Abstract
Background
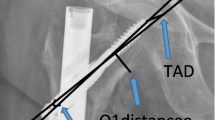
Periprosthetic femur fractures (PPFF) distal to a femoral stem are traditionally treated with open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) with plate and screws. To our knowledge, no studies exist comparing outcomes following ORIF vs retrograde intramedullary nails (RIMN) for this injury.
Methods
This is a retrospective comparison of PPFFs distal to a femoral stem treated by ORIF (n = 17) vs RIMN (n = 13). The primary outcome was unplanned re-operation.
Results
There was no difference in unplanned re-operation (17.6 vs 23.1%, p > 0.99), infection, nonunion, refracture, and alignment between groups. The RIMN group had shorter surgical time (89 vs 157 min, p < 0.01), less blood loss (137 vs 291 ml, p = 0.03), and greater obesity.
Conclusion
RIMN is a potential option for operative fixation of PPFF distal to a femoral stem worthy of additional study.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel MP, Watts CD, Houdek MT, Lewallen DG, Berry DJ (2016) Epidemiology of periprosthetic fracture of the femur in 32,644 primary total hip arthroplasties: a 40-year experience. Bone Joint J 98-B:461–467
Cook RE, Jenkins PJ, Walmsley PJ, Patton JT, Robinson CM (2008) Risk factors for periprosthetic fractures of the hip: a survivorship analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466:1652–1656
Lindahl H (2007) Epidemiology of periprosthetic femur fracture around a total hip arthroplasty. Injury 38:651–654
Della Rocca GJ, Leung KS, Pape HC (2011) Periprosthetic fractures: epidemiology and future projections. J Orthop Trauma 25(suppl 2):S66–S70
Rupprecht M, Schlickewei C, Fensky F, Morlock M, Püschel K, Rueger JM, Lehmann W (2015) Periprosthetic and interimplant femoral fractures: biomechanical analysis. Unfallchirurg 118(12):1025–1032
Lehmann W, Rupprecht M, Nuechtern J, Melzner D, Sellenschloh K, Kolb J, Fensky F, Hoffmann M, Püschel K, Morlock M, Rueger JM (2012) What is the risk of stress risers for interprosthetic fractures of the femur? A biomechanical analysis. Int Orthop 36(12):2441–2446
Rupprecht M, Sellenschloh K, Grossterlinden L, Püschel K, Morlock M, Amling M, Rueger JM, Lehmann W (2011) Biomechanical evaluation for mechanisms of periprosthetic femoral fractures. J Trauma 70(4):E62–E66
Lehmann W, Rupprecht M, Hellmers N, Sellenschloh K, Briem D, Püschel K, Amling M, Morlock M, Rueger JM (2010) Biomechanical evaluation of peri- and interprosthetic fractures of the femur. J Trauma 68(6):1459–1463
Unified Classification System for Periprosthetic Fractures (UCPF) (2018) J Orthop Trauma 32:S141–S144
Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR (1987) A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis 40(5):373–383
Brodke DJ, Saltzman CL, Brodke DS (2016) PROMIS for orthopaedic outcomes measurement. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 24(11):744–749
Jildeh TR, Lizzio VA, Meta F, Fidai MS, Kaat AJ, Makhni EC (2018) The correlation between PROMIS pain interference and VAS pain in ambulatory orthopedic patients. Orthopedics 41(6):e813–e819
Paley D (2002) Principles of Deformity Correction, 1st edn. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, New York, pp 1–18
Helfet DL, Lorich DG (1998) Retrograde intramedullary nailing of supracondylar femoral fractures. Clin Orthop 350:80–84
Della Rocca GJ (2013) Periprosthetic fractures about the knee – an overview. J Knee Surg 26(1):3–7
Zhou S, Jung S, Hwang J (2019) Mechanical analysis of femoral stress-riser fractures. Clin Biomech 63:10–15
Mamczak CN, Gardner MJ, Bolhofner B, Borrelli J Jr, Streubel PN, Ricci WM (2010) Interprosthetic femoral fractures. J Orthop Trauma 24(12):740–744
Harris T, Ruth JT, Szivek J, Haywood B (2003) The effect of implant overlap on the mechanical properties of the femur. J Trauma 54(5):930–935
