Abstract
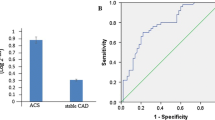
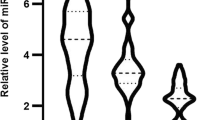
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression. It seems that microRNA-21 (miR-21) and Visfatin, a novel adipocytokine, play roles in inflammation and atherosclerosis. The aim of this study was to investigate the association of miR-21 with Visfatin, inflammation, atherosclerosis and acute coronary syndrome (ACS). Based on coronary angiography and electrocardiogram (ECG), 53 patients with ACS and 52 patients with stable CAD were enrolled in this study. We assayed serum miR-21, Visfatin, and routine chemistries using quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (QRT-PCR), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and automated analyzer, respectively. We used a regression analysis to describe the relationship between the variables. Serum miR-21 level in 2−ΔCt value was significantly higher in ACS patients (10.52 ± 1.01-fold) than the stable CAD patients (4.4 ± 0.79-fold) (F = 4.59, p < 0.001). In addition, serum Visfatin was significantly higher in ACS patients (17.5 ± 0.61 ng/ml) than the stable CAD patients (12.7 ± 0.49 ng/ml) (F = 2.62, p < 0.001). Furthermore, the serum miR-21 level correlated positively with serum Visfatin level (r = 0.26, p = 0.008), hs-CRP (r = 0.29, p = 0.003), age (r = 0.21, p = 0.034) and negatively with HDL-cholesterol (r = -0.28, p = 0.004). We concluded that the increased serum miR-21 and Visfatin may be involved in the pathogenesis of ACS through promoting inflammation or may result from inflammatory responses to ACS. Furthermore, the potential role of miR-21 and Visfatin in plaque instability and inflammation warrants further investigations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sarrafzadegan N, Gotay C (2015) CVD prevention in 2014: Advances in the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol 12:71–73
Anwaruddin S, Askari AT, Topol EJ (2007) Redefining risk in acute coronary syndromes using molecular medicine. J Am Coll Cardiol 49:279–289
Alfieri O, Mayosi BM, Park S-J, Sarrafzadegan N, Virmani R (2014) Exploring unknowns in cardiology. Nat Rev Cardiol 11:664–670
Armstrong EJ, Morrow DA, Sabatine MS (2006) Inflammatory biomarkers in acute coronary syndromes part I: introduction and cytokines. Circulation 113:e72–e75
Varnava AM, Mills PG, Davies MJ (2002) Relationship between coronary artery remodeling and plaque vulnerability. Circulation 105:939–943
Sakamoto N, Hoshino Y, Misaka T, Mizukami H, Suzuki S, Sugimoto K, Yamaki T, Kunii H, Nakazato K, Suzuki H, Saitoh SI (2014) Serum tenascin-C level is associated with coronary plaque rupture in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Heart Vessels 29:165–170
W van Lammeren G, L Moll F, Jan De Borst G, PV de Kleijn D, PM de Vries JP, Pasterkamp G (2011) Atherosclerotic plaque biomarkers: beyond the horizon of the vulnerable plaque. Curr Cardiol Rev 7:22–27
Hellings WE, Peeters W, Moll FL, Pasterkamp G (2007) From vulnerable plaque to vulnerable patient: the search for biomarkers of plaque destabilization. Trends Cardiovasc Med 17:162–171
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Valencia-Sanchez MA, Liu J, Hannon GJ, Parker R (2006) Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and siRNAs. Genes Dev 20:515–524
Small EM, Olson EN (2011) Pervasive roles of microRNAs in cardiovascular biology. Nature 469:336–342
Thum T, Galuppo P, Wolf C, Fiedler J, Kneitz S, van Laake LW, Doevendans PA, Mummery CL, Borlak J, Haverich A, Gross C (2007) MicroRNAs in the human heart a clue to fetal gene reprogramming in heart failure. Circulation 116:258–267
Kumarswamy R, Volkmann I, Thum T (2011) Regulation and function of miRNA-21 in health and disease. RNA Biol 8:706–713
Ji R, Cheng Y, Yue J, Yang J, Liu X, Chen H, Dean DB, Zhang C (2007) MicroRNA expression signature and antisense-mediated depletion reveal an essential role of MicroRNA in vascular neointimal lesion formation. Circ Res 100:1579–1588
