Abstract
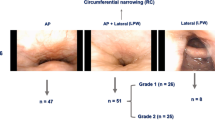
This prospective study aimed to evaluate the relationship between sleep endoscopy findings, the apnea–hypopnea index (AHI) or the Epworth sleepiness scale in patients and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS). Patients with symptoms of OSAS were searched, and their polysomnography findings, Epworth sleepiness scales and sleep endoscopy findings were recorded. Those who were diagnosed with mild, moderate or heavy OSAS were included in the study. Patients included in the study were observed under sedative-induced sleep in the operation room using flexible nasopharyngoscopy. The obstruction levels and degrees were recorded and compared with other variables. Of the 88 patients included in the study, 67 (76.1 %) were male, and 21 (23.9 %) were female. The mean age (±standard deviation) of all 88 patients was 43.77 ± 10.07 years (range 21–65 years). Sleep endoscopy findings were classified as uvulopalatal, lateral pharyngeal, tongue base and laryngeal collapses. The Epworth sleepiness scale showed no significant correlation with the sleep endoscopy findings. No significant relationship was found between the AHI and collapses in the uvulopalatal, lateral and laryngeal zones (p > 0.05). However, tongue base collapse was correlated with AHI (p < 0.05). AHI increased with the degree of collapse in the tongue base. No meaningful relationship was noted among the Epworth sleepiness scale, AHI, and number of involved zones (p > 0.05). The degree of collapse in the related zones was not meaningfully associated with AHI, which is accepted as the indicator of disease severity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Croft CB, Pringle M (1990) Sleep nasendoscopy: a technique od assessment in snoring and obstructive sleep apnoea. Clin Otolaryngol 16:504–509
Johns MW (1991) A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep 14:540–545
Vroeqop et al (2013) Observer variation in drug-induced sleep endoscopy: experienced versus nonexperienced ear, nose, and throat surgeons. Sleep 36:947–953
Sher AE, Schechtman KB, Piccirillo JF (1996) The efficacy of surgical modifications of the upper airway in adults with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep 19:156–177
Rabelo et al (2013) Polysomnographic evaluation of propofol-induced sleep in patients with respiratory sleep disorders and controls. Laryngoscope 123:2300–2305
Rodrigez-Bruno K, Goldberg AN, McCulloch EC, Kezirian EJ (2009) Test-retest reliability of drug induced sleep edoscopy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 140:646–651
Cavaliere M, Russo F, Iemma M (2013) Awake versus drug-induced sleep endoscopy: evaluation of airway obstruction in obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. Laryngoscope 123:2315–2318
Pringle MB, Croft CB (1991) A comparison of sleep nasendoscopy and Muller manoeuvre. Clin Otolaryngol 16:559–562
Marchese-Ragona et al (2013) Sleep-related adductor laryngeal dystonia causing sleep apnea: a sleep-related breathing disorder diagnosed with sleep endoscopy and treated with botulinum toxin. Laryngoscope 123:1560–1563
Hessel NS, de Vries N (2013) Results of uvulopalatopharynoplasty after diagnostic workup with polysomnography and sleep endoscopy: a report of 136 snoring patients. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 260:91–95
Hong SD et al (2013) Change of obstruction level during drug-induced sleep endoscopy according to sedation depth in obstructive sleep apnea. Laryngoscope 123:2896–2899
Borek RC et al (2012) Quantitative airway analysis during drug-induced sleep endoscopy for evaluation of sleep apnea. Laryngoscope 122:2592–2599
Abdullah VJ, Lee DLY, van Hasselt CA (2012) Sleep endoscopy with midazolam: sedation level evaluation with bispectral analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 148:331–337
Heo SJ, Park CM, King JS (2013) Time-dependent changes in the obstruction pattern during drug-induced sleep endoscopy. Am J Otolaryngol 35(1):42–47
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests and any financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belgü, A.U., Erdoğan, B., San, T. et al. The relationship between AHI, Epworth scores and sleep endoscopy in patients with OSAS. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272, 241–245 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3220-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3220-2