Iesaka K, Kummer FJ, DiCesare PE (2005) Stress risers between two ipsilateral intramedullary stems: a finite-element and biomechanical analysis. J Arthroplasty 20(3):386–391
Stoffel K, Sommer C, Kalampoki V, Blumenthal A, Joeris A (2016) The influence of the operation technique and implant used in the treatment of periprosthetic hip and interprosthetic femur fractures: a systematic literature review of 1571 cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 136(4):553–561
Dennis MG, Simon JA, Kummer FJ, Koval KJ, DiCesare PE (2000) Fixation of periprosthetic femoral shaft fractures occurring at the tip of the stem: a biomechanical study of 5 techniques. J Arthroplasty 15(4):523–528
Hussain MS, Dailey SK, Avilucea FR (2018) Stable fixation and immediate weight-bearing after combined retrograde intramedullary nailing and open reduction internal fixation of noncomminuted distal interprosthetic femur fractures. J Orthop Trauma 32(6):e237–e240
Rozell JC, Delagrammaticas D, Schwarzkopf R (2019) Interprosthetic femoral fractures: management challenges. Orthop Res Rev 11:119–128
Kampshoff J, Stoffel KK, Yates PJ, Erhardt JB, Kuster MS (2010) The treatment of periprosthetic fractures with locking plates: effect of drill and screw type on cement mantles: a biomechanical analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130(5):627–632
Fulkerson E, Koval K, Preston CF, Iesaka K, Kummer FJ, Egol KA (2006) Fixation of periprosthetic femoral shaft fractures associated with cemented femoral stems: a biomechanical comparison of locked plating and conventional cable plates. J Orthop Trauma 20(2):89–93
Schmotzer H, Tchejeyan GH, Dall DM (1996) Surgical management of intra- and postoperative fractures of the femur about the tip of the stem in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 11(6):709–717
Pelfort X, Torres-Claramunt R, Hinarejos P, Leal J, Gil-Gonzalez S, Puig L (2013) Extension malunion of the femoral component after retrograde nailing: no sequelae at 6 years. J Orthop Trauma 27(3):158–161
Service BC, Kang W, Turnbull N, Langford J, Haidukewych G, Koval KJ (2015) Influence of femoral component design on retrograde femoral nail starting point. J Orthop Trauma 29(10):e380–e384
Auston D, Donohue D, Stoops K, Cox J, Diaz M, Santoni B, Mir H (2018) Long segment blocking screws increase the stability of retrograde nail fixation in geriatric supracondylar femur fractures: eliminating the “bell-clapper effect.”. J Orthop Trauma 32(11):559–564
Virkus WW, Kempton LB, Sorkin AT, Gaski GE (2018) Intramedullary nailing of periarticular fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 26(18):629–639
Matlovich NF, Langting BA, Vasarhelyi EM, Naudie DD, McCalden RW, Howard JL (2017) Outcomes of surgical management of supracondylar periprosthetic femur fractures. J Arthroplasty 32(1):189–192
Kerkhoffs GM, Servien E, Dunn W, Dahm D, Bramer JA, Haverkamp D (2012) The influence of obesity on the complication rate and outcome of total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis and systematic literature review. J Bone Joint Surg Am 94(20):1839–1844
Jeschke E, Citak M, Günster C, Halder AM, Heller KD, Malzahn J, Niethard FU, Schräder P, Zacher J, Gehrke T (2018) Obesity increases the risk of postoperative complications and revision rates following primary total hip arthroplasty: an analysis of 131,576 total hip arthroplasty cases. J Arthroplasty 33(7):2287–2292
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Investigation performed at Indiana University Methodist Hospital in Indianapolis, Indiana
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richard, R.D., Natoli, R.M., Sorkin, A.T. et al. Retrograde intramedullary nailing below a hip arthroplasty prosthesis: a viable fixation option for periprosthetic and interprosthetic femur fractures. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 44, 2283–2289 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-020-04734-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-020-04734-3