Abstract
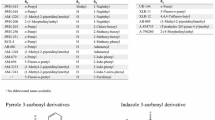
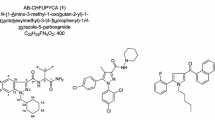
Illicit new psychoactive substances (NPS) are a serious threat to health throughout the world. Such NPS do not usually pass preliminary pharmacological trials. In 2014, we identified a series of five new synthetic cannabinoids with an indazole-3-carboxamide structure bearing an N-1-methoxycarbonylalkyl group. The compounds have very high cannabimimetic activity which has caused mass severe intoxication and deaths. The compounds were identified by means of gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS), including high-resolution mass spectrometry (GC–HRMS), ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC–HRMS2), and 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR). The peculiarities of mass-spectral fragmentation of the compounds after electron ionization (EI) ionization and collision-induced dissociation (CID) were studied. The analytical characteristics reported for the compounds will enable their identification in a variety of materials seized from criminals.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
United Nation Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) (2013) World Drug Report 2013. http://www.unodc.org/unodc/secured/wdr/wdr2013/World_Drug_Report_2013.pdf. Accessed 21 Dec 2014
United Nation Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) (2013) The challenge of new psychoactive substances. A Report from the Global SMART Programme March 2013. http://www.unodc.org/documents/scientific/NPS_2013_SMART.pdf. Accessed 21 Dec 2014
Seely KA, Patton AL, Moran CL, Womack ML, Prather PL, Fantegrossi WE, Radominska-Pandya A, Endres GW, Channell KB, Smith NH, McCain KR, James LP, Moran JH (2013) Forensic investigation of K2, Spice, and “bath salt” commercial preparations: A three-year study of new designer drug products containing synthetic cannabinoid, stimulant, and hallucinogenic compounds. Forensic Sci Int 233:416–422
Brandt SD, King LA, Evans-Brown M (2014) The new drug phenomenon. Drug Test Anal 6:587–597
ElSohly MA, Gul W, Wanas AS, Radwan MM (2014) Synthetic cannabinoids: Analysis and metabolites. Life Sci 97:78–90
Znaleziona J, Ginterová P, Petr J, Ondra P, Válka I, Ševčik J, Chrastina J, Maier V (2015) Determination and identification of synthetic cannabinoids and their metabolites in different matrices by modern analytical techniques – a review. Anal Chim Acta. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2014.12.055
Mazzarino M, de la Torre X, Botrè F (2014) A liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry method based on class characteristic fragmentation pathways to detect the class of indole-derivative synthetic cannabinoids in biological samples. Anal Chim Acta 837:70–82
Gwak S, Arroyo-Mora LE, Almirall JR (2015) Qualitative analysis of seized synthetic cannabinoids and synthetic cathinones by gas chromatography triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry. Drug Test Anal 7:121–130
Nakajima J, Takahashi M, Seto T, Kanai C, Suzuki J, Yoshida M, Hamano T (2011) Identification and quantitation of two benzoylindoles AM-694 and (4-methoxyphenyl)(1-pentyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methanone, and three cannabimimetic naphthoylindoles JWH-210, JWH-122, and JWH-019 as adulterants in illegal products obtained via the Internet. Forensic Toxicol 29:95–110
Uchiyama N, Kawamura M, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y (2011) Identification and quantitation of two cannabimimetic phenylacetylindoles JWH-251 and JWH-250, and four cannabimimetic naphthoylindoles JWH-081, JWH-015, JWH-200, and JWH-073 as designer drugs in illegal products. Forensic Toxicol 29:25–37
Kneisel S, Bisel P, Brecht V, Broecker S, Müller M, Auwärter V (2012) Identification of the cannabimimetic AM-1220 and its azepane isomer (N-methylazepan-3-yl)-3-(1-naphthoyl)indole in a research chemical and several herbal mixtures. Forensic Toxicol 30:126–134
Westphal F, Sönnichsen FD, Thiemt S (2012) Identification of 1-butyl-3-(1-(4-methyl)naphthoyl)indole in a herbal mixture. Forensic Sci Int 215:8–13
Jankovics P, Varadi A, Tolgyesi L, Lohner S, Nemeth-Palotas J, Balla J (2012) Detection and identification of the new potential synthetic cannabinoids 1-pentyl-3-(2-iodobenzoyl)indole and 1-pentyl-3-(1-adamantoyl)indole in seized bulk powders in Hungary. Forensic Sci Int 214:27–32
Uchiyama N, Kawamura M, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y (2012) Identification of two new-type synthetic cannabinoids, N-(1-adamantyl)-1-pentyl-1H-indole-3-carboxamide (APICA) and N-(1-adamantyl)-1-pentyl-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (APINACA), and detection of five synthetic cannabinoids, AM-1220, AM-2233, AM-1241, CB-13 (CRA-13), and AM-1248, as designer drugs in illegal products. Forensic Toxicol 30:114–125
Uchiyama N, Kawamura M, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y (2013) URB-754: a new class of designer drug and 12 synthetic cannabinoids detected in illegal products. Forensic Sci Int 227:21–32
