Abstract
Purpose
To identify the efficacy of isolated trochleoplasty (TP) as an independent treatment for severe trochlear dysplasia compared with TP combined with medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) reconstruction.
Methods
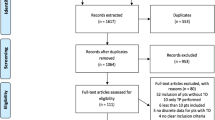
Search of current literature using terms (trochleoplasty and medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction) in the electronic search engines PubMed and Embase, and Medline databases was performed on February 25, 2018, and it yielded 515 abstracts for review. At the end of the search, six articles met specific inclusion criteria and were included in this review. Means were calculated for population size, age and follow-up time. The Kujala score was analyzed as the primary clinical outcome parameter in the meta-analysis. Pooled estimates were calculated for postoperative complications.
Results
Six studies with a total of 192 knees (168 patients) were included in this analysis. The isolated TP group comprised of 3 articles with a total of 111 knees, and the TP combined with MPFL group comprised of 3 articles with a total of 81 knees. At the final follow-up, the preoperative Kujala score increased significantly by 21.39 (95% CI 18.94, 23.84; P < 0.00001) points in the isolated TP group and by 24.91 (95% CI 15.47, 34.36; P < 0.00001) points in the TP combined with MPFL group. The rates of subjective patellar instability including subluxation and anterior knee pain were 1.03% and8.45% respectively. Meanwhile, the rate of objective patellar redislocation was 2.06% in isolated TP group and 0% in TP combined with MFPL group. A total of 8.24% returned to the operating room for additional procedures in the isolated TP group and 7.04% in the TP combined with MPFL group.
Conclusion
Trochleoplasty is a useful and reliable surgical technique to improve patellofemoral instability in patients with a dysplastic trochlea. However, it as isolated treatment for patients has lower outcome and higher residual instability compared with combined MPFL and trochleoplasty.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balcarek P, Rehn S, Howells NR, et al (2016) Results of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction compared with trochleoplasty plus individual extensor apparatus balancing in patellar instability caused by severe trochlear dysplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc
Bartsch A, Lubberts B, Mumme M, Egloff C, Pagenstert G (2018) Does patella alta lead to worse clinical outcome in patients who undergo isolated medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction? A systematic review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg
Beaufils P, Thaunat M, Pujol N, Scheffler S, Rossi R, Carmont M (2012) Trochleoplasty in major trochlear dysplasia: current concepts. Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Ther Technol SMARTT 4:7
Blond L, Haugegaard M (2014) Combined arthroscopic deepening trochleoplasty and reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament for patients with recurrent patella dislocation and trochlear dysplasia. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22(10):2484–2490
Blond L, Schottle PB (2010) The arthroscopic deepening trochleoplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18(4):480–485
Bollier M, Fulkerson JP (2011) The role of trochlear dysplasia in patellofemoral instability. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 19(1):8–16
Camathias C, Studer K, Kiapour A, Rutz E, Vavken P (2016) Trochleoplasty as a solitary treatment for recurrent patellar dislocation results in good clinical outcome in adolescents. Am J Sports Med 44(11):2855–2863
Dejour D, Byn P, Ntagiopoulos PG (2013) The Lyon's sulcus-deepening trochleoplasty in previous unsuccessful patellofemoral surgery. Int Orthop 37(3):433–439
Dejour D, Saggin P (2010) The sulcus deepening trochleoplasty: the Lyon's procedure. Int Orthop 34(2):311–316
Fitzpatrick CK, Steensen RN, Tumuluri A, Trinh T, Bentley J, Rullkoetter PJ (2016) Computational analysis of factors contributing to patellar dislocation. J Orthop Res 34(3):444–453
Frosch KH, Schmeling A (2016) A new classification system of patellar instability and patellar maltracking. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 136(4):485–497
Fucentese SF, Zingg PO, Schmitt J, Pfirrmann CW, Meyer DC, Koch PP (2011) Classification of trochlear dysplasia as predictor of clinical outcome after trochleoplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19(10):1655–1661
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J et al (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med 6(7):e1000100
