Abstract
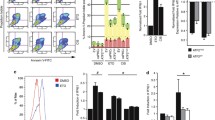
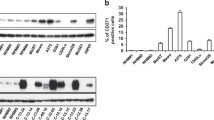
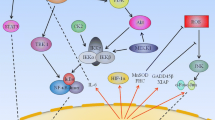
Owing to activation of several resistance-mediating pathways including NF-κB signaling, metastasized melanoma is almost universally resistant against chemotherapy. Given that blocking of NF-κB either by proteasome-, pan-IKK- or selective IKKβ-inhibitors may increase the susceptibility of melanoma cells to chemotherapy, we have assessed the role of the second kinase within the IKK complex, IKKα. While expression of IKKα and overall activation of NF-κB were heterogeneous, the IKKα-specific p100/p52 processing was detected in a small subset of melanomas (1/9 primary and 1/12 metastatic melanomas) as well as in 1/8 melanoma cell lines. Down-modulation of IKKα by siRNA resulted in diminution of doxorubicin-induced NF-κB activation, constitutive and TNFα-stimulated expression of CXCL8 and ICAM-1, and cell migration. In contrast, overexpression of IKKα in melanoma cells did not significantly affect progression-related functions. Thus, IKKα may be a worthwhile target only in selected individualized therapies but not in general melanoma therapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amschler K, Schön MP, Pletz N, Wallbrecht K, Erpenbeck L, Schön M (2010) NF-kappaB inhibition through proteasome inhibition or IKKbeta blockade increases the susceptibility of melanoma cells to cytostatic treatment through distinct pathways. J Invest Dermatol 130:1073–1086
Amundson SA, Do KT, Vinikoor LC, Lee RA, Koch-Paiz CA, Ahn J, Reimers M, Chen Y, Scudiero DA, Weinstein JN, Trent JM, Bittner ML, Meltzer PS, Fornace AJ Jr (2008) Integrating global gene expression and radiation survival parameters across the 60 cell lines of the National Cancer Institute Anticancer Drug Screen. Cancer Res 68:415–424
Chua R, Setzer S, Govindarajan B, Sexton D, Cohen C, Arbiser JL (2009) Maspin expression, angiogenesis, prognostic parameters, and outcome in malignant melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol 60:758–766
De Donatis GM, Pape EL, Pierron A, Cheli Y, Hofman V, Hofman P, Allegra M, Zahaf K, Bahadoran P, Rocchi S, Bertolotto C, Ballotti R, Passeron T (2016) NF-kB2 induces senescence bypass in melanoma via a direct transcriptional activation of EZH2. Oncogene 35:2735–2745
Diehl JA (2002) Cycling to cancer with cyclin D1. Cancer Biol Ther 1:226–231
Guo F, Kang S, Zhou P, Guo L, Ma L, Hou J (2011) Maspin expression is regulated by the non-canonical NF-kappaB subunit in androgen-insensitive prostate cancer cell lines. Mol Immunol 49:8–17
Huang WC, Hung MC (2013) Beyond NF-kappaB activation: nuclear functions of IkappaB kinase alpha. J Biomed Sci 20:3
Johnson JP, Stade BG, Holzmann B, Schwable W, Riethmüller G (1989) De novo expression of intercellular-adhesion molecule 1 in melanoma correlates with increased risk of metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:641–644
Kwak YT, Li R, Becerra CR, Tripathy D, Frenkel EP, Verma UN (2005) IkappaB kinase alpha regulates subcellular distribution and turnover of cyclin D1 by phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 280:33945–33952
Kwong LN, Davies MA (2014) Targeted therapy for melanoma: rational combinatorial approaches. Oncogene 33:1–9
Li Q, Lu Q, Hwang JY, Büscher D, Lee KF, Izpisua-Belmonte JC, Verma IM (1999) IKK1-deficient mice exhibit abnormal development of skin and skeleton. Genes Dev 13:1322–1328
Liu B, Park E, Zhu F, Bustos T, Liu J, Shen J, Fischer SM, Hu Y (2006) A critical role for I kappaB kinase alpha in the development of human and mouse squamous cell carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:17202–17207