Shevyrin V, Melkozerov V, Nevero A, Eltsov O, Morzherin Y, Shafran Y (2013) Identification and analytical properties of new synthetic cannabimimetics bearing 2,2,3,3-tetramethylcyclopropanecarbonyl moiety. Forensic Sci Int 226:62–73
Hermanns-Clausen M, Kneisel S, Hutter M, Szabo B, Auwärter V (2013) Acute intoxication by synthetic cannabinoids – Four case reports. Drug Test Anal 5:790–794
Shevyrin V, Melkozerov V, Nevero A, Eltsov O, Shafran Y (2013) Analytical characterization of some synthetic cannabinoids, derivatives of indole-3-carboxylic acid. Forensic Sci Int 232:1–10
Shevyrin V, Melkozerov V, Nevero A, Eltsov O, Morzherin Y, Shafran Y (2014) 3-Naphthoylindazoles and 2-naphthoylbenzoimidazoles as novel chemical groups of synthetic cannabinoids: Chemical structure elucidation, analytical characteristics and identification of the first representatives in smoke mixtures. Forensic Sci Int 242:72–80
Shevyrin V, Melkozerov V, Nevero A, Eltsov O, Baranovsky A, Shafran Y (2014) Synthetic cannabinoids as designer drugs: New representatives of indol-3-carboxylates series and indazole-3-carboxylates as novel group of cannabinoids. Identification and analytical data. Forensic Sci Int 244:263–275
Buchler IP, Hayes MJ, Hedge SG, Hockerman SL, Jones DE, Kortum SW, Rico JG, Tenbrink RE, Wu KK (2009) Indazole derivatives. WO Patent 106982
Buchler IP, Hayes MJ, Hedge SG, Hockerman SL, Jones DE, Kortum SW, Rico JG, Tenbrink RE, Wu KK (2009) Indazole derivatives. WO Patent 106980
Uchiyama N, Matsuda S, Wakana D, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y (2013) New cannabimimetic indazole derivatives, N-(1-amino-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-pentyl-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (AB-PINACA) and N-(1-amino-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (AB-FUBINACA), identified as designer drugs. Forensic Toxicol 31:93–100
Uchiyama N, Matsuda S, Kawamura M, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y (2013) Two new-type cannabimimetic quinolinyl carboxylates, QUPIC and QUCHIC, two new cannabimimetic carboxamide derivatives, ADB-FUBINACA and ADBICA, and five synthetic cannabinoids detected with a thiophene derivative α-PVT and an opioid receptor agonist AH-7921 identified in illegal products. Forensic Toxicol 31:223–240
Uchiyama N, Shimokawa Y, Kawamura M, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Hakamatsuka T (2014) Chemical analysis of a benzofuran derivative, 2-(2-ethylaminopropyl)benzofuran (2-EAPB), eight synthetic cannabinoids, five cathinone derivatives, and five other designer drugs newly detected in illegal products. Forensic Toxicol 32:266–281
Shevyrin V, Morzherin Y, Melkozerov V, Nevero A (2014) New synthetic cannabinoid – methyl 2-{[1-(5-fluoropentyl)-3-methyl-1H-indol-3-ylcarbonyl]amino}butyrate – as a designer drug. Chem Heterocycl Compd 50(4):583–586
Hasegawa K, Wurita A, Minakata K, Gonmori K, Yamagishi I, Nozawa H, Watanabe K, Suzuki O (2015) Identification and quantitation of 5-fluoro-ADB, one of the most dangerous synthetic cannabinoids, in the stomach contents and solid tissues of a human cadaver and in some herbal products. Forensic Toxicol 33:112–121
Explanatory note to the project of Regulation of the Government of Russian Federation ‘About Changes in Some Acts of the Government of Russian Federation Connected with Improvement of Control of Turnover of Narcotic Drugs’ (in Russian) (2014) http://regulation.gov.ru/get.php?view_id=12&doc_id=55037. Accessed 21 Dec 2014
Bulygina I (2014) Clinical presentations of intoxication by new psychoactive compound MDMB(N)-Bz-F. Thesis of The II Scientific and Practical Seminar ‘Methodical, Organizational and Law Problems of Chemical and Toxicological Laboratories of Narcological Services’, Moscow, October 21–22, 2014 (in Russian) www.narkotiki.ru/objects/narkotiki02/1414709242.ppt. Accessed 21 Dec 2014
Arntson A, Ofsa B, Lancaster D, Simon JR, McMullin M, Logan B (2013) Validation of novel immunoassay for the detection of synthetic cannabinoids and metabolites in urine specimens. J Anal Toxicol 37:284–290
Kronstrand R, Brinkhagen L, Birath-Karlsson C, Roman M, Josefsson M (2014) LC-QTOF-MS as a superior strategy to immunoassay for the comprehensive analysis of synthetic cannabinoids in urine. Anal Bioanal Chem 406:3599–3609
Lebedev AT (2013) Environmental mass spectrometry. Annu Rev Anal Chem 6:163–189
Stoliarov BV, Savinov IM, Vitenberg AG, Kartsova LA, Zenkevich IG, Kalmanovsky VI, Kalambet YA (2002) Practical gas and liquid chromatography. St. Petersburg University, St. Petersburg (in Russian)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in the topical collection High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry in Food and Environmental Analysis with guest editor Aldo Laganà.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 3.24 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shevyrin, V., Melkozerov, V., Nevero, A. et al. Identification and analytical characteristics of synthetic cannabinoids with an indazole-3-carboxamide structure bearing a N-1-methoxycarbonylalkyl group. Anal Bioanal Chem 407, 6301–6315 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8612-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8612-7