskeleton in renal epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:6971–6975
Snyder PM, Cheng C, Prince LS, Rogers JC, Welsh MJ (1998) Electropyhsiological and biochemical evidence that DEG/ENaC cation channels are composed of nine subunits. J Biol Chem 273:681–684
Staruschenko A, Adams E, Booth RE, Stockand JD (2005) Epithelial Na+ channel subunit stoichiometry. Biophys J 88:3966–3975
Staub O, Dho S, Henry P, Correa J, Ishikawa T, McGlade J, Rotin D (1996) WW domains of Nedd4 bind to the proline-rich PY motifs in the epithelial Na + channel deleted in Liddle's syndrome. EMBO J 15:2371–2380
Stewart AP, Haerteis S, Diakov A, Korbmacher C, Edwardson JM (2011) Atomic force microscopy reveals the architecture of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC). J Biol Chem 286:31944–31952
Suckling RJ, He FJ, Markandu ND, MacGregor GA (2012) Dietary salt influences postprandial plasma sodium concentration and systolic blood pressure. Kidney Int 81:407–411
Titze J, Machnik A (2010) Sodium sensing in the interstitium and relationship to hypertension. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 19:385–392
Van Huysse JW, Amin MS, Yang B, Leenen FH (2012) Salt-induced hypertension in a mouse model of Liddle syndrome is mediated by epithelial sodium channels in the brain. Hypertension 60:691–696
Verrey F, Loffing J, Zecevic M, Heitzmann D, Staub O (2003) SGK1: aldosterone-induced relay of Na + transport regulation in distal kidney nephron cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 13:21–28
Volk T, Konstas A-A, Bassalaý P, Ehmke H, Korbmacher C (2000) Extracellular Na+ removal reduces 'run-down' of epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Pflugers Arch 447:884–894
Volk T, Konstas AA, Bassalay P, Ehmke H, Korbmacher C (2004) Extracellular Na + removal attenuates rundown of the epithelial Na + -channel (ENaC) by reducing the rate of channel retrieval. Pflugers Arch 447:884–894
Wang S, Meng F, Mohan S, Champaneri B, Gu Y (2009) Functional ENaC channels expressed in endothelial cells: a new candidate for mediating shear force. Microcirculation 16:276–287
Warnock DG (2013) The amiloride-sensitive endothelial sodium channel and vascular tone. Hypertension 61:952–954
Wildling L, Hinterdorfer P, Kusche-Vihrog K, Treffner Y, Oberleithner H (2009) Aldosterone receptor sites on plasma membrane of human vascular endothelium detected by a mechanical nanosensor. Pflugers Arch 458:223–230
Young MJ, Rickard AJ (2012) Mechanisms of mineralocorticoid salt-induced hypertension and cardiac fibrosis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 350:248–255
Zhou ZH, Bubien JK (2001) Nongenomic regulation of ENaC by aldosterone. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 281:C1118–C1130
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Koselleck-OB 63/18, KU 1496/7-1), the ‘Innovative Medical Research’ of the University of Muenster Medical School (KU 120808) and the Else-Kröner-Fresenius Stiftung (2010 A116).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kusche-Vihrog, K., Jeggle, P. & Oberleithner, H. The role of ENaC in vascular endothelium. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 466, 851–859 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1356-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1356-3