Liu F, Xia Y, Parker AS, Verma IM (2012) IKK biology. Immunol Rev 246(1):239–253
Luo JL, Tan W, Ricono JM, Korchynskyi O, Zhang M, Gonias SL, Cheresh DA, Karin M (2007) Nuclear cytokine-activated IKKalpha controls prostate cancer metastasis by repressing Maspin. Nature 446:690–694
Madonna G, Ullman CD, Gentilcore G, Palmieri G, Ascierto PA (2012) NF-kappaB as potential target in the treatment of melanoma. J Transl Med 10:53
Mahato R, Qin B, Cheng K (2011) Blocking IKKalpha expression inhibits prostate cancer invasiveness. Pharm Res 28:1357–1369
Min FL, Zhang H, Li WJ, Gao QX, Zhou GM (2005) Effect of exogenous wild-type p53 on melanoma cell death pathways induced by irradiation at different linear energy transfer. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 41:284–288
Oeckinghaus A, Ghosh S (2009) The NF-kappaB family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1:a000034
Perkins ND (2007) Integrating cell-signalling pathways with NF-kappaB and IKK function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:49–62
Pletz N, Schön M, Ziegelbauer K, Emmert S, Liu N, Dobbelstein M, Schön MP (2012) Doxorubicin-induced activation of NF-kappaB in melanoma cells is abrogated by inhibition of IKKbeta, but not by a novel IKKalpha inhibitor. Exp Dermatol 21:301–304
Schneider P, Schön M, Pletz N, Seitz CS, Liu N, Ziegelbauer K, Zachmann K, Emmert S, Schön MP (2014) The novel PI3 kinase inhibitor, BAY 80-6946, impairs melanoma growth in vivo and in vitro. Exp Dermatol 23:579–584
Schön M, Wienrich BG, Kneitz S, Sennefelder H, Amschler K, Vöhringer V, Weber O, Stiewe T, Ziegelbauer K, Schön MP (2008) KINK-1, a novel small-molecule inhibitor of IKKbeta, and the susceptibility of melanoma cells to antitumoral treatment. J Natl Cancer Inst 100:862–875
Senftleben U, Cao Y, Xiao G, Greten FR, Krahn G, Bonizzi G, Chen Y, Hu Y, Fong A, Sun SC, Karin M (2001) Activation by IKKalpha of a second, evolutionary conserved, NF-kappa B signaling pathway. Science 293:1495–1499
Tanaka M, Fuentes ME, Yamaguchi K, Durnin MH, Dalrymple SA, Hardy KL, Goeddel DV (1999) Embryonic lethality, liver degeneration, and impaired NF-kappa B activation in IKK-beta-deficient mice. Immunity 10:421–429
Ueda Y, Richmond A (2006) NF-kappaB activation in melanoma. Pigment Cell Res 19:112–124
Wu S, Singh S, Varney ML, Kindle S, Singh RK (2012) Modulation of CXCL-8 expression in human melanoma cells regulates tumor growth, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis. Cancer Med 1:306–317
Yang H, Higgins B, Kolinsky K, Packman K, Go Z, Iyer R, Kolis S, Zhao S, Lee R, Grippo JF, Schostack K, Simcox ME, Heimbrook D, Bollag G, Su F (2010) RG7204 (PLX4032), a selective BRAFV600E inhibitor, displays potent antitumor activity in preclinical melanoma models. Cancer Res 70:5518–5527
Yang J, Splittgerber R, Yull FE, Kantrow S, Ayers GD, Karin M, Richmond A (2010) Conditional ablation of Ikkb inhibits melanoma tumor development in mice. J Clin Invest 120:2563–2574
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to B. Messerschmidt for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dewert, N., Amschler, K., Lorenz, V. et al. The IKKα-dependent non-canonical pathway of NF-κB activation is constitutively active and modulates progression-related functions in a subset of human melanomas. Arch Dermatol Res 308, 733–742 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-016-1696-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-016-1696-x