Abstract
Purpose
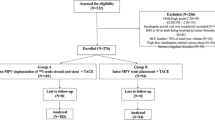
To investigate the feasibility and safety of a helical iodine-125 (I-125) seed implant combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with main portal vein tumor thrombus (MPVTT).
Methods
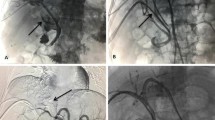
From December 2016 to February 2018, 26 cases of HCC with MPVTT patients were enrolled in this prospective study. Helical I-125 seed implants were placed into the portal vein through the percutaneous transhepatic route. Subsequently, TACE was performed. Follow-up with enhanced CT was performed every 6–8 weeks and TACE was repeated if the residual or recurrent tumor was found. Treatment response was measured with the modified response evaluation criteria in solid tumors. Complication rates and overall survival were also evaluated.
Results
Implantation and TACE were successful in all patients. There were no grade ≥ 3 complications observed in the patients. The objective response rates (ORR) and disease control rates (DCR) of MPVTT at 3 months after implantation were 42.3% and 84.6%, respectively, whereas ORR and DCR of the liver lesions were 34.6% and 46.2%, respectively. The median overall survival was 10.7 months (95% CI 6.2–15.2 months).
Conclusion
Helical I-125 seed implants can be safely placed into the human main portal vein. Helical I-125 seed implants combined with TACE for HCC with MPVTT are safe and feasible.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108.
Llovet JM, Bustamante J, Castells A, Vilana R, Ayuso Mdel C, Sala M, et al. Natural history of untreated nonsurgical hepatocellular carcinoma: rationale for the design and evaluation of therapeutic trials. Hepatology. 1999;29(1):62–7.
Villa E, Moles A, Ferretti I, Buttafoco P, Grottola A, Del Buono M, et al. Natural history of inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma: estrogen receptors’ status in the tumor is the strongest prognostic factor for survival. Hepatology. 2000;32(2):233–8.
Minagawa M, Makuuchi M. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma accompanied by portal vein tumor thrombus. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12(47):7561–7.
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(1):25–34.
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(4):378–90.
Huang M, Lin Q, Wang H, Chen J, Bai M, Wang L, et al. Survival benefit of chemoembolization plus Iodine125 seed implantation in unresectable hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma with PVTT: a retrospective matched cohort study. Eur Radiol. 2016;26(10):3428–36.
Zhang ZH, Zhang W, Gu JY, Liu QX, Ma JQ, Liu LX, et al. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombus with the use of iodine-125 seed strand implantation and transarterial chemoembolization: a propensity-score analysis. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2018;29(8):1085–93.
Geschwind JF, Kudo M, Marrero JA, Venook AP, Chen XP, Bronowicki JP, et al. TACE treatment in patients with sorafenib-treated unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in clinical practice: final analysis of GIDEON. Radiology. 2016;279(2):630–40.
Chao Y, Chung YH, Han G, Yoon JH, Yang J, Wang J, et al. The combination of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and sorafenib is well tolerated and effective in Asian patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: final results of the START trial. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(6):1458–67.
Yu JI, Park HC. Radiotherapy as valid modality for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(30):6851–63.
Zhang FJ, Li CX, Jiao DC, Zhang NH, Wu PH, Duan GF, et al. CT guided 125iodine seed implantation for portal vein tumor thrombus in primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Chin Med J (Engl). 2008;121(23):2410–4.
Luo J, Yan Z, Liu Q, Qu X, Wang J. Endovascular placement of iodine-125 seed strand and stent combined with chemoembolization for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombus in main portal vein. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2011;22(4):479–89.
Luo JJ, Zhang ZH, Liu QX, Zhang W, Wang JH, Yan ZP. Endovascular brachytherapy combined with stent placement and TACE for treatment of HCC with main portal vein tumor thrombus. Hepatol Int. 2016;10(1):185–95.
Lu J, Guo JH, Zhu HD, Zhu GY, Chen L, Teng GJ. Safety and efficacy of irradiation stent placement for malignant portal vein thrombus combined with transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: a single-center experience. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017;28(6):786–94 e3.
Wang C, Wang W, Shen J, Ren B, Zhu X, Ni C. Feasibility of helical I-125 seed implant in the portal vein. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2019;42(1):121–9.
Shuqun C, Mengchao W, Han C, Feng S, Jiahe Y, Guanghui D, et al. Tumor thrombus types influence the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma with the tumor thrombi in the portal vein. Hepatogastroenterology. 2007;54(74):499–502.
Yang M, Fang Z, Yan Z, Luo J, Liu L, Zhang W, et al. Transarterial chemoembolisation (TACE) combined with endovascular implantation of an iodine-125 seed strand for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumour thrombosis versus TACE alone: a two-arm, randomised clinical trial. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014;140(2):211–9.
Yao LH, Su L, Liu L, Sun HT, Wang JJ. Stenting of the portal vein combined with different numbers of iodine-125 seed strands: dosimetric analyses. Chin Med J (Engl). 2017;130(18):2183–9.
Lawrence TS, Robertson JM, Anscher MS, Jirtle RL, Ensminger WD, Fajardo LF. Hepatic toxicity resulting from cancer treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;31(5):1237–48.
Yamakado K, Tanaka N, Nakatsuka A, Matsumura K, Takase K, Takeda K. Clinical efficacy of portal vein stent placement in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma invading the main portal vein. J Hepatol. 1999;30(4):660–8.
Yamakado K, Nakatsuka A, Tanaka N, Fujii A, Terada N, Takeda K. Malignant portal venous obstructions treated by stent placement: significant factors affecting patency. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001;12(12):1407–15.
Yu TZ, Zhang W, Liu QX, Li WH, Ma JQ, Zhang ZH, et al. Endovascular brachytherapy combined with portal vein stenting and transarterial chemoembolization improves overall survival of hepatocellular carcinoma patients with main portal vein tumor thrombus. Oncotarget. 2017;8(7):12108–19.
Ling CC. Permanent implants using Au-198, Pd-103 and I-125: radiobiological considerations based on the linear quadratic model. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992;23(1):81–7.
Funding
This study was funded by Jiangsu Provincial Medical Talent funding (No. ZDRCA2016038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for Publication
Consent for publication was obtained for every individual person’s data included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Shen, J., Wang, C. et al. Safety and Feasibility of Helical I-125 Seed Implants Combined with Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization in Hepatocellular Carcinomas with Main Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 42, 1420–1428 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-019-02256-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-019-02256-z