Suárez Y, Fernández-Hernando C, Pober JS, Sessa WC (2007) Dicer dependent microRNAs regulate gene expression and functions in human endothelial cells. Circ Res 100:1164–1173
Kim YJ, Hwang SJ, Bae YC, Jung JS (2009) MiR-21 regulates adipogenic differentiation through the modulation of TGF-β signaling in mesenchymal stem cells derived from human adipose tissue. Stem Cells 27:3093–3102
Cheng KH, Chu CS, Lee KT, Lin TH, Hsieh CC, Chiu CC, Voon WC, Sheu SH, Lai WT (2008) Adipocytokines and proinflammatory mediators from abdominal and epicardial adipose tissue in patients with coronary artery disease. Int J Obes (Lond) 32:268–274
Fukuhara A, Matsuda M, Nishizawa M, Segawa K, Tanaka M, Kishimoto K, Matsuki Y, Murakami M, Ichisaka T, Murakami H, Watanabe E (2005) Visfatin: a protein secreted by visceral fat that mimics the effects of insulin. Science 307:426–430
Moschen AR, Kaser A, Enrich B, Mosheimer B, Theurl M, Niederegger H, Tilg H (2007) Visfatin, an adipocytokine with proinflammatory and immunomodulating properties. J Immunol 178:1748–1758
Jia SH, Li Y, Parodo J, Kapus A, Fan L, Rotstein OD, Marshall JC (2004) Pre–B cell colony–enhancing factor inhibits neutrophil apoptosis in experimental inflammation and clinical sepsis. J Clin Invest 113:1318–1327
Dahl TB, Yndestad A, Skjelland M, Øie E, Dahl A, Michelsen A, Damås JK, Tunheim SH, Ueland T, Smith C, Bendz B (2007) Increased expression of Visfatin in macrophages of human unstable carotid and coronary atherosclerosis possible role in inflammation and plaque destabilization. Circulation 115:972–980
Dattaroy D, Pourhoseini S, Das S, Alhasson F, Seth RK, Nagarkatti M, Michelotti GA, Diehl AM, Chatterjee S (2015) Micro-RNA 21 inhibition of SMAD7 enhances fibrogenesis via leptin-mediated NADPH oxidase in experimental and human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 308:G298–G312
Estep JM, Goodman Z, Sharma H, Younossi E, Elarainy H, Baranova A, Younossi Z (2015) Adipocytokine expression associated with miRNA regulation and diagnosis of NASH in obese patients with NAFLD. Liver Int 35:1367–1372
Estep JM, Goodman Z, Sharma H, Younossi E, Elarainy H, Baranova A, Younossi Z (2015) Adipocytokine expression associated with miRNA regulation and diagnosis of NASH in obese patients with NAFLD. Liver Int 35:1367–1372
Levey AS, Coresh J, Balk E, Kausz AT, Levin A, Steffes MW, Hogg RJ, Perrone RD, Lau J, Eknoyan G (2003) National Kidney Foundation practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Ann Intern Med 139:137–147
American Diabetes Association (2013) Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 36(Suppl 1):S67–S74
Wintersperger BJ, Nikolaou K (2005) Basics of cardiac MDCT: techniques and contrast application. Eur Radiol 15:B2–B9
Desjardins P, Conklin D (2010) NanoDrop microvolume quantitation of nucleic acids. J Vis Exp 45
Becker C, Hammerle-Fickinger A, Riedmaier I, Pfaffl MW (2010) mRNA and microRNA quality control for RT-qPCR analysis. Methods 50:237–243
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Kroh EM, Parkin RK, Mitchell PS, Tewari M (2010) Analysis of circulating microRNA biomarkers in plasma and serum using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR). Methods 50:298–301
Anzai A, Maekawa Y, Kodaira M, Mogi S, Arai T, Kawakami T, Kanazawa H, Hayashida K, Yuasa S, Kawamura A, Fukuda K (2015) Prognostic implications of optimal medical therapy in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention for acute coronary syndrome in octogenarians. Heart Vessels 30:186–192
Libby P (2012) Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32:2045–2051
Hosin AA, Prasad A, Viiri LE, Davies AH, Shalhoub J (2014) MicroRNAs in atherosclerosis. J Vasc Res 51:338–349
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K, Guo J, Zhang Y, Chen J, Guo X, Li Q (2008) Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res 18:997–1006
Kadoglou NP, Gkontopoulos A, Kapelouzou A, Fotiadis G, Theofilogiannakos EK, Kottas G, Lampropoulos S (2011) Serum levels of vaspin and Visfatin in patients with coronary artery disease—Kozani study. Clin Chim Acta 412:48–52
