Abstract
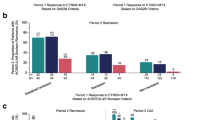
In this transglobal, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, treat-to-target study, the maintenance of efficacy was compared between biologic–and biologic-free–disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) combination regimens after low disease activity (LDA) was achieved with biologic DMARD induction therapy. Patients with moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate therapy received open-label etanercept 50 mg subcutaneously once weekly plus methotrexate with or without other conventional synthetic (cs) DMARDs for 24 weeks. Patients achieving LDA [disease activity score in 28 joints based on erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-ESR) <3.2] at week 24 were randomized to receive etanercept–methotrexate combination therapy or placebo–methotrexate combination therapy, with or without other csDMARDs, for 28 weeks. In the open-label period, 72% of patients achieved DAS28-ESR LDA at week 24. Patients enrolled in the double-blind period had long-standing rheumatoid arthritis and high disease activity at baseline (mean duration, 8.1 years; DAS28-ESR, 6.4). In the etanercept and placebo combination groups, 44% versus 17% achieved DAS28-ESR LDA and 34 versus 13% achieved DAS28-ESR remission at week 52 (p < 0.001). Adverse events were reported in 37 and 43%, serious adverse events in 0 and 4%, and serious infections in 0 and 2% in these groups, respectively, in the double-blind period. After induction of response with etanercept combination therapy following a treat-to-target approach in patients with long-standing rheumatoid arthritis and high disease activity at baseline, the etanercept combination regimen was significantly more effective in maintaining LDA and remission than a biologic-free regimen.
ClinicalTrials.gov identifier. NCT01578850.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
van der Heijde DM, van Riel PL, van Leeuwen MA, van't Hof MA, van Rijswijk MH, van de Putte LB (1991) Older versus younger onset rheumatoid arthritis: results at onset and after 2 years of a prospective followup study of early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 18:1285–1289
Plant MJ, Jones PW, Saklatvala J, Ollier WE, Dawes PT (1998) Patterns of radiological progression in early rheumatoid arthritis: results of an 8 year prospective study. J Rheumatol 25:417–426
Singh JA, Saag KG, Bridges SL Jr, Akl EA, Bannuru RR, Sullivan MC, Vaysbrot E, McNaughton C, Osani M, Shmerling RH, Curtis JR, Furst DE et al (2016) 2015 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 68:1–26. doi:10.1002/art.39480
Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, Cohen SB, Pavelka K, van Vollenhoven R, Sharp J, Perez JL, Spencer-Green GT (2006) The PREMIER study: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trial of combination therapy with adalimumab plus methotrexate versus methotrexate alone or adalimumab alone in patients with early, aggressive rheumatoid arthritis who had not had previous methotrexate treatment. Arthritis Rheum 54:26–37. doi:10.1002/art.21519
Emery P, Breedveld F, van der Heijde D, Ferraccioli G, Dougados M, Robertson D, Pedersen R, Koenig AS, Freundlich B (2010) Two-year clinical and radiographic results with combination etanercept-methotrexate therapy versus monotherapy in early rheumatoid arthritis: a two-year, double-blind, randomized study. Arthritis Rheum 62:674–682. doi:10.1002/art.27268
Kekow J, Moots RJ, Emery P, Durez P, Koenig A, Singh A, Pedersen R, Robertson D, Freundlich B, Sato R (2010) Patient-reported outcomes improve with etanercept plus methotrexate in active early rheumatoid arthritis and the improvement is strongly associated with remission: the COMET trial. Ann Rheum Dis 69:222–225. doi:10.1136/ard.2008.102509
Smolen JS, Han C, van der Heijde DM, Emery P, Bathon JM, Keystone E, Maini RN, Kalden JR, Aletaha D, Baker D, Han J, Bala M et al (2009) Radiographic changes in rheumatoid arthritis patients attaining different disease activity states with methotrexate monotherapy and infliximab plus methotrexate: the impacts of remission and tumour necrosis factor blockade. Ann Rheum Dis 68:823–827. doi:10.1136/ard.2008.090019
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH, Luthra HS et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324
Smolen JS, Landewe R, Breedveld FC, Buch M, Burmester G, Dougados M, Emery P, Gaujoux-Viala C, Gossec L, Nam J, Ramiro S, Winthrop K et al (2014) EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2013 update. Ann Rheum Dis 73:492–509. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204573
Lau CS, Chia F, Harrison A, Hsieh TY, Jain R, Jung SM, Kishimoto M, Kumar A, Leong KP, Li Z, Lichauco JJ, Louthrenoo W et al (2015) APLAR rheumatoid arthritis treatment recommendations. Int J Rheum Dis 18:685–713. doi:10.1111/1756-185X.12754
Smolen JS, Nash P, Durez P, Hall S, Ilivanova E, Irazoque-Palazuelos F, Miranda P, Park MC, Pavelka K, Pedersen R, Szumski A, Hammond C et al (2013) Maintenance, reduction, or withdrawal of etanercept after treatment with etanercept and methotrexate in patients with moderate rheumatoid arthritis (PRESERVE): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 381:918–929. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61811-X
Emery P, Hammoudeh M, FitzGerald O, Combe B, Martin-Mola E, Buch MH, Krogulec M, Williams T, Gaylord S, Pedersen R, Bukowski J, Vlahos B (2014) Sustained remission with etanercept tapering in early rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 371:1781–1792. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1316133
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank all patients who participated in the trial and all investigators and medical staff of all participating centers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Karel Pavelka has received honoraria for lectures and consultancies from Amgen, AbbVie, Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS), Merck Sharp & Dohme (MSD), and Pfizer. Nurullah Akkoç has received honoraria from and is an advisory board member for Pfizer, AbbVie, MSD, UCB, Novartis, and Amgen; research funding from Pfizer and UCB; and other grants from MSD. Cristiano Zerbini has received research grants from Novartis, Pfizer, BMS, Lilly, Amgen, Sanofi, and MSD; consulting fees from Pfizer, BMS, Lilly, and MSD; and is an advisory board member for Pfizer, Lilly, and Sanofi. Dmitry E. Karateev has received consulting and speakers’ bureau fees from AbbVie, BMS, Egis, Medac, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche. Mustafa Al-Maini and Evgeny L. Nasonov declare no conflicts of interest. Mahboob Rahman was an employee of Pfizer during the conception/conduct of the study and owns Pfizer stock. Ron Pedersen, Andrew Dinh, Qi Shen, Radu Vasilescu, Sameer Kotak, Ehab Mahgoub, and Bonnie Vlahos are employees of Pfizer and Pfizer stockholders.
Funding
This study was funded by Pfizer. Editorial/medical writing support was provided by Donna McGuire of Engage Scientific Solutions and was funded by Pfizer.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavelka, K., Akkoç, N., Al-Maini, M. et al. Maintenance of remission with combination etanercept–DMARD therapy versus DMARDs alone in active rheumatoid arthritis: results of an international treat-to-target study conducted in regions with limited biologic access. Rheumatol Int 37, 1469–1479 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-017-3749-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-017-3749-7