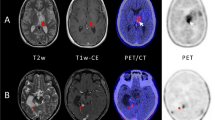
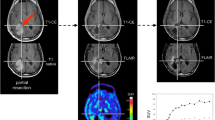
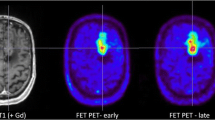
Abstract
Purpose
O-(2-[18F]Fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine (18F-FET) is a well-established PET tracer for the imaging of cerebral gliomas, but little is known about 18F-FET uptake in meningiomas. The aim of this study was to explore 18F-FET kinetics and tumour-to-background contrast in meningiomas of various histologies.
Methods
A group of 24 patients with suspected cerebral meningioma on MRI/CT had an additional dynamic 18F-FET PET scan prior to surgery. Time–activity curves (TAC) of 18F-FET uptake in the tumours and tumour-to-brain ratios (TBR) for early (3 – 14 min after injection) and late 18F-FET uptake (20 – 40 min after injection) were analysed and compared with histological subtypes and WHO grade. 18F-FET uptake in critical structures in the skull base was also evaluated in terms of tumour-to-tissue (T/Tis) ratio.
Results
TBR of 18F-FET uptake in meningiomas was significantly higher in the early phase than in the late phase (3.5 ± 0.8 vs. 2.2 ± 0.3; P < 0.001). The difference in TBR between low-grade meningiomas (WHO grade I, 18 patients) and high-grade meningiomas (WHO grade II or III, 6 patients) was significant in the late phase of 18F-FET uptake (2.1 ± 0.2 vs. 2.5 ± 0.2, P = 0.003) while there was no significant difference in the early phase. ROC analysis showed that TBR of 18F-FET uptake in the late phase had significant power to differentiate low-grade from high-grade meningiomas (AUC 0.87 ± 0.18, sensitivity 83 %, specificity 83 %, optimal cut-off 2.3; P < 0.01). Evaluation of TAC yielded three different curve patterns of 18F-FET PET uptake. Combination of TBR (cut-off value 2.3) and TAC pattern slightly improved the differentiation of high-grade from low-grade meningiomas (accuracy 92 %; P = 0.001). Analysis of background radioactivity in the skull base indicated that 18F-FET uptake may be helpful in distinguishing meningioma tissue in the late phase. T/Tis ratios were >1.2 in all patients for the periorbita, sphenoidal sinus, pituitary gland, tentorium, bone and brain, in more than 90 % of patients for the mucosa and dura, but in only 63 % of patients for the cavernous sinus.
Conclusion
18F-FET PET may provide additional information for noninvasive grading of meningiomas and possibly for the discrimination of tumour in critical areas of the skull base. A further evaluation of 18F-FET PET in meningiomas appears to be justified.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wiemels J, Wrensch M, Claus EB. Epidemiology and etiology of meningioma. J Neurooncol. 2010;99:307–14.
Kinjo T, al-Mefty O, Kanaan I. Grade zero removal of supratentorial convexity meningiomas. Neurosurgery. 1993;33:394–9.
Goyal N, Kakkar A, Sarkar C, Agrawal D. Does bony hyperostosis in intracranial meningioma signify tumor invasion? A radio-pathologic study. Neurol India. 2012;60:50–4.
Pieper DR, Al-Mefty O, Hanada Y, Buechner D. Hyperostosis associated with meningioma of the cranial base: secondary changes or tumor invasion. Neurosurgery. 1999;44:742–6.
Qi ST, Liu Y, Pan J, Chotai S, Fang LX. A radiopathological classification of dural tail sign of meningiomas. J Neurosurg. 2012;117:645–53.
Modha A, Gutin PH. Diagnosis and treatment of atypical and anaplastic meningiomas: a review. Neurosurgery. 2005;57:538–50.
Simpson D. The recurrence of intracranial meningiomas after surgical treatment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1957;20:22–39.
Yang SY, Park CK, Park SH, Kim DG, Chung YS, Jung HW. Atypical and anaplastic meningiomas: prognostic implications of clinicopathological features. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008;79:574–80.
Jaaskelainen J. Seemingly complete removal of histologically benign intracranial meningioma: late recurrence rate and factors predicting recurrence in 657 patients. A multivariate analysis. Surg Neurol. 1986;26:461–9.
Cornelius JF, Langen KJ, Stoffels G, Hanggi D, Sabel M, Jakob SH. Positron emission tomography imaging of meningioma in clinical practice: review of literature and future directions. Neurosurgery. 2012;70:1033–41.
Liu RS, Chang CP, Guo WY, Pan DH, Ho DM, Chang CW, et al. 1-11C-acetate versus 18F-FDG PET in detection of meningioma and monitoring the effect of gamma-knife radiosurgery. J Nucl Med. 2010;51:883–91.
Henze M, Schuhmacher J, Hipp P, Kowalski J, Becker DW, Doll J, et al. PET imaging of somatostatin receptors using [68GA]DOTA-D-Phe1-Tyr3-octreotide: first results in patients with meningiomas. J Nucl Med. 2001;42:1053–6.