Santovito D, Mezzetti A, Cipollone F (2012) MicroRNAs and atherosclerosis: new actors for an old movie. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 22:937–943
Small EM, Frost RJ, Olson EN (2010) MicroRNAs add a new dimension to cardiovascular disease. Circulation 121:1022–1032
Elzenaar I, Pinto YM, Oort R (2013) MicroRNAs in heart failure: new targets in disease management. Clin Pharmacol Ther 94:480–489
Wang GK, Zhu JQ, Zhang JT, Li Q, Li Y, He J, Qin YW, Jing Q (2010) Circulating microRNA: a novel potential biomarker for early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction in humans. Eur Heart J 31:659–666
Selcuklu SD, Donoghue MT, Spillane C (2009) miR-21 as a key regulator of oncogenic processes. Biochem Soc Trans 37:918–925
Zhang C (2008) MicroRNomics: a newly emerging approach for disease biology. Physiol Genomics 33:139–147
Raitoharju E, Oksala N, Lehtimäki T (2013) MicroRNAs in the atherosclerotic plaque. Clin Chem 59:1708–1721
Tsai P-C, Liao Y-C, Wang Y-S, Lin H-F, Lin R-T, Juo S-H (2013) Serum microRNA-21 and microRNA-221 as potential biomarkers for cerebrovascular disease. J Vasc Res 50(4):346–354
Fan X, Wang E, Wang X, Cong X, Chen X (2014) MicroRNA-21 is a unique signature associated with coronary plaque instability in humans by regulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 via reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs. Exp Mol Pathol 96:242–249
Sethi JK, Vidal-Puig A (2005) Visfatin: the missing link between intra-abdominal obesity and diabetes? Trends Mol Med 11:344–347
Adya R, Tan BK, Punn A, Chen J, Randeva HS (2008) Visfatin induces human endothelial VEGF and MMP-2/9 production via MAPK and PI3 K/Akt signaling pathways: novel insights into Visfatin-induced angiogenesis. Cardiovasc Res 78:356–365
Van der Wal AC, Becker AE (1999) Atherosclerotic plaque rupture–pathologic basis of plaque stability and instability. Cardiovasc Res 41:334–344
Olivares R, Ducimetière P, Claude JR (1993) Monocyte count: a risk factor for coronary heart disease? Am J Epidemiol 137:49–53
Nian M, Lee P, Khaper N, Liu P (2004) Inflammatory cytokines and postmyocardial infarction remodeling. Circ Res 94:1543–1553
Liu SW, Qiao SB, Yuan JS, Liu DQ (2009) Association of plasma visfatin levels with inflammation, atherosclerosis, and acute coronary syndromes (ACS) in humans. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 71:202–207
Assmann G, Schulte H, von Eckardstein A, Huang Y (1996) High-density lipoprotein cholesterol as a predictor of coronary heart disease risk. The PROCAM experience and pathophysiological implications for reverse cholesterol transport. Atherosclerosis 124:S11–S20
Keller P, Gburcik V, Petrovic N, Gallagher IJ, Nedergaard J, Cannon B, Timmons JA (2011) Gene-chip studies of adipogenesis regulated microRNAs in mouse primary adipocytes and human obesity. BMC Endocr Disord 11:7
Kida K, Nakajima M, Mohri T, Oda Y, Takagi S, Fukami T, Yokoi T (2011) PPARα is regulated by miR-21 and miR-27b in human liver. Pharm Res 28:2467–2476
Yang CC, Deng SJ, Hsu CC, Liu BH, Lin EC, Cheng WT, Wang PH, Ding ST (2010) Visfatin regulates genes related to lipid metabolism in porcine adipocytes. J Anim Sci 88:3233–3241
Acknowledgments
The authors express their heartfelt gratitude to the staff and members of the Isfahan Cardiovascular Research Institute and Isfahan School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences for their assistance in various measurements and other organizational aspects of this study. We also thank all the patients who participated in this study. This project supported by a Grant 394289 from the Isfahan University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Darabi, F., Aghaei, M., Movahedian, A. et al. Association of serum microRNA-21 levels with Visfatin, inflammation, and acute coronary syndromes. Heart Vessels 32, 549–557 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-016-0913-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-016-0913-z