Lippacher S, Dejour D, Elsharkawi M et al (2012) Observer agreement on the Dejour trochlear dysplasia classification: a comparison of true lateral radiographs and axial magnetic resonance images. Am J Sports Med 40(4):837–843
Lobner S, Krauss C, Reichwein F, Patzer T, Nebelung W, Venjakob AJ (2017) Surgical treatment of patellar instability: clinical and radiological outcome after medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction and tibial tuberosity medialisation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 137(8):1087–1095
Longo UG, Berton A, Salvatore G et al (2016) Medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction combined with bony procedures for patellar instability: current indications, outcomes, and complications. Arthrosc J Arthrosc Relat Surg 32(7):1421–1427
Longo UG, Rizzello G, Ciuffreda M et al (2016) Elmslie-Trillat, Maquet, Fulkerson, Roux Goldthwait, and other distal realignment procedures for the management of patellar dislocation: systematic review and quantitative synthesis of the literature. Arthrosc J Arthrosc Relat Surg 32(5):929–943
Longo UG, Vincenzo C, Mannering N, et al. (2017) Trochleoplasty techniques provide good clinical results in patients with trochlear dysplasia. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc
Nelitz M, Dreyhaupt J, Lippacher S (2013) Combined trochleoplasty and medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction for recurrent patellar dislocations in severe trochlear dysplasia: a minimum 2-year follow-up study. Am J Sports Med 41(5):1005–1012
Ntagiopoulos PG, Byn P, Dejour D (2013) Midterm results of comprehensive surgical reconstruction including sulcus-deepening trochleoplasty in recurrent patellar dislocations with high-grade trochlear dysplasia. Am J Sports Med 41(5):998–1004
Ntagiopoulos PG, Dejour D (2014) Current concepts on trochleoplasty procedures for the surgical treatment of trochlear dysplasia. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22(10):2531–2539
Rouanet T, Gougeon F, Fayard JM, Remy F, Migaud H, Pasquier G (2015) Sulcus deepening trochleoplasty for patellofemoral instability: a series of 34 cases after 15 years postoperative follow-up. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res OTSR 101(4):443–447
Ryzek DF, Schottle P (2015) Patellofemoral dysfunction in sports trochleoplasty: indications and techniques. J Knee Surg 28(4):297–302
Schneider DK, Grawe B, Magnussen RA et al (2016) Outcomes after isolated medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction for the treatment of recurrent lateral patellar dislocations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med 44(11):2993–3005
Schottle PB, Fucentese SF, Pfirrmann C, Bereiter H, Romero J (2005) Trochleaplasty for patellar instability due to trochlear dysplasia: a minimum 2-year clinical and radiological follow-up of 19 knees. Acta Orthop 76(5):693–698
Senavongse W, Amis AA (2005) The effects of articular, retinacular, or muscular deficiencies on patellofemoral joint stability: a biomechanical study in vitro. J Bone Jt Surg Br 87(4):577–582
Slim K, Nini E, Forestier D, Kwiatkowski F, Panis Y, Chipponi J (2003) Methodological index for non-randomized studies (minors): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J Surg 73(9):712–716
Thaunat M, Bessiere C, Pujol N, Boisrenoult P, Beaufils P (2011) Recession wedge trochleoplasty as an additional procedure in the surgical treatment of patellar instability with major trochlear dysplasia: early results. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res OTSR 97(8):833–845
Utting MR, Mulford JS, Eldridge JD (2008) A prospective evaluation of trochleoplasty for the treatment of patellofemoral dislocation and instability. J Bone Jt Surg Br 90(2):180–185
Verdonk R, Jansegers E, Stuyts B (2005) Trochleoplasty in dysplastic knee trochlea. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 13(7):529–533
von Knoch F, Bohm T, Burgi ML, von Knoch M, Bereiter H (2006) Trochleaplasty for recurrent patellar dislocation in association with trochlear dysplasia A 4- to 14-year follow-up study. J Bone Jt Surg Br 88(10):1331–1335
Weber AE, Nathani A, Dines JS et al (2016) An algorithmic approach to the management of recurrent lateral patellar dislocation. J Bone Jt Surg Am 98(5):417–427
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (No. 2016JM8138).
Funding
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (No. 2016JM8138).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, B., Zhang, X., Zhang, L. et al. Isolated trochleoplasty for recurrent patellar dislocation has lower outcome and higher residual instability compared with combined MPFL and trochleoplasty: a systematic review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 139, 1617–1624 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-019-03244-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-019-03244-1