Henze M, Dimitrakopoulou-Strauss A, Milker-Zabel S, Schuhmacher J, Strauss LG, Doll J, et al. Characterization of 68Ga-DOTA-D-Phe1-Tyr3-octreotide kinetics in patients with meningiomas. J Nucl Med. 2005;46:763–9.
Yilmaz S, Ocak M, Asa S, Gulsen F, Halac M, Kabasakal L. Appearance of intracranial meningioma in FDG and 68Ga-DOTATOC PET/CT. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2013;32:60–1.
Afshar-Oromieh A, Giesel FL, Linhart HG, Haberkorn U, Haufe S, Combs SE, et al. Detection of cranial meningiomas: comparison of 68Ga-DOTATOC PET/CT and contrast-enhanced MRI. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012;39:1409–15.
Grosu AL, Weber WA, Astner ST, Adam M, Krause BJ, Schwaiger M, et al. 11C-methionine PET improves the target volume delineation of meningiomas treated with stereotactic fractionated radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;66:339–44.
Rutten I, Cabay JE, Withofs N, Lemaire C, Aerts J, Baart V, et al. PET/CT of skull base meningiomas using 2-18F-fluoro-L-tyrosine: initial report. J Nucl Med. 2007;48:720–5.
Pauleit D, Floeth F, Hamacher K, Riemenschneider MJ, Reifenberger G, Muller HW, et al. O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine PET combined with MRI improves the diagnostic assessment of cerebral gliomas. Brain. 2005;128:678–87.
Wester HJ, Herz M, Weber W, Heiss P, Senekowitsch-Schmidtke R, Schwaiger M, et al. Synthesis and radiopharmacology of O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine for tumor imaging. J Nucl Med. 1999;40:205–12.
Graf R, Plotkin M, Nyuyki F, Wust P, Wurm R, Budach V, et al. Contribution of (18)F-fluoro-ethyl-tyrosine positron emission tomography to target volume delineation in stereotactic radiotherapy of malignant cranial base tumours: first clinical experience. Int J Mol Imaging. 2012;2012:412585.
Pauleit D, Stoffels G, Bachofner A, Floeth FW, Sabel M, Herzog H, et al. Comparison of (18)F-FET and (18)F-FDG PET in brain tumors. Nucl Med Biol. 2009;36:779–87.
Pauleit D, Zimmermann A, Stoffels G, Bauer D, Risse J, Fluss MO, et al. 18F-FET PET compared with 18F-FDG PET and CT in patients with head and neck cancer. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:256–61.
Cornelius JF, Slotty PJ, Stoffels G, Galldiks N, Langen KJ, Steiger HJ. 5-aminolevulinic acid and 18F-FET-PET as metabolic imaging tools for surgery of a recurrent skull base meningioma. J Neurol Surg B. 2013;74:211–6.
Hamacher K, Coenen HH. Efficient routine production of the 18F-labelled amino acid O-2-18F fluoroethyl-L-tyrosine. Appl Radiat Isot. 2002;57:853–6.
Langen KJ, Bartenstein P, Boecker H, Brust P, Coenen HH, Drzezga A, et al. German guidelines for brain tumour imaging by PET and SPECT using labelled amino acids. Nuklearmedizin. 2011;50:167–73.
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, et al. The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;114:97–109.
Watanabe Y, Yamasaki F, Kajiwara Y, Takayasu T, Nosaka R, Akiyama Y, et al. Preoperative histological grading of meningiomas using apparent diffusion coefficient at 3T MRI. Eur J Radiol. 2013;82:658–63.
Herholz K, Langen KJ, Schiepers C, Mountz JM. Brain tumors. Semin Nucl Med. 2012;42:356–70.
Weckesser M, Langen KJ, Rickert CH, Kloska S, Straeter R, Hamacher K, et al. O-(2-[18F]fluorethyl)-L-tyrosine PET in the clinical evaluation of primary brain tumours. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005;32:422–9.
Langen KJ, Broer S. Molecular transport mechanisms of radiolabeled amino acids for PET and SPECT. J Nucl Med. 2004;45:1435–6.
Dharmalingam P, Roopesh Kumar VR, Verma SK. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression and angiogenesis in various grades and subtypes of meningioma. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2013;56:349–54.
Rapp M, Floeth FW, Felsberg J, Steiger HJ, Sabel M, Langen KJ, et al. Clinical value of O-(2-[(18)F]-fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine positron emission tomography in patients with low-grade glioma. Neurosurg Focus. 2013;34:E3. doi:10.3171/2012.12.FOCUS12336.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Lutz Tellmann, Suzanne Schaden, Elisabeth Theelen, Kornelia Frey and Natalie Judov for assistance in the PET studies, and Silke Grafmüller, Erika Wabbals, Sascha Rehbein and Dr. Johannes Ermert for radiosynthesis of 18F-FET.
Disclosure
The authors have no personal financial or institutional interest in any of the drugs, materials, or devices described in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cornelius, J.F., Stoffels, G., Filß, C. et al. Uptake and tracer kinetics of O-(2-18F-fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine in meningiomas: preliminary results. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 42, 459–467 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-014-2934-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-014